Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to PARTITION BY in SQL
The following article provides an outline on PARTITION BY in SQL. The PARTITION BY is used to divide the result set into partitions. After that, perform computation on each data subset of partitioned data. We use ‘partition by’ clause to define the partition to the table. The ‘partition by ‘clause is used along with the sub clause ‘over’. We use window functions to operate the partition separately and recalculate the data subset. Window functions are defined as RANK (), LEAD (), MIN (), ROUND(), MAX () and COUNT () etc. The ‘partition by ‘clause is a scalar subquery. Which always return single value.
Syntax:
window_function ( expression ) OVER (
PARTITION BY expression_1, expression_2...
order_clause
)Here expression, we can use two or more columns to partition the data result set. The expression_1, expression_2 only refer to the columns by ‘FROM’ clause. We can’t refer to the alias in the select statement.
How to Implement PARTITION BY in SQL?
Let us take two tables as below and implementation
Below are “Package” and “Loan” table. Here once we apply the ‘PARTITION BY’ join we get the common rows between two tables.
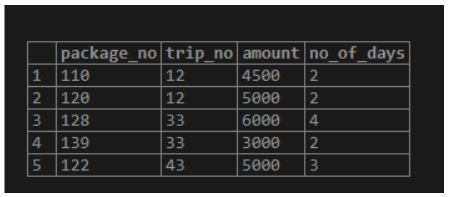
Package Table
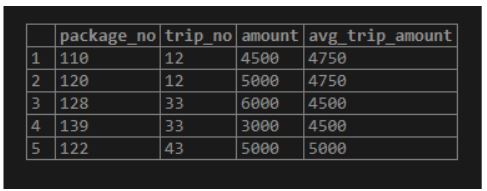
Below is the partition by condition applied as per the ‘amount’ partitioning by the ‘trip_no’.
Code:
SELECT
Package_no,
Trip_no,
Amount,
ROUND (AVG(Amount) OVER ( PARTITION BY Trip_no )) AS avg_trip_amount
FROM
Package;Output:
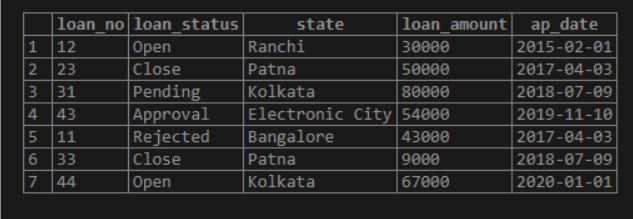
Loan Table:
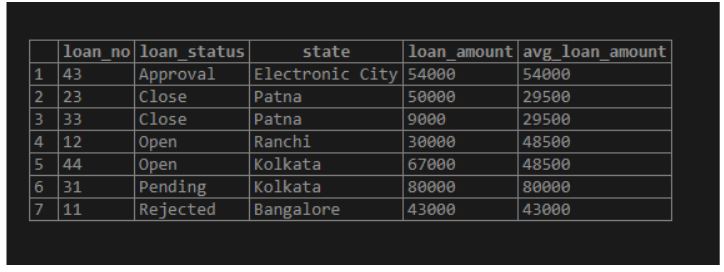
Below the partition by condition is applied as per the ‘loan_amount’ partitioning by the ‘loan_no’.
Code:
SELECT
loan_no,
loan_status,
state,
loan_amount,
ROUND (AVG(loan_amount) OVER ( PARTITION BY loan_status )) AS avg_loan_amount FROM
LOAN;Output:
ROW_NUMBER with PARTITION BY Clause
We use ROW_NUMBER for the paging purpose in SQL. It is used to provide the consecutive numbers for the rows in the result set by the ‘ORDER’ clause. The sequence starts from 1.
Not necessarily, we need a ‘partition by’ clause while we use the row_number concept.
Syntax:
ROW_NUMBER() OVER( PARTITION BY exp1,exp2,.. ORDER BY col1,col2,..)Example:
a. Without using the ‘Partition by’ clause.
Code:
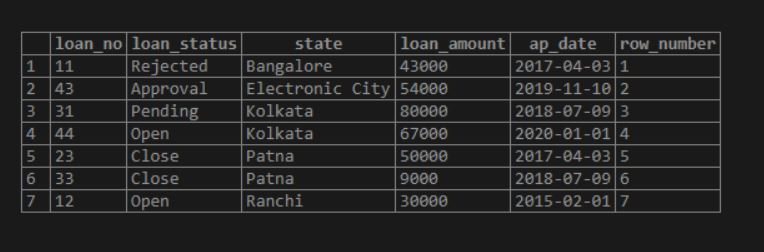
SELECT *, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY state) AS Row_Number
FROM LOAN;Output:
b. By using the partition by clause.
