Updated July 17, 2023
Definition of SQL Between Dates
A range of values is provided using the WHERE clause and the SQL BETWEEN operator. When used sequentially, the SQL BETWEEN operator is quite similar to the SQL IN operators. In addition to dates, text values, and numeric values, the BETWEEN operator can be utilized. The SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands can all be used with this operator.
Key Takeaways
- When we use a BETWEEN AND statement in SQL, selecting data between two values or dates is simple.
- One can use a variety of SQL operators to return the appropriate data when one wishes to SELECT data in SQL that is located between two values.
- However, it can be easier for data scientists to analyse queries when analysing code later because the BETWEEN operator is arguably the most logical one to comprehend rationally.
What is SQL Between Dates Operator?
A different approach to select the same data using standard SQL operators. It is highly advised that we use min() and max() to double-check that the query is giving the data we anticipate whenever we are picking data between ranges. It may be a little trickier than we think to use BETWEEN. Whether the column is a DATE or DATETIME, the column determines how to proceed.
Syntax:
The Syntax between Operator is given below:
SELECT Col FROM table WHERE column BETWEEN min value1 AND max value2;Values can be defined as a component of the BETWEEN operator using the syntax mentioned above.
Test expression: It is the expression or column that needs a range to be defined.
Min value(expression): For the between operator, a minimum range is established. It should have the same data type as the Test expression.
Max value(expression): It represents the between operator’s widest possible range. Additionally, it must share the same data type as the test expression and min value(expression).
Use of SQL Between Dates Operator (numeric value, text value, and date value)
These limitations must be met by the three expressions in a BETWEEN condition:
- All three statements should evaluate numeric, time, or character data types that are compatible with one another.
- The value of the expression that comes after the keyword BETWEEN must be lower than the value of the expression that comes after the keyword AND.
Numeric Value
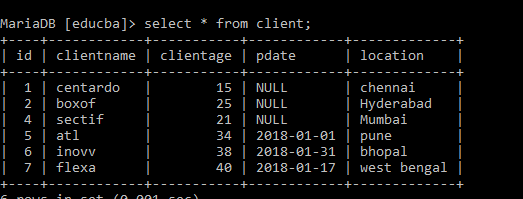
For Numeric, let’s use an existing Table.
The existing Table name is Client, and the structure of a Table is Shown as:
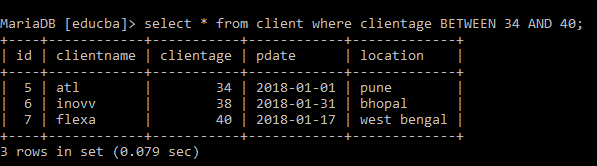
Next, by Using the below Query to take the Numeric value using Between Operator and the Output is Shown as:
Code:
Select * from client where clientage BETWEEN 34 AND 40SQL Between Operator using Text
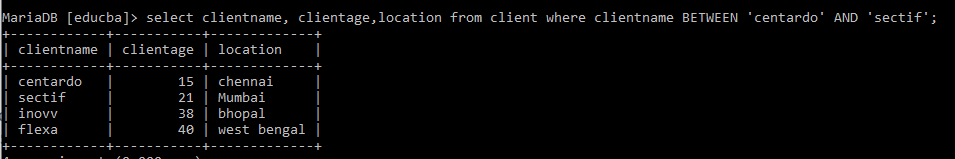
Between a Text data, the Between Operator plays an action, and the Output is shown below, which lists the Student name Between centrado and sectif.
Code:
Select clientname, clientage, location from client where clientname BETWEEN 'centrado' AND 'sectif';SQL Between Two Dates
When the test expression is more than or equivalent to the start expression’s values but less than or equal to the end expression’s value, the BETWEEN operator returns TRUE. The larger than (>) and less than (<) operators can be used in place of the BETWEEN operator.
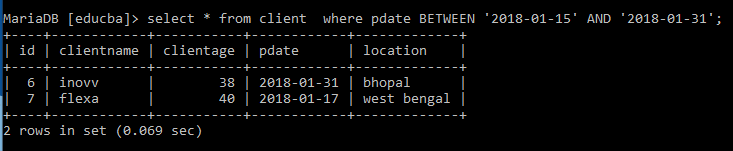
Retrieving the details of the Transaction between two dates ‘2018-01-15’ & ‘2018-01-31’.
Code:
Select * from client where pdate BETWEEN '2018 -01015' AND '2018-01-31'And the result is given as:
SQL Between Dates Multiple
The DATEDIFF() method enables to compare the years, months, weeks, etc., between two dates:
Syntax:
DATEDIFF(date_part, start, end);The date part, start date, and end date are the three inputs that the DATEDIFF() function accepts.
The date part is the period between the start date and the end date that you wish to compare, such as a year, a quarter, a month, or a week.
The dates to be compared are the start date and end date. They have to be converted into DATE, DATETIME, or DATETIME values.
How to Find SQL Between Dates?
But it’s important to remember that the between operators is inclusive. The start and end boundaries are thus a part of the final set.
First, Create a Database:
We need to create a connection to mysql using XaampServer using username and password.
Code:
C:\Users\Suryakala KRAV>cd..
C:\Users>cd/
C:\>cd xampp
C:\xampp>cd mysql/bin
C:\xampp\mysql\bin>mysql -h localhost -u root;
MariaDB [(none)]> use test;
Database changed
MariaDB [test]> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| course |
| school |
+----------------+Creation of a Table:
Code:
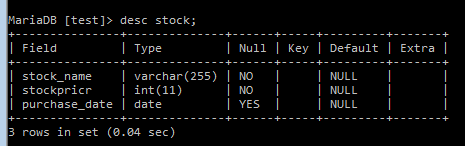
MariaDB [test]> create table stock (stock_name varchar(255) NOT NULL, stockpricr
INT NOT NULL, purchase_date DATE);The above query creates a table named Stock in the Test Database, And we added three columns respectively.
Inserting a value into a Table:
The sample values as shown:
Code:
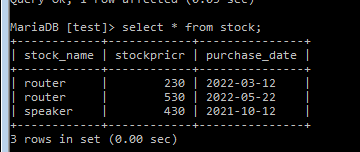
MariaDB [test]> insert into stock values('router', 230, '2022-03-12');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec)
MariaDB [test]> insert into stock values('router', 530, '2022-05-22');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.57 sec)
MariaDB [test]> insert into stock values('speaker', 430, '2021-10-12');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)Once a Query inserts all the values, it can be validated using select Query.
To view a Table:
Code:
Select * from stock;Now choose a date between.
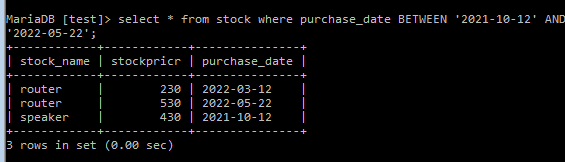
Code:
MariaDB [test]> select * from stock where purchase_date BETWEEN '2021-10-12' AND
'2022-05-22';And the Output is given as follows:
There is no need for a LIKE because BETWEEN works with DateTime values. As an alternative, we only define the column we need to query—in this case, order date—and then use BETWEEN and AND to distinguish between the minimum value and the maximum value.
We may modify the queries to acquire the necessary information if we know all the SQL Between operator rules and syntax. With the help of this tool and other SQL tools, we may create various sorts of crucial queries.
Conclusion
In this post, we looked at the SQL Between operator and some of its applications. We want to be knowledgeable about the function of obtaining a particular set of facts. Additionally, we discussed using the BETWEEN operator to create a condition that evaluates a range of values.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Between Dates” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.