Updated August 30, 2023
Introduction to SQL DESCRIBE TABLE
SQL DESCRIBE TABLE is a SQL statement that is accountable for telling something about a specific table in the database. If we want to show the structure of a database table or tables in the server then, we will use the SQL command DESCRIBE or other keyword DESC, which is identical to DESCRIBE one. To get information about the table present in the database and find the attributes related to it, we will use either DESCRIBE or DESC, where both are Case Insensitive and produce a similar output. We implement the DESCRIBE TABLE statement for getting the info about the name of the column, data type of the column, NULL or NOT NULL attributes of column, and table with database size accuracy along with If NUMERIC type scale.
Syntax of SQL DESCRIBE TABLE
Let us elaborate the elementary syntax to show the structure of DESCRIBE TABLE command in SQL server:
DESCRIBE | DESC [TableName | ViewName];The terms mentioned above are described below:
- The TableName denotes the name of the table in the database for which we want to see the structure.
- ViewName also denotes the name of the view created for the table and we wish to describe the view structure.
We can also monitor another syntax type in advance level as follows:
[DESCRIBE | DESC] TABLE{name}[ TYPE = (STAGE | COLUMNS) ];- Here, the {name} defines an identifier for the particular table mentioned to describe it. We can enclose the whole string using double quotes which are case-sensitive when the identifier includes spaces or special characters.
- The TYPE = (STAGE | COLUMNS) term defines whether to show the table columns or the stage properties which comprises of their default and current values for the table.
- But by default the server uses TYPE = COLUMNS, if the TYPE keyword not provided in the query.
- Also, it should be remembered that the query with criteria TYPE = STAGE cannot be applied for views as views do not contain stage properties.
How to DESCRIBE TABLE in SQL?
- DESCRIBE can be said as a synonym for the command EXPLAIN TABLE. These both statements when executed will provide information about all table columns.
- Therefore, using DESCRIBE TABLE in SQL it will tell you either about the columns present in that specific table or its current values type and also the default values for a table’s stage properties.
- When we execute DESCRIBE TABLE command in our database we will be able to view the structure of the table in a describe tab but not on the console tab of the system software.
- The SQL DESCRIBE TABLE query will make us to know about the organization of table that consists of name of table column with data type values such as VARCHAR, CHAR, INT, FLOAT, TIME, DATE, NUMBER or any XML type, used for the respective fields in the table, also it displays column having NULL or NOT NULL database objects that says if the column do include null values or not.
- Thus, the SQL DESCRIBE TABLE is beneficial for fetching out details about the current table present in the database.
Examples of SQL DESCRIBE TABLE
Given below are the examples of SQL DESCRIBE TABLE:
Example #1
Simple Example using DESCRIBE TABLE command.
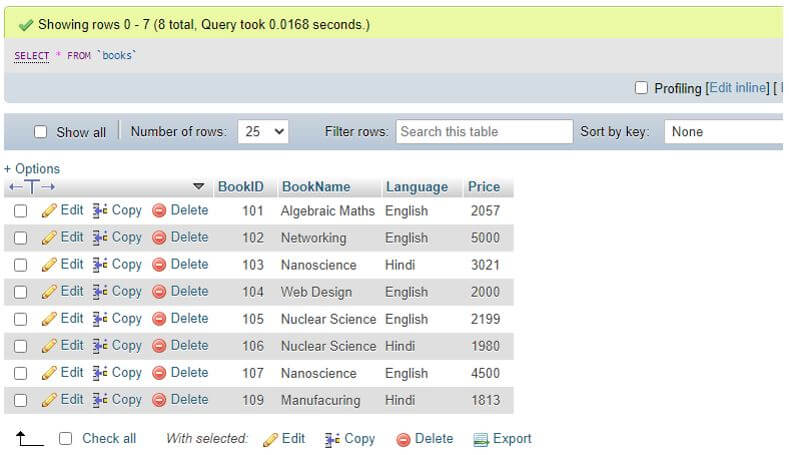
Suppose, we have taken a table as demo to use the DESCRIBE. TABLE command on it and view the result. We have a table named Books in our database with fields as BookID, BookName, Language, Price and each having different data type defined at the time of table creation.
The contents of the table can be shown as below:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Books;Output:
Now, let us apply simply the DESCRIBE TABLE query written as below:
Code:
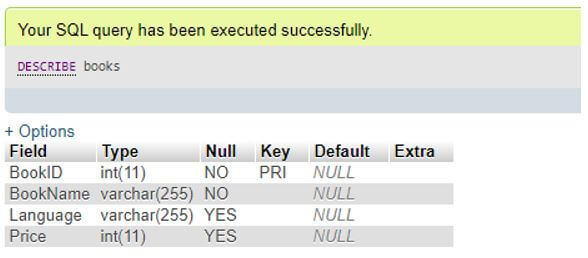
DESCRIBE Books;Output:
As you can see in the output above that the column names of the table Books with Type, NULL attribute, Key, Default values and even Extra attribute are described by the DESCRIBE TABLE statement.
The data type values with its length and NULL attribute with YES/NO values for its presence and PRIMARY key are also provided in the structure of the table. Note that the YES in NULL column says that the value for that specific column of table can be NULL and NO denotes we cannot place or insert NULL values.
Example #2
Example using DESC TABLE command.
