Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL Minus
Minus is one of the four important set operators in standard query language (SQL). Set operators are used to combine the results obtained from two or more queries into a single result. The queries which contain two or more subqueries are known as compounded queries. The MINUS set operator is used to combine all the results of two or more SELECT statements. It returns only those records that are present exclusively in the first table.
Syntax
The generic syntax for working with SQL MINUS operators is as follows:
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_1
MINUS
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_2
MINUS
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name_3
.
.
.Parameters
The different parameters used in the syntax are:
- column_name: Mention the column name on which you want to perform the set operation and want in the result set
- FROM table_name_1: Mention the first table name from which the column has to be fetched
- FROM table_name_2: Mention the second table name from which the column has to be fetched
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters are mandatory. You may use WHERE GROUP BY and HAVING clauses based on your requirement.
SQL Minus Set Operator
Here is a list of few points which we should be kept in mind while working with SQL MINUS or EXCEPT operator:
- The number of columns in the SELECT statement on which we have applied SQL set operators must be the same.
- The selected columns must have the same data type.
- The order of the columns must be in the same order as mentioned in the SELECT statement.
Going ahead we will be discussing the above mentioned SQL MINUS set operator in great detail.
In order to illustrate the same, let us first create two tables “skills” and “skills_updated”. The former contains the old skills of an employee and the later contains the updated skills of an employee along with skill id, employee id, and proficiency. Both tables have the same structure. We can use the following code snippet to create the above-mentioned tables.
Code:
create table skills(
id number not null constraint skills_id_pk primary key,
employee_id number
constraint skills_employee_id_fk
references employees on delete cascade,
skill varchar2(255),
proficiency number constraint skills_proficiency_cc
check (proficiency in (1,2,3,4,5))
);
create table skills_updated (
id number not null constraint skills_id primary key,
employee_id number
constraint skills_employee_id
references employees on delete cascade,
skill varchar2(255),
proficiency number constraint skills_proficiency
check (proficiency in (1,2,3,4,5))
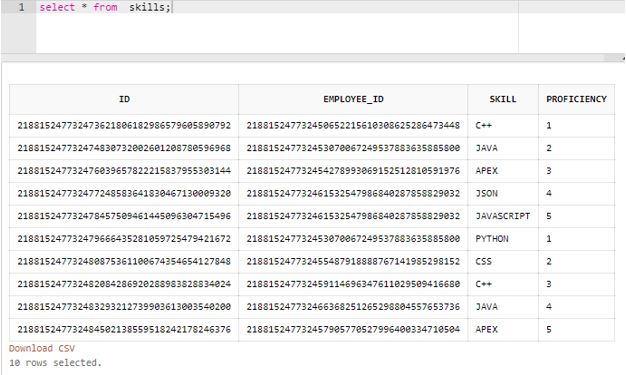
);After performing some random insert operations, the data in the “skills” table looks something like this.
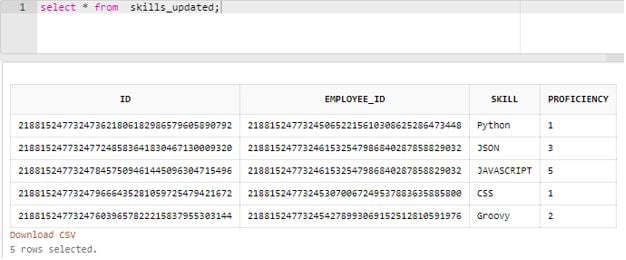
The inserted data in the “skills_updated” table looks as follows.
Examples to Implement SQL Minus
Below are some examples to implement SQL Minus:
Example #1
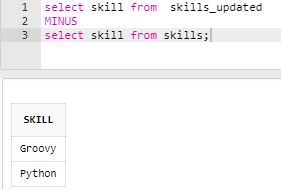
Find the skills that are new and added only after skill upgradation exercise.
Code:
select skill from skills_updated
MINUS
select skill from skills;Output:
Example #2
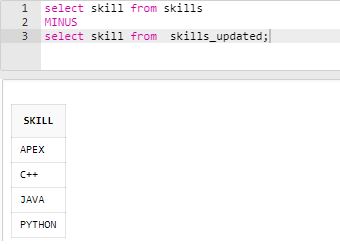
Find the skills that are not mentioned in the skill up-gradation table.
