Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL Expressions
SQL expressions are the collective formula consisting of values, column names, operators, and functions present in SQL. The expressions in SQL are further classified as Boolean expressions, numeric expressions, and date-time expressions. The expressions are formulas that evaluate a particular value that can be further used according to our necessity. Boolean expressions are used to evaluate a condition that results in either true or false and can be used anywhere but mostly used in the where clause to perform restrictions on column values.
The numeric expressions are used to evaluate the summarized and cumulative numeric values that are mostly used for reporting purposes. The numeric expressions can be formed by using aggregate functions of SQL such as SUM, COUNT, AVG, etc, and operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc. Date and time-related expressions are used to evaluate and retrieve the current date and time or some manipulated dates and times.
Expressions in SQL with Examples
In this article, we will learn about expressions in SQL and implement some examples to demonstrate Boolean, numeric, and date-time expressions.
1. Boolean Expressions
The use of Boolean expressions is mainly done in the where clause of the SQL queries which can be either SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Note that the conditions and expressions used in the WHERE clause can make the use of AND, OR, NOT, etc operators so that the final value retrieved from the condition will be a Boolean value. This is called a Boolean expression. Let us see the syntax of the usage of Boolean expressions in SELECT query inside the WHERE clause
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_nameN
FROM name of the table
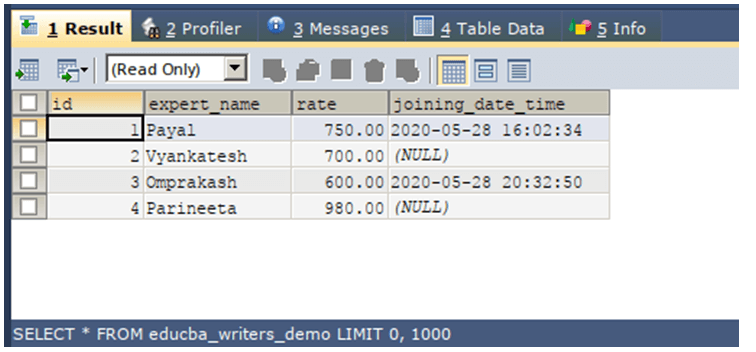
WHERE boolean expression;Let us consider a simple example where we have an existing table named educba_writers_demo that has the contents as retrieved from the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM educba_writers_demo ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
Now, we will apply a boolean condition in where a clause specifies that the value of the rate column should be greater than 700. The condition will return either true or false for each of the records in the table. If it’s true then the record will be added in the final resultset or not. Let us execute the following query and observe the output –
SELECT
*
FROM
educba_writers_demo
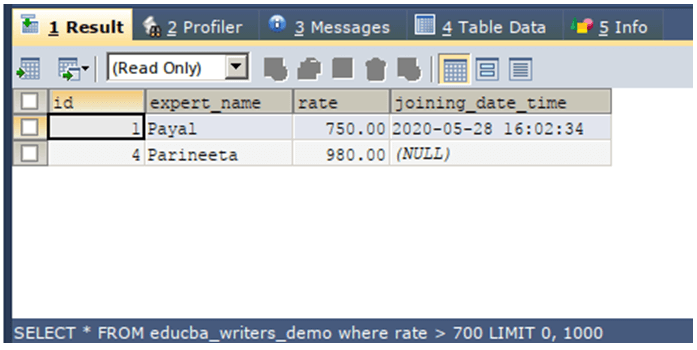
WHERE rate > 700 ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
We can observe that the records for which, where clause condition was satisfied that is the expression rate > 700, evaluates to true are only retrieved in the resultset.
