Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to SQL Clear Table
We can clear the table contents in SQL using two ways. One of the ways of doing so is to use the data definition language command named TRUNCATE that deletes all the records present in the particular table that exists in our SQL database server. Another way of clearing the table is by using the Data manipulation language command DELETE FROM in which we can delete all the contents of the particular table by skipping any restriction on the columns of the table in the where clause and clearing the contents of the table. In this article, we will see how we can clear the table contents in SQL by using truncate command and delete command.
Using Truncate Command
We can use the ready-made method that is provided in the data definition language commands of SQL named TRUNCATE to remove all the contents of the table in SQL.
Syntax of Truncate Command:
TRUNCATE TABLE name of table;In the above syntax, the name of the table is the table name of which we want to clear all the contents and records that exist in that table. The keyword TABLE needs to be used when using the TRUNCATE command.
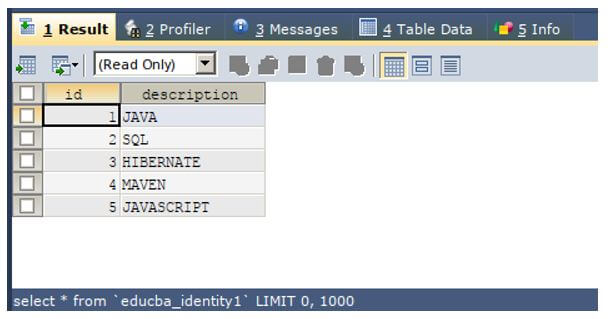
Let us consider one example. The table named educba_identity1 which contains 5 rows and has the structure and contents as shown in the output of the below query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_identity1`;Output:
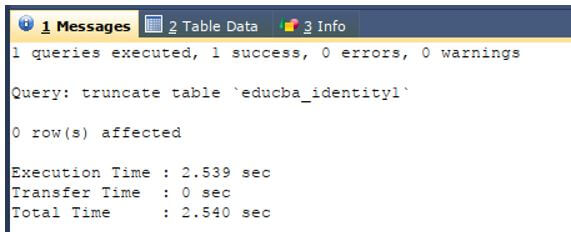
Now to delete all the rows and clear the table named educba_identity1 using the truncate command, we can make the use of the following query statement.
Code:
TRUNCATE TABLE `educba_identity1`;Output:
Let us once again check the contents of the table educba_identity1 and see whether the table is cleared using the following SQL command.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_identity1`;Output:
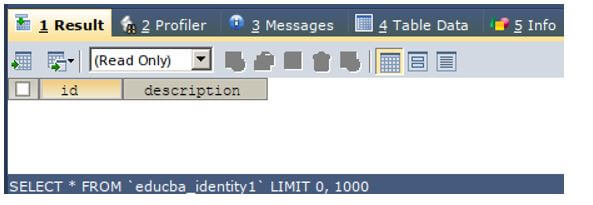
We can observe that the table named educba_identity1 has been cleared successfully and there is none of the record present in the table.
Using Delete Command
We can clear the contents of the table by using the delete command which is one of SQL command of the set of the data manipulation language commands that are available in SQL. This command is most often used to delete the selected rows present in the table.
Syntax of Delete Command:
DELETE FROM name_of_table;In the above syntax, the name of the table is the table name of which we want to clear all the contents and records that exist in that table. The keyword TABLE needs to be used when using the TRUNCATE command.
Let us consider one example. The table named educba_identity2 which contains 5 rows and has the structure and contents as shown in the output of the below query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_identity2`Output:
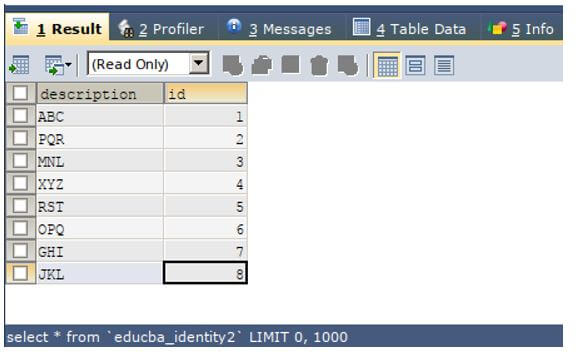
Now to delete all the rows and clear the table named educba_identity2 using the truncate command, we can make the use of the following query statement.