Code:
select skill from skills
MINUS
select skill from skills_updated;Output:
Example #3
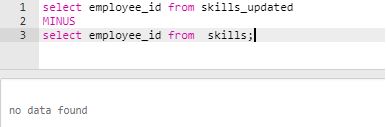
Find the employees who have not updated their skills in the upgradation table.
Code:
select employee_id from skills
MINUS
select employee_id from skills_updated;Output:
Example #4
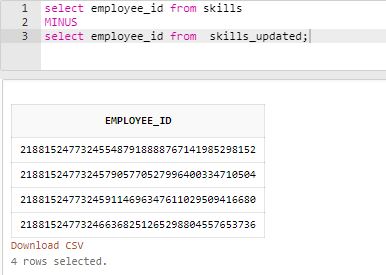
Find the employees or employee_ids in particular who were not present in the old skills table.
Code:
select employee_id from skills_updated
MINUS
select employee_id from skills;Output:
Example #5
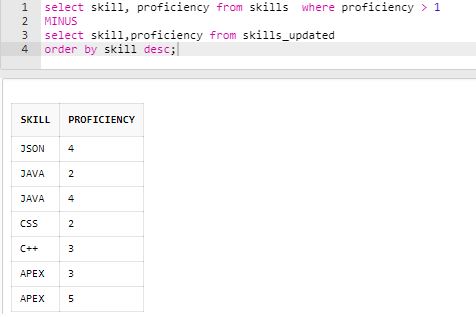
Find the skills and proficiencies having proficiency scores more than 1 which are present in the old skills table.
Code:
select skill, proficiency from skills where proficiency > 1
MINUS
select skill,proficiency from skills_updated
order by skill desc;Output:
Illustrate the use of EXCEPT Operator:
Consider two tables named “customers_jan” and “customers_dec” for demonstration purposes only. The data in them looks something like this :
customers_jan Table:
| customer_id | Name | city |
| 1 | Rahul Vyas | new Delhi |
| 2 | Sneha Srivastava | new Delhi |
| 3 | kabita Pandey | Kolkata |
| 4 | Akshay Gupta | Bangalore |
| 5 | Abhishek sheel | Bangalore |
| 6 | akansha Singh | Pune |
| 7 | Poonam Mahajan | surat |
| 8 | Aditya Awasthi | new Delhi |
| 9 | Mohit Chauhan | solan |
| 10 | Neha Singh | Mumbai |
customers_dec Table:
| customer_id | Name | city |
| 1 | Akshay Gupta | New Delhi |
| 2 | Heena | Mumbai |
| 3 | Sneha Choudhary | Jaipur |
| 4 | Abhishek sheel | Bangalore |
| 5 | Tushar Dixit | Jaipur |
| 6 | Mohit Chauhan | solan |
| 7 | akansha Singh | Chennai |
| 8 | Mohit Chaudhary | Gurgaon |
| 9 | Avni Mukherjee | new Delhi |
| 10 | Poonam Mahajan | surat |
Example #6
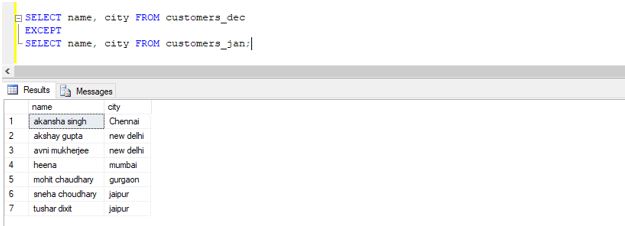
Find the details of customers who shopped only in December but not January.
Code:
SELECT name, city FROM customers_dec
EXCEPT
SELECT name, city FROM customers_jan;Output:
Conclusion
So in this article, we have learned about SQL MINUS set operators which are very useful in checking membership of data. It returns the results which are exclusively present in the first table. It also helps in summarizing and understanding the patterns in a huge dataset.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Minus” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.