Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Snowflake Schema
Snowflake is one of the many schema types used for the implementation of the Data Warehouse systems Architecture. In this type of schema, the data warehouse structure contains one fact table in the middle, multiple dimension tables connected to it and connected with one another as well. It should have all the dimension tables to be normalized to the last level of normalization, until there is no more space for further normalization.
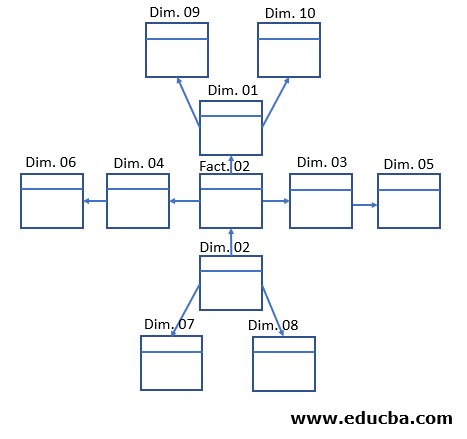
Snowflake Schema must contain a single Fact Table in the center, with single or multiple levels of Dimension Table. All the Dimension Tables are completely Normalized that can lead to any number of levels. Normalization is nothing but breaking down one Dimension table into two or more Dimension tables, to make sure minimum or no redundancy. While all the first level Dimension tables are linked to the center Fact table, all the other Dimension tables can be linked to one another if required. This Structure resembles a Snowflake (Fig. 01), hence the name ‘Snowflake Schema’.
Why Snowflake Schema?
Snowflake Schema type is selected based on multiple limitations that are considered crucial for the specific Project, by the Project Management team. Here are the basic characteristics of the Snowflake
The schema that can help in this decision-making process,
- This model can involve only one fact table and multiple dimension tables which must be further normalized until there is no more room for further normalization.
- Snowflake Schema makes it possible for the data in the Database to be more defined, in contrast to other schemas, as normalization is the main attribute in this schema type.
- Normalization is the key feature that distinguishes Snowflake schema from other schema types available in the Database Management System Architecture.
- The Fact Table will have all the facts/ measures, while the Dimension Tables will have foreign keys to connect with the Fact Table.
- Snowflake Schema allows the Dimension Tables to be linked to other Dimension tables, except for the Dimension Tables in the first level.
- This Multidimensional nature makes it easy to implement on complex Relational Database systems, thus resulting in effective Analysis & Reporting processes.
- In terms of Accessibility, Complex multiple levels of Join queries are required to fetch aggregated data from the central fact table, using the foreign keys to access all the required Dimension tables.
- Multiple Dimension tables, which are created as a result of normalization, serve as lookup tables when querying with Joins.
- The process of breaking down all the Dimension tables into multiple small Dimensions until it is completely normalized takes up a lot of storage space compared to other schemas.
- As the querying process is complex, the pace for Data Retrieval is by far low.
Workflow of Snowflake Schema
Here we will discuss the Workflow of Snowflake Schema by explaining how to create snowflake schema along with the pros and cons.
How to Create a Snowflake Schema?
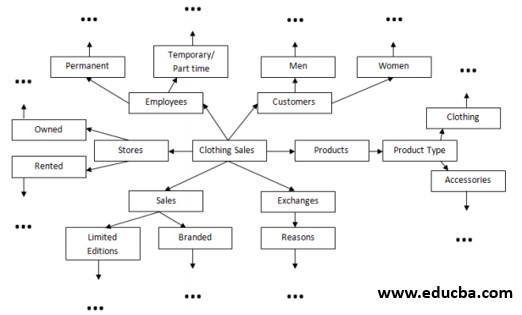
When the requirement is to create a schema with a fact table ‘A’ that has 6 dimension tables ‘B, C, D, E, F, G’, and each of these dimension tables has furthermore normalization in-scope, then Snowflake schema will be the right pick in this case.
These Dimension tables ‘B, C, D, E, F, G’ are further disintegrated into further more Dimension tables. This process continues up until there is no further approach to break the already normalized Dimension tables.
Say our ‘A’ is a ‘Clothing Sales’, it could have the below dimensions as its ‘B, C, D, E, F, G’, which has the scope for further normalization –
- Employees
- Customer
- Store
- Products
- Sales
- Exchange
Now let us design a Snowflake Schema for this –
The above Dimension tables can be further broken as –
- Stores – Owned & Rented, which can be further broken into location, country, state, region, city/ town, etc in each level, depending on the available data and requirements.
- Sales – Limited Editions & other Branded, which can be further broken into seasonal, nonseasonal, etc.
- Exchanges – Reasons as the second level, Exchange for ‘money-back’ & ‘different product’ as the third level of Dimensions.
- Products – ‘Product Types’ table as second-level Dimensions, and levels for each type of product. This can be continued until the last level of normalization.
- Customers – ‘customer types’ as Men & Women, which can be additionally split as members, non-members, types of membership, etc.
- Employees – the type of employees as ‘Permanent’, ‘Temporary/ Part-time’ employees. The next level here can be departments, location, Salary Grade, etc.
This can be further normalized to its final level of dimension tables, as it helps in reducing redundancy in final data. This Schema can be used for Analysis or Reporting when the focus is mainly on the Clothing Sales alone (fact table), and the first level dimensions as specified above.
Pros and Cons of Snowflake Schema
The following pros and cons are mention below –
- Minimum or no redundancy, as a result of Normalization, which is the core quality for Snowflake Schema.
- Snowflake Schema is a complex system, as it can have any number of levels of normalization depending on the depth of the given database.
- Data Quality will be exceptional, as Normalization grants the benefit for the well-defined form of tables/ data.
- If any new requirement creates a need for denormalization, data quality will be taken back and redundancy may occur. This may be lead to restructuring the entire Schema.
- When queried with Joins, clear & accurate data is retrieved.
- Maintenance is difficult as the higher-level dimensions need to be expanded constantly.
- High Data quality & accuracy helps in facilitating efficient Reporting & Analysis.
- Low performance as it required complex Join queries.
- Easy implementation process when provided with multipart Relational Databases.
- Large storage space is required for full Normalization and elaborate querying process.
Conclusion
To sum up, if the requirement comes with options for more storage, tolerance for low performance, complex tables which allow structuring with the single fact table, time & space for complete normalization, Snowflake Schema will be the best option. Though it uses complex Join queries, the output will be an accurate compilation of data that can make Analysis and Report exceptionally efficient.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Snowflake Schema. Here we discuss the Workflow of Snowflake Schema by explaining how to create snowflake schema. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –