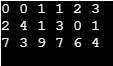Definition of Sparse Matrix
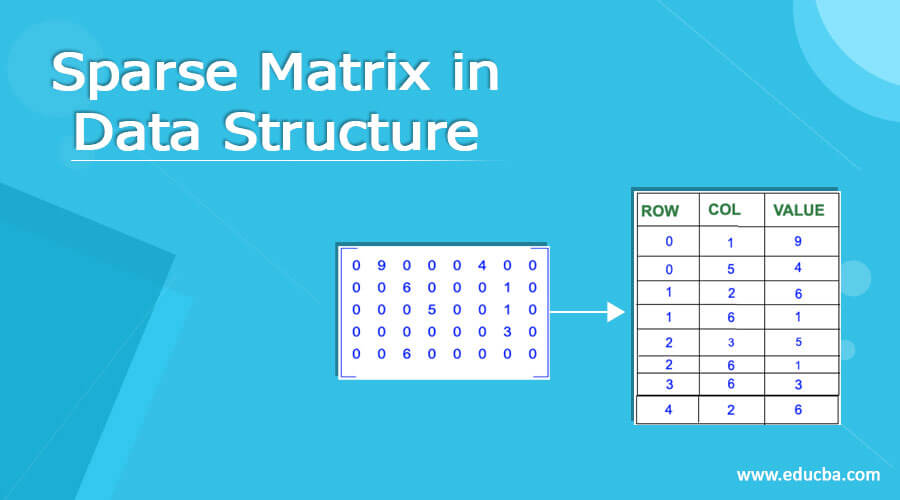
Sparse Matrix is a matrix that contains a few non-zero elements. Almost all the places are filled with zero. Matrix of m*n dimension refers to a 2-D array with m number of rows and n number of columns. And if the zero elements in the matrix are more than the non-zero elements in the matrix, then it is called a sparse matrix. And in case the size of the matrix is big, a lot of space is wasted to represent such a small number of non-zero elements. Similarly for scanning the same non-zero will take more time.
Syntax:
Thus to limit the processing time and space usage instead of storing a lesser number of non-zero elements in a matrix, we use the below 2 representation:
1. Array representation
The 2D array is converted to 1 D array with 3 columns representing:
a. Row – Row index of non-zero element
b. Column – Column index of non-zero element
c. Value – value at the same row, column index in 2D matrix
2. LinkedList representation:
In linked list representation, each node has four fields as given below:
- Row: Row index of the non-zero elements in the matrix.
- Column: Column index of the non-zero elements in the matrix.
- Value: Value of the non zero elements at (row, column) position in the matrix
- Next node: Reference to the next node.
How Sparse matrix works in data structure?
Sparse matrix is the type of 2 -D matrix where a number of zero elements are large as compared to non-zero elements. Storing such matrices in memory creates many space problems as a lot of space is wasted in storing such zeroes. Also, a lot of time is wasted to find the non-zero elements in the pool of many zeroes.
Sparse matrix representations store the non – zero elements of the 2-D matrix. Thus avoids the wastage of space in storing the zeroes present in such matrices. Also, it saves time to find the non-zero elements in such a matrix with large dimensions.
We can store them using any of the following representations:
I -Array representation- This type of representation is for those scenarios where we need to access the elements more often. Since array store, the elements based on the indices thus is much helpful.
II – Linkedlist Representation – This type of representation is for those scenarios where the frequency of insertion and deletion operation in the matrix is more since it is easier to delete and insert elements in the linked list as compared to the arrays.
Examples
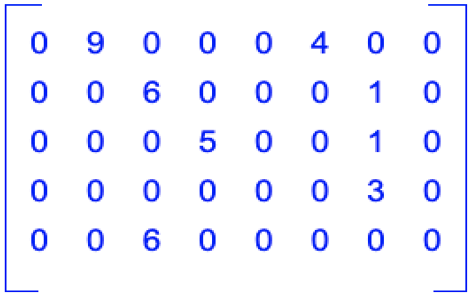
Let us illustrate the concept of a sparse matrix with an example. Consider below 2-D matrix with 5 rows and 8 columns.
