Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to SQL Formatter
SQL Formatter is used for formatting SQL scripts automatically to make the code appear more pretty, structured, easy to read, understand and review. A code in SQL can be formatted by providing indentions, spaces and tabs in between the statements etc. At present, many popular SQL database management servers like postgreSQL do not have an auto query formatter. While other management servers like SQL server provide some basic query formatters, which helps you in indenting the SQL code, removing and adding white spaces in between code, word wrapping, line number inclusion etc.
SQL Query Formatting using Query Designer
Consider the following query. It is most formatted for sure.
Code:
select * from dbo.books_audit_table;In order to format this query, we can use the query designer.
Here are the steps to do the same.
Step 1: Click on the Query tab in the bar just below the main bar. On clicking on the Query tab, a drop-down menu as shown below will appear on the screen. Select Design Query in Editor option from it.
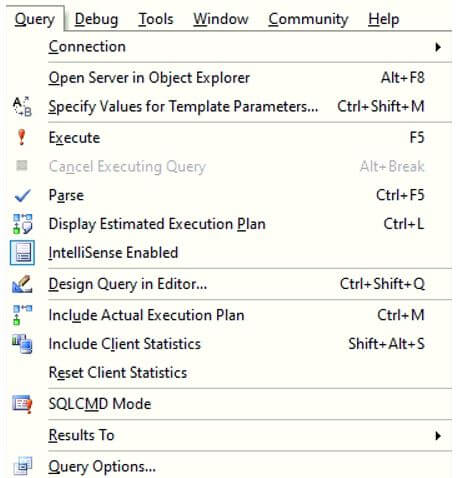
Step 2: Once you select the Design Query in Editor option, a Query Designer dialog box as shown below will appear in front of you. Make changes as necessary. You can select the names of the columns you want in the formatted query and all.
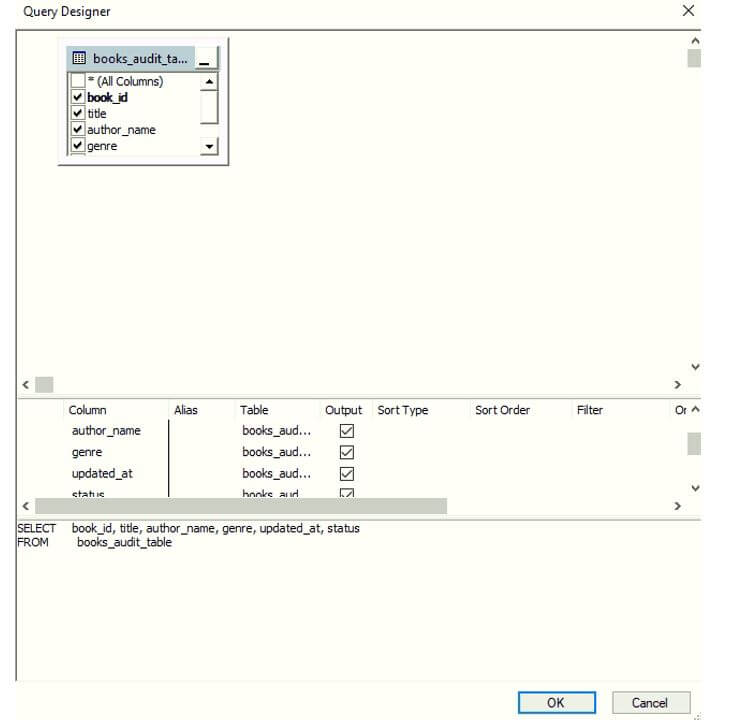
Step 3: After you have formatted the query in the desired manner, click on OK. You can even see the preview of your formatted query in the lower section. And when you click on Ok and the original query will get formatted automatically as shown below.

This might seem like a lot of steps but you can open the query designer by using a shortcut Ctrl+Shift+Q.
Let’s try this one as well.
Code:
select * from dbo.books_audit_table where
author_name like 'A%';In order to format this SQL query, we will use the shortcut. Just select the query you want to format and press Ctrl+Shift+Q on the keyword.