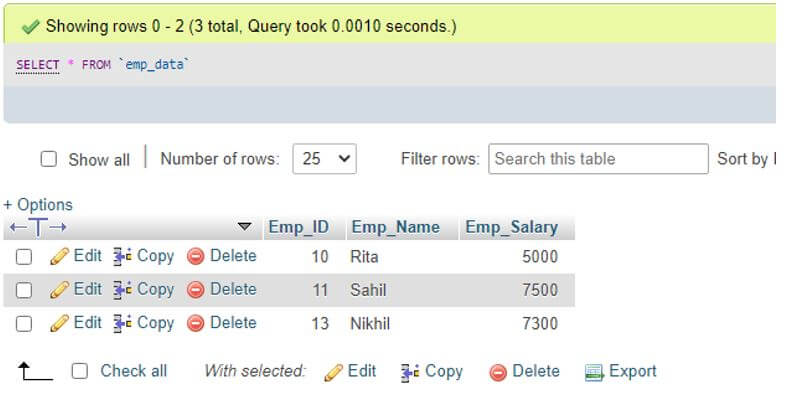
Assume that we are having a table named Emp_Data present in our database created as follows:
Code:
CREATE TABLE Emp_Data(Emp_ID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, Emp_Name VARCHAR(255), Emp_Salary INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0);After completing the structure of table let us fill in some records as below:
Code:
INSERT INTO `emp_data`(`Emp_ID`, `Emp_Name`, `Emp_Salary`) VALUES
(10,'Rita',5000),
(11, 'Sahil',7500)
(13, 'Nikhil',7300);Now, displaying the contents of table Emp_Data:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Emp_Data;Output:
Next, we will query using DESC TABLE command to get the details of the table by the statement below:
Code:
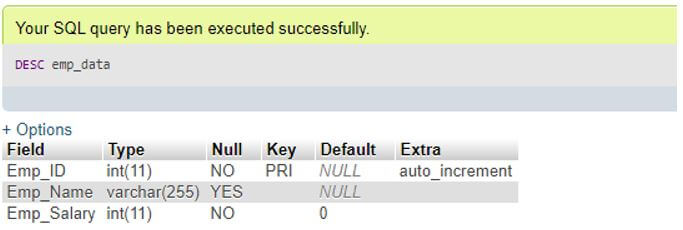
DESC Emp_Data;
OR,
DESCRIBE Emp_Data;Output:
As you can view while creating we have added default value for the Emp_Salary column and therefore when described the result shows DEFAULT as 0 in Emp_Salary row. Similarly, for in Emp_ID row you can see the auto_increment value in the Extra column which is the attribute added in table making time as mentioned in the above query.
Example #3
Example with DESCRIBE TABLE command Vs EXPLAIN TABLE command.
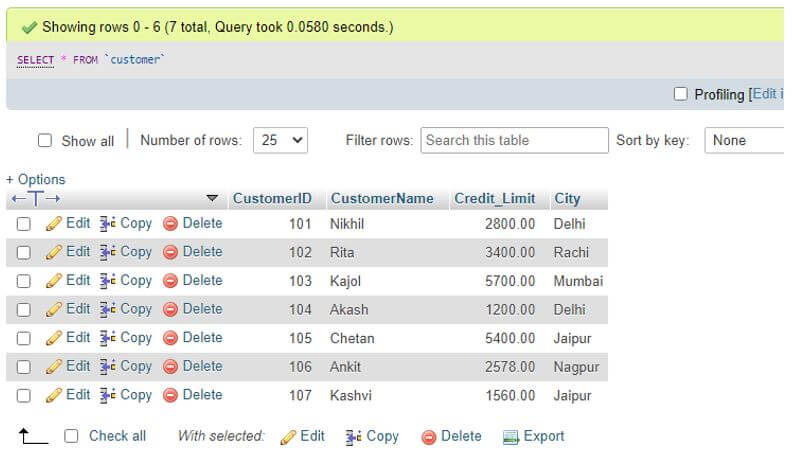
Let us take the table Customer with fields: CustomerID, CustomerName, Credit_Limit and City having their respective data types and other attributes.
View the table:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Customer;Output:
The EXPLAIN Table and DESCRIBE Table commands are similar in working and generates the same result rows. We can say that both are synonyms to each other and any of them in SQL server can be applied to retrieve information about a particular table.
See the queries below with output simultaneously:
Code:
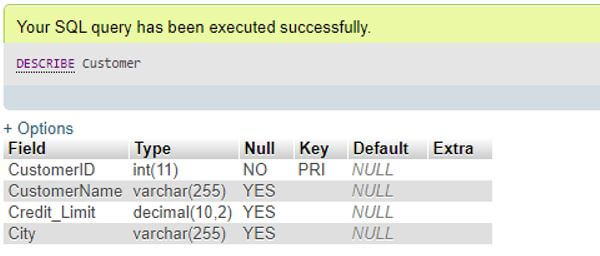
DESCRIBE Customer;Output:
Code:
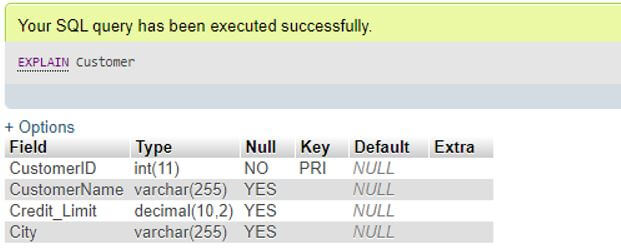
EXPLAIN Customer;Output:
As you can see both outputs are identical with DESCRIBE and EXPLAIN Table commands as well.
Conclusion
The DESCRIBE query in SQL is implemented to display the definitions of a list of columns for a specified database table. SQL DESCRIBE Table command should be executed on only our system software not it any editor because it won’t run there. We need to run this DESCRIBE query on the database installed on our own system server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DESCRIBE TABLE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.