Updated June 3, 2023
Introduction to Socio Technical System
Socio technical system is a mixture of people and technology and much more. It is an approach to complex organizational design recognizing workplace interaction between people and technology. This system can perform multiple complex computations and return the result to its environment. It illustrates the fundamental characteristics of the system.
Socio Technical System Components
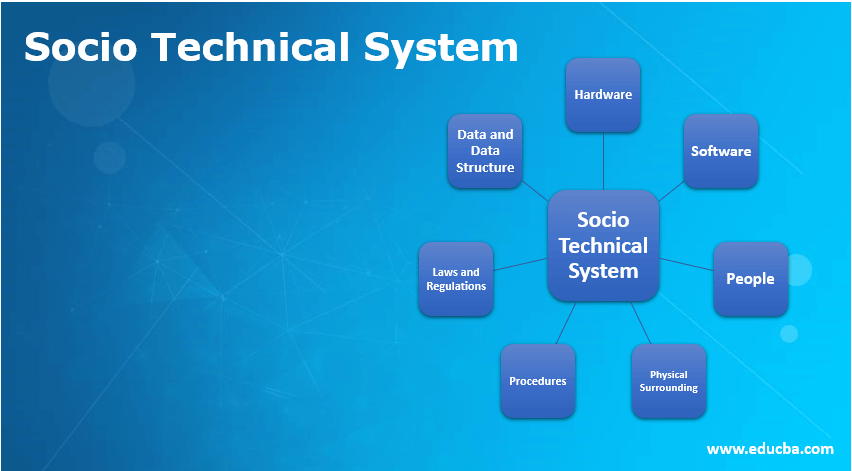
Different components are mentioned below:
1. Hardware
It includes mainframes, workstations, peripherals, and connecting networks. For example, consider a set of 10 microcomputers connected by a network. These networked computers differ based on the circumstances. These networked computers are part of the emergency room, a small public lab at a university, an elementary school computing lab, a risk analysis tool in an insurance form, or part of military supplier testing manufactured parts. In this socio-technical system, hardware is the microcomputer, connecting wires, hubs, routers, etc.
2. Software
Software is an integral part of any socio-technical system. Software and hardware incorporate social rules and organizational procedures into their design: operating systems, utilities, application programs, and specialized code. An operating system is a software that probably does not change and is designed more with the socio-technical system in mind.
3. People
Individuals, groups, agencies. These different roles of a person in different socio-technical systems bring different responsibilities and ethical issues.
4. Physical Surrounding
The building also influences social rules, and their design can affect technology use. Moving technology from one physical environment to another may cause mismatch problems.
5. Procedures
Both official and actual management models, reports relationship, documentation, data flow, rules, and norms. It describes the way things are to be done in an organization. The rules and their implementation are important in understanding a socio-technical system. Those who know the rules, for instance, know how to make complaints, get a questionnaire passed, and how find the answers to technical questions.
6. Laws and Regulations
These procedures are the same as above, but they carry special societal sanctions if the violators are caught. They are the laws regarding privacy protection or testing of chips in military use. These societal laws and regulations might conflict with each other. For example, some companies have expectations that employees will share commercial Software. Obviously, these illegal expectations cannot be made explicit, but they can be made aware of.
7. Data and Data Structures
Data is collected, how they are documented, to whom they are made available, and the format in which they are stored are all decisions of designing part of the socio technical system. Data archiving in an emergency room will differ from that in an insurance company and is subject to ethical issues.
Characteristics of Socio Technical System
- Socio technical system is often non-deterministic. This means there is no guarantee that they will always generate the same output for specific input. The system behavior depends on the human operators, who do not always react similarly. Also, using the system may create a new relationship between components, changing its emergent behavior.
- Socio technical systems have emergent properties of the system as a whole rather than associated with individual components of the system. Emergent properties depend on both system components and the relationship between them. Thus emergent properties can only be assessed once the system has been integrated.
- The extent to which the system supports organizational objectives depends not just on the system itself. It also depends on the stability of these objectives, the relationship and conflicts between them, and how they interpret these objectives.
Emergent System Properties
An emergent property is a result of the relationship between system components. They can only be assessed and measured once the components have been integrated into a system.
Types of emergent properties are as follows:
- Functional properties: Functional properties appear when all system components work together to achieve some objective. For example, a bullock cart has the functional property of a transportation device once assembled from its components like wheels, seating arrangement, OX pair, etc.
- Non-functional properties: Non-functional properties state the system’s behavior in its functional environment. For example, performance, reliability, portability, and security. The system’s reliability depends on the system components’ reliability and the relation between the components, but expected interaction can cause new types of failure. The security of the system is its ability to resist attacks. Some attacks may be such that the system designers did not expect them and may crush the built-in safeguards.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Socio Technical System. Here we discuss the introduction, characteristics, socio technical system components, and emergent system properties. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –