Difference between SHA1 vs MD5
The following article provides an outline for SHA1 vs MD5. Sha1 and md5 are used in hashing, both algorithms are hashing algorithms. Md5 is secured as compared to sha1, but it does not provide good security as compared to other hashing algorithms. Sha1 is complex as compared to md5, and it will provide