Code:
DELETE FROM `educba_identity2`;Output:
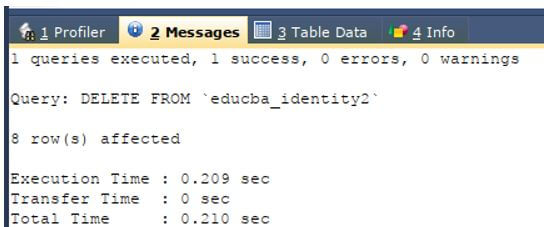
Let us once again check the contents of the table educba_identity1 and see whether the table is cleared using the following SQL command.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_identity2`;Output:
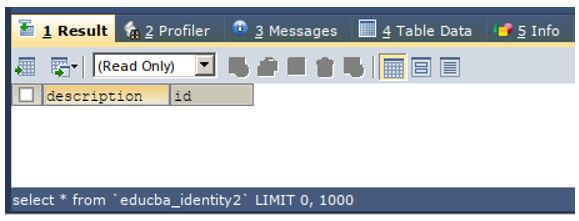
We can observe that the table named educba_identity2 has been cleared successfully and there is none of the record present in the table.
Using Drop Table
We can alternatively use the drop command to delete the whole table along with its contents and structure that completely vanishes the existence of that table in our database in the SQL. But we will have to create the same table again using the CREATE table command in SQL. Note that drop command not only clears the table contents but also the structure of the table.
Let us consider one example in which we have one existing table named educba_writers_demo that has the columns and the contents of the table that are as shown in the output of the below query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_writers_demo`;Output:
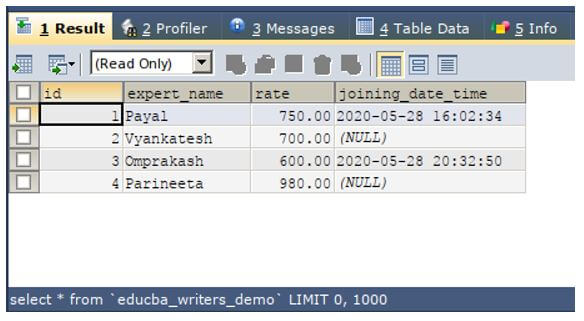
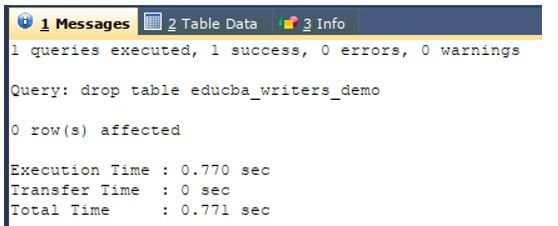
Now, let us drop the table by using the drop command in SQL that clears the table contents as well as the table existence in our database.
Code:
DROP TABLE educba_writers_demo;Output:
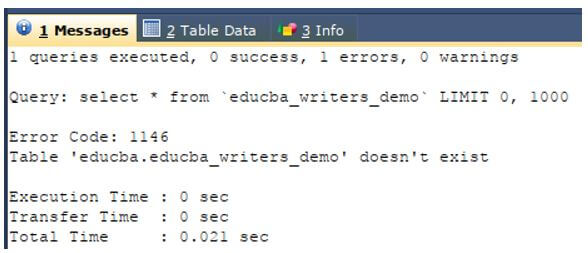
Let us check the contents of the table by using the following query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_writers_demo`;The execution of output of the above query statement is as shown below that shows the error saying that the table does not exist.
Output:
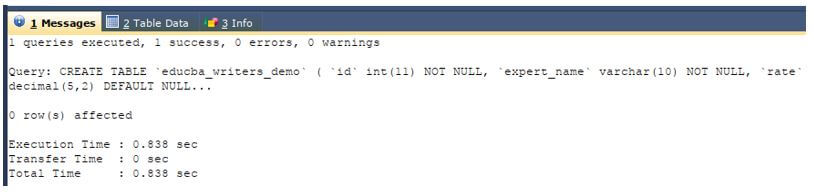
Let us recreate the table using the following create table command.
Code:
CREATE TABLE `educba_writers_demo` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL,
`expert_name` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`rate` DECIMAL(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`joining_date_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL
) ;Output:
This successfully creates the table named educba_writers_demo that has the same structure. Let us try rechecking the contents of the table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `educba_writers_demo`;Output:
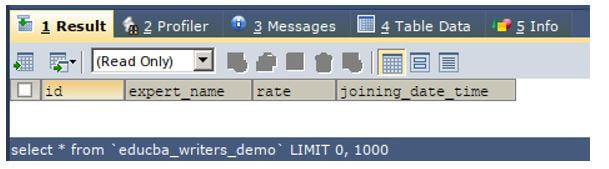
This shows that the table contents have been cleared.
Conclusion – SQL Clear Table
We can clear the contents of the table in SQL by using multiple methods that include the usage of the data definition language command name truncates or data manipulation command named DELETE. An alternative method of clearing the contents of the table involves dropping the table that deleted the table as well as the contents of the table and recreates the table again using the CREATE table command.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Clear Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