2. Numeric Expressions
Numeric expressions involve usage of literal values and column values and that are manipulated with the usage of operators like add, subtract, divide and multiply and different functions that are available in SAQL such as aggregate functions containing SUM(), COUNT(), AVG(), MAX(), MIN(), etc to retrieve a value that can be used further. Most of the time, numerical expressions are used in the retrieval list of the SELECT query statement to retrieve the summarized data that is sent to the client mostly for analysis purposes such as reporting and dashboarding. Let us consider simple examples that use numerical expressions. Syntax of using numerical expressions is as shown below:
SELECT Numerical expression
FROM name of the table
[WHERE restriction];Let us firstly consider a simple example that we used above to explain the working of the AVG() function. We will calculate the average value of SQL numbers using the AVG() function. Let us create one simple table named numbers and store the num column value in it. We will use the following query statement to create our table –
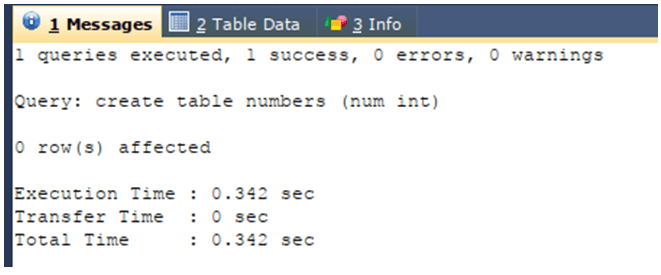
CREATE TABLE numbers (num INT) ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
Now, we will insert the above records in the table. Our query statement will be as follows –
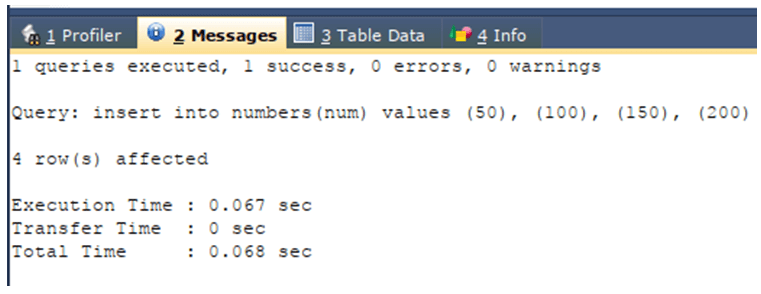
INSERT INTO numbers(num) VALUES (50), (100), (150), (200);The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
Let us now retrieve the records once:
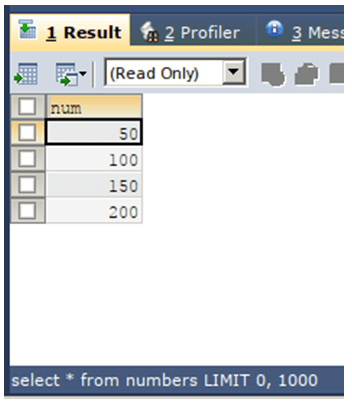
SELECT * FROM numbers ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
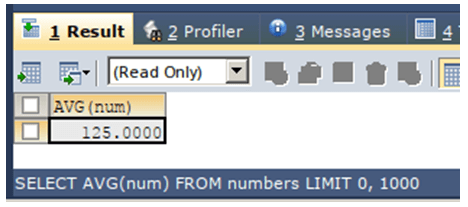
Now, we will calculate the average of num column of numbers table using AVG() function using the following query statement –
SELECT AVG(num) FROM numbers ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
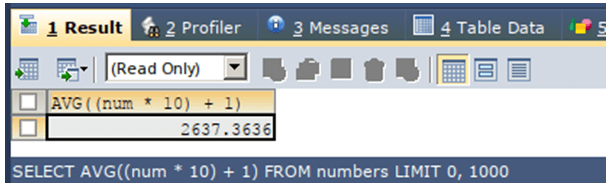
Similarly, we can use COUNT(), MAX(), and various other functions and also formulas involving operators. Let us consider the usage of operators along with avg() function in the following example –
SELECT AVG((num * 10) + 1) FROM numbers ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
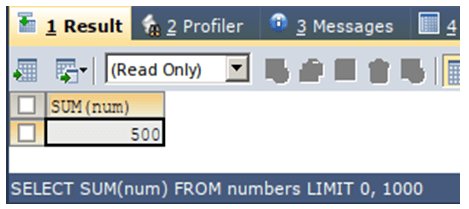
Now, we will calculate the total of num column of numbers table using SUM() function using the following query statement –
SELECT SUM(num) FROM numbers ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
3. Date Time Expressions
The expressions that are related to date and time help in fetching the information such as current date, time, and timestamp. This is used for informative purposes and to store temporal values in the table to record the time and date during which the data was being inserted and also for assigning a default value to the fields with datatype like date, time, DateTime, and timestamp. Let us firstly use a simple query statement that retrieves the current timestamp –
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output:
Further, we can use the different functions that are available in SQL to handle temporal values such as GETDATE() to retrieve the current date and so on.
Conclusion
SQL expressions can be used to evaluate a value that results from the combination of functions, operators, literal values, and column values. The returned value of the expression is further used either for decision making as summarized data or informational purposes. The expressions are classified into three types in SQL that are boolean expressions, numerical expressions, and date time-related expressions respectively.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Expressions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.