As we can see only 8 elements out of 8 * 5 = 40 elements in the matrix are non-zero. That depicts that we just need to store these 8 elements to store in the memory. Since the rest are zero elements thus can be ignored.
There are 2 ways to represent such elements in the memory:
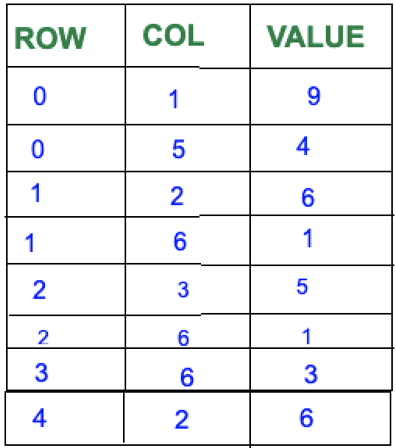
I. Array representation:
Step 1: List the non-zero elements in the matrix with their row and column index.
Step 2: Create a new array with the following dimensions:
- Rows = number of non-zero elements in the matrix.
- Columns = 3( Row, Column and value)
Step 3: Fill the array with the non-zero elements.
Since element 9 is located at position (0,1) thus array is filled with row =0 col =1 and value 9.
Similarly element 4 is located at position (0,5) thus array is filled with row = 0 and col =5 and value = 4.
Advantages of Arraylist representation
ArrayList representation is helpful when access operations are more frequent because elements in the array list can be accessed on the basis of their indexes. Thus it is easier to access an element in an array list as compared to linked list.
Implementation:
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int mySparseMatrix[][]
= {
{0, 0, 7, 0, 3},
{0, 9, 0, 7, 0},
{6, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 0}
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (mySparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
size++;
}
}
}
int resMatrix[][] = new int[3][size];
// Making of new matrix
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (mySparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
resMatrix[0][k] = i;
resMatrix[1][k] = j;
resMatrix[2][k] = mySparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
System.out.printf("%d ", resMatrix[i][j]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
}
Output:
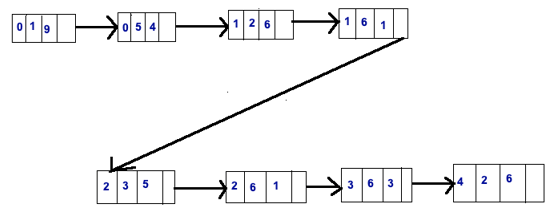
II. LinkedList representation: This type of representation is similar to array representation in storing row, column index, and value of the non-zero elements. However, instead of creating an array of size equal to a number of non-zero elements present in the matrix, we create linked list nodes of the above syntax.
Step 1: List the non-zero elements in the matrix with their row and column index.
Step 2: Create new nodes with the above-given structure and put values of row and column index and the value of the non-zero elements.
Step 3: Point the next pointer of the elements to the next element to form the linked list.
Advantages of linked list representation:
Linked list representation is helpful when insertion and deletion operations are more frequent because the complexity of inserting and deleting a node in linked list is very less than arraylist.
Implementation:
class Node {
int row;
int col;
int value;
Node next;
Node(int r,int c, int val) { row =r;col=c;this.value =val; }
}
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int mySparseMatrix[][]
= {
{0, 0, 7, 0, 3},
{0, 9, 0, 7, 0},
{6, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 0}
};
Node start=null;
Node tail =null;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (mySparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
Node temp = new Node(i,j,mySparseMatrix[i][j]);
temp.next = null;
if(start == null){
start = temp;
tail=temp;
}
else{
tail.next = temp;
tail = tail.next;
}
}
}
}
Node itr = start;
while(start !=null){
System.out.println(start.row +" "+start.col+" " +start.value);
start = start.next;
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Sparse matrix is considered as a solution to the problem of representing a 2-D matrix with most of zero elements. We can either use array representation or linked list representation to store elements of such matrix and enhance the time complexity of the program. As well as we can save a lot of space storing just 0 elements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Sparse Matrix in Data Structure. Here we discuss the Definition, How Sparse matrix works in data structure? example with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –