Updated March 8, 2023
Koi
Introduction to SQL MIN()
MIN() function in standard query language (SQL) is an aggregate function that returns the smallest or minimum value of a specified column obtained in the result set of a SELECT query. It is a very versatile function. It can be used on its own in a SELECT query or used with GROUP BY and HAVING clauses for preparing summary tables in data analytics.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing SQL queries with MIN() function is as follows:
SELECT MIN(column_name)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;Parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax:
- column_name: Field or column for which we want to return the minimum value.
- table_name: The database table from which the column_name has to be fetched from.
- WHERE condition: Any filtering clause for rows if required.
The syntax for writing MIN function in GROUPBY clauses:
SELECT MIN(column_name1), column_name2
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name2;Most of the parameters used in this syntax are similar to the former syntax.
- column_name1: column_name1 corresponds to the column for which the min value has to be returned.
- column_name2: column_name2 corresponds to the field or column on the basis of which grouping has to be done.
Here we have seen the basic syntax for writing SQL queries with MIN() function. We may use HAVING, ORDER BY etc., based on our requirements.
Examples of SQL MIN()
Given below are the examples of SQL MIN():
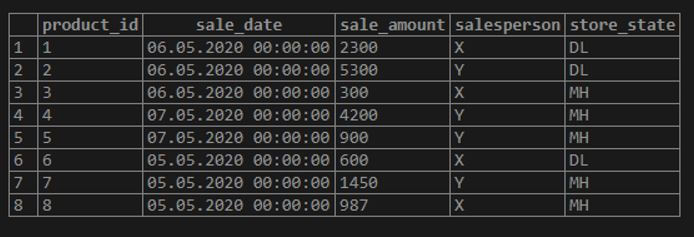
In order to illustrate the working of the MIN() function in SQL, let us create a dummy table called “sales”. This table contains details of sales made by different salespeople in a paper company.
The CREATE statement for creating this table is as follows:
Code:
CREATE TABLE sales
(
product_id integer NOT NULL,
sale_date date NOT NULL,
sale_amount numeric NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT product_key PRIMARY KEY (product_id)
)Once the table is successfully created, insert the following records in it to work with.
Code:
INSERT INTO sales(
product_id, sale_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES (1,'2020-05-06',2300,'X','DL'),
(2,'2020-05-06',5300,'Y','DL'),
(3,'2020-05-06',300,'X','MH'),
(4,'2020-05-07',4200,'Y','MH'),
(5,'2020-05-07',900,'Y','MH'),
(6,'2020-05-05',600,'X','DL'),
(7,'2020-05-05',1450,'Y','MH'),
(8,'2020-05-05',987,'X','MH');
select * from sales;Output:
Example #1 – Basic function of MIN()
Find the minimum amount of sale made overall.
Code:
SELECT MIN(sale_amount)
FROM sales;Output:
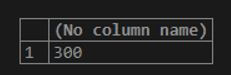
In this example, MIN() has been used on the sale_amount column to find the minimum value in this column.
Example #2
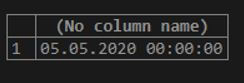
Find the earliest date on which the first sale was made (as per the sales table).
Code:
SELECT MIN(sale_date)
FROM sales;Output:
Example #3 – MIN() with WHERE CLAUSE.
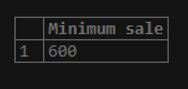
Find the minimum amount of sale made for the Delhi or DL store location.
Code:
SELECT MIN(sale_amount) as "Minimum sale"
FROM sales
WHERE store_state = 'DL';Output:
Example #4 – MIN() with GROUP BY CLAUSE.
Find the minimum amount of sale made overall grouped together by store location.
Code:
SELECT store_state, MIN(sale_amount) as "Minimum sale"
FROM sales
GROUP BY store_state;Output:
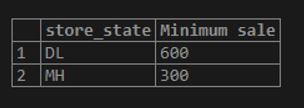
Here, the SELECT statement results are grouped together by store_state, and then the corresponding minimum value for each group has been fetched using MIN() function.
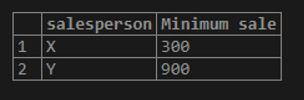
Example #5
Find the minimum amount of sale made overall grouped together by the salesperson.
Code:
SELECT salesperson, MIN(sale_amount) as "Minimum sale"
FROM sales
GROUP BY salesperson;Output:
Example #6
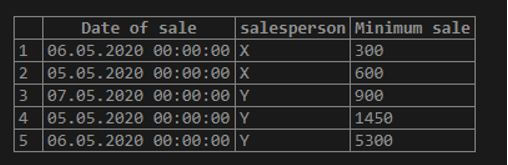
Find the minimum amount of sale made overall grouped together by the date of sale and salesperson.
Code:
SELECT sale_date as "Date of sale",
salesperson, MIN(sale_amount) as "Minimum sale"
FROM sales
GROUP BY sale_date, salesperson;Output:
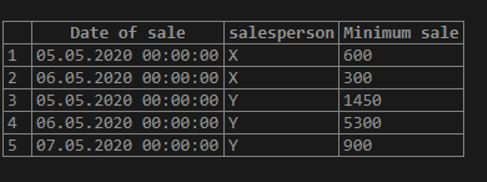
In this example, we have grouped the result set by two fields, namely sale_date and salesperson and then summarized each group using MIN().
Example #7 – MIN() with HAVING CLAUSE.
Find the total sale amount grouped together by the salesperson having the earliest date of the first sale as 5th May 2020.
Code:
SELECT salesperson, SUM(sale_amount) as "Total sales"
FROM sales
GROUP BY salesperson
HAVING MIN(sale_date) = '2020-05-05';Output:
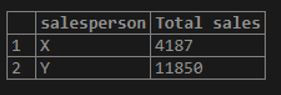
Here, HAVING MIN(sale_date) acts as a filtering clause for this aggregate query.
Example #8 – MIN() with ORDER BY CLAUSE.
Find the minimum amount of sale made overall grouped together by the date of sale and salesperson, ordered by minimum sale amount.
Code:
SELECT sale_date as "Date of sale",
salesperson, MIN(sale_amount) as "Minimum sale"
FROM sales
GROUP BY sale_date, salesperson
ORDER BY MIN(sale_amount);Output:
Advantages of SQL MIN()
Given below are the advantages mentioned:
- MIN() is a statistical function that helps to find the minimum value of a specific field in the result set of a SELECT query.
- MIN(), when used as a summary function in the GROUP BY clause, it helps in finding the Minimum value of records in each group.
- MIN() when used with a HAVING clause, it helps to filter records based on the minimum requisite value.
Conclusion
MIN() function is an aggregate function that is used to find the minimum value of a selected column.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL MIN()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