A query designer dialog box will appear in front of you. Modify the query as you want and click on Ok.
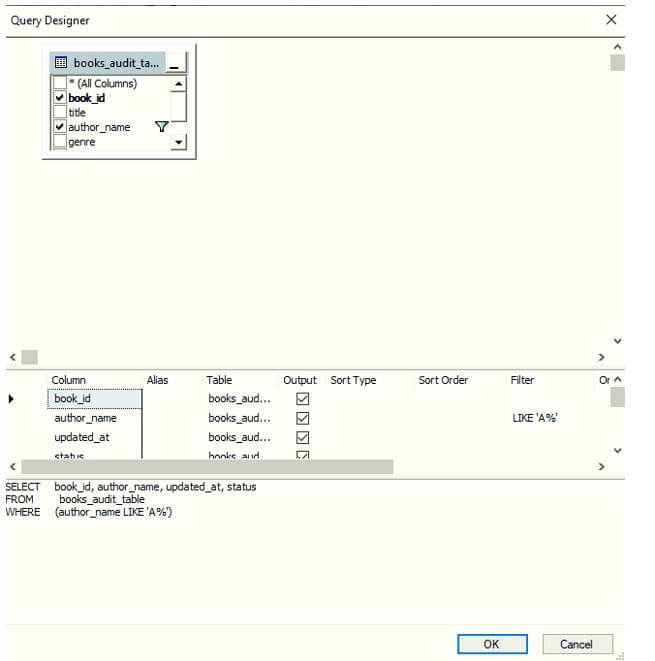
When you will click on Ok. The formatted SQL query would look something as shown below. Voila !! the query has been formatted.

Until now, we have been formatting the query using an automatic query designer. We can even format a query with personal customization, by giving indentations, tab spaces, commenting and uncommenting etc.
Custom SQL Query Formatting using SQL Editor, Text Editor and Edit Tools
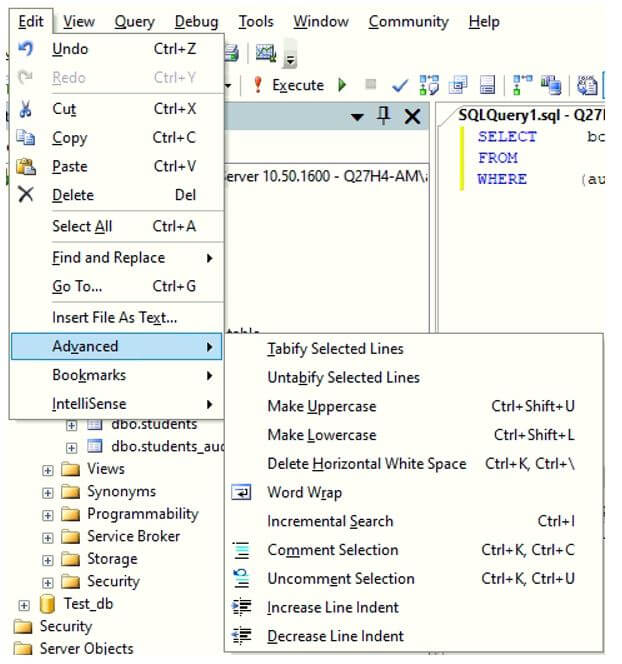
There are multiple ways of giving indents and changing the length of tab spaces for a SQL query in MS SQL Server management studio. First one is using the Edit tab. When you will click on the Edit tab in your SQL management studio, if you will select Advanced option, you will get multiple options such as Tabify Selected Lines, Untabify Selected Lines, Make Uppercase, Comment Selection etc. So, there are plenty of options to format your query.
If you do not want your edit tab for some reasons, you can use SQL editor and Text editor to format the SQL queries as shown below.
Formatting Options in SQL Editor:
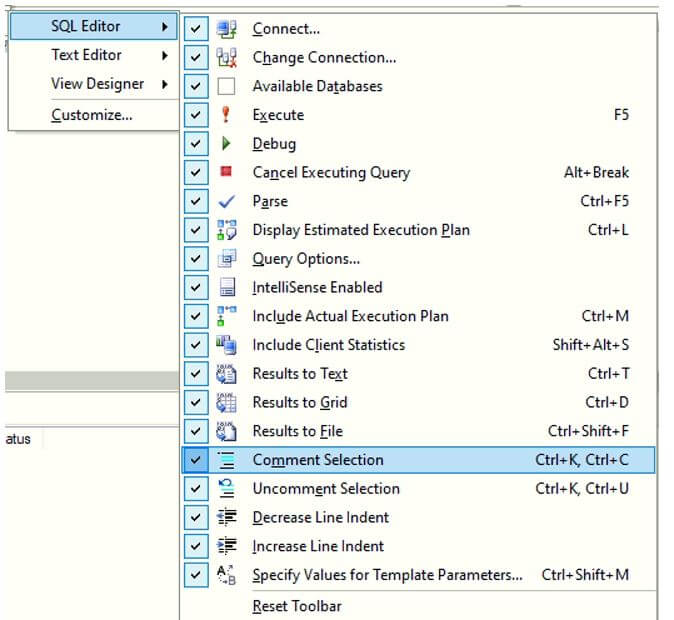
Formatting Options in Text Editor:
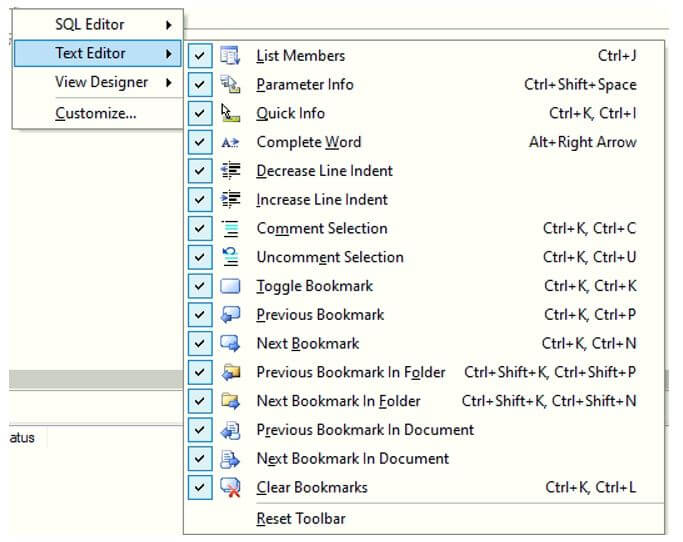
Having seen various options for custom formatting a SQL query in SQL server management studio, let us try a few examples to illustrate the usage of the given commands.
Code:
select count(book_id), author_name
from dbo.books_audit_table
where genre = 'memoir'
group by author_name
order by count(book_id);Suppose if you wish to give some indent for some of the lines in your query, then select those lines and click on Increase Indent. The tool will increase the indent for the selected lines.