Code:
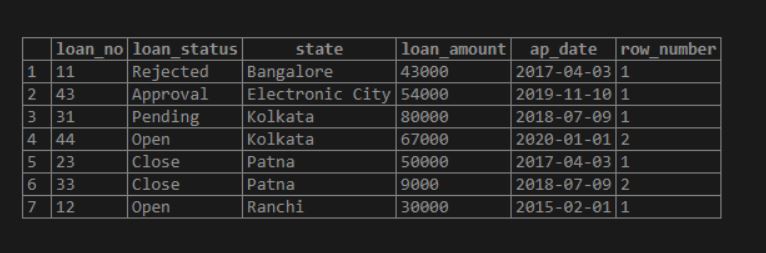
SELECT *, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY state ORDER BY state) AS Row_Number
FROM LOAN;Output:
Examples of PARTITION BY in SQL
Given below are the examples of PARTITION BY in SQL:
Let’s us create the table.
Code:
create table customer_order_data(
customer_name varchar(20),
customer_city varchar(20),
customer_order_amount int,
customer_orderofcount int
);Below commands to insert the data into the tables.
Code:
insert into customer_order_data values ('sam','agile',560,3),
('suppu','kakinada',890,12),
('Ram','kakinada',980,6),
('Raj','korea',780,11),
('Rose','korea',1780,21),
('Jack','korea',120,4),
('Goldy','Japan',320,5),
('Spongy','Japan',1320,15),
('Smarty','USA',520,10),
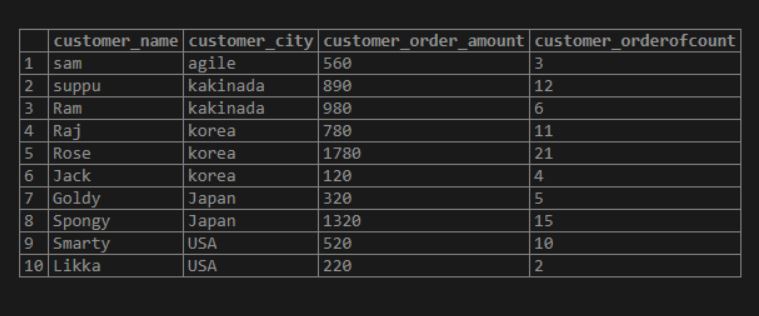
('Likka','USA',220,2)Now lets select the table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM customer_order_data;Output:
Now let’s get the partition by applied for the above table:
Example #1
Code:
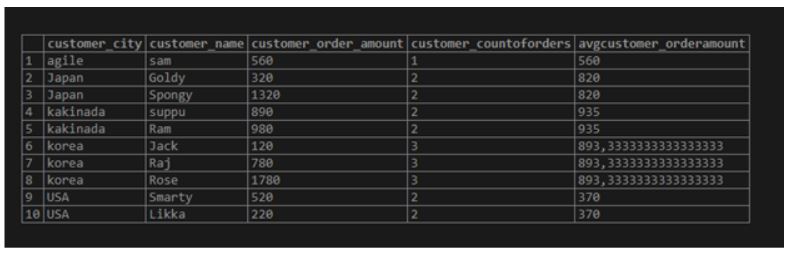
SELECT Customer_city,
Customer_Name,
customer_order_amount,
COUNT(customer_orderofcount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS customer_CountOfOrders,
AVG(customer_order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS Avgcustomer_OrderAmount from CUSTOMER_ORDER_DATA;Output:
Example #2
Code:
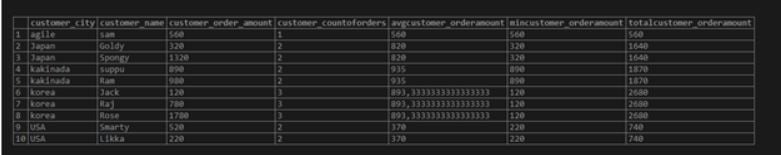
SELECT Customer_city,
Customer_Name,
customer_order_amount,
COUNT(customer_orderofcount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS customer_CountOfOrders,
AVG(customer_order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS Avgcustomer_OrderAmount,
MIN(customer_order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS Mincustomer_OrderAmount,
SUM(customer_order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY Customer_city) AS Totalcustomer_OrderAmount
from
CUSTOMER_ORDER_DATA;Output:
Conclusion
Things that need to be considered in the topic ‘partition by’ in sql are the ‘partition by ‘clause is used along with the sub clause ‘over’. We use window functions to operate the partition separately and recalculate the data subset. Window functions are defined as RANK (), LEAD (), MIN (), ROUND(), MAX () and COUNT () etc The ‘partition by ‘clause is a scalar subquery. Which always return single value. We use ROW_NUMBER for the paging purpose in SQL. It is used to provide the consecutive numbers for the rows in the result set by the ‘ORDER’ clause. The sequence starts from 1. Not necessarily, we need a ‘partition by’ clause while we use the row_number concept.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PARTITION BY in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.