Next, if you wish to comment a few lines in your code, then select those lines and click on Comment out the selected lines tool as shown below.
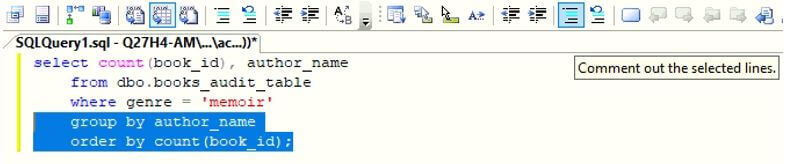
Next, you will observe that the said lines have been commented successfully.
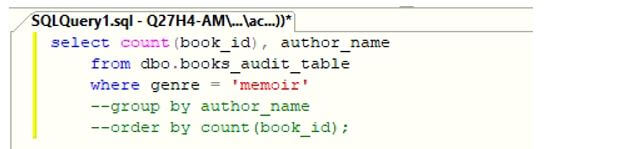
There are numerous ways in which you can format and design your SQL query.
For example, you want to convert a few sentences or words in the query to capital letters, you can do so using the edit tab from the toolbar as shown below.
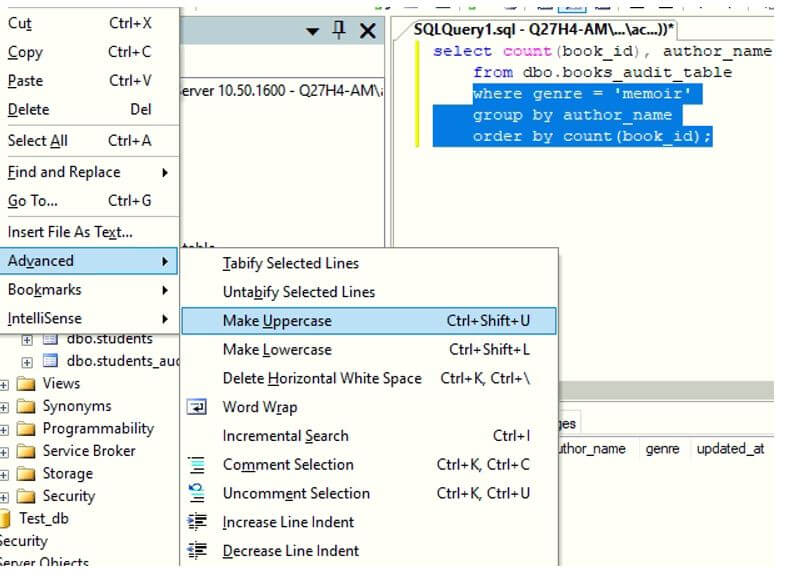
There are many more options under the edit tab’s advanced option. You can try as many options as you wish. Once you have clicked on the Make Uppercase tool, the selected lines in the SQL query will be automatically converted to uppercase as shown below.

Also, by now you might have figured out that beside each option in the edit menu, its corresponding shortcut has been mentioned. So, don’t forget to make use of them to make the process much faster.
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen to beautify and format SQL queries using Query designer and edit toolbar options. A formatted query not just looks beautiful, it also improves the readability of the query for others and hence the process of debugging and reviewing becomes much easier and faster. However, you should note that automatic query designers might not be available in all the database management servers, but the edit option will always be there.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Formatter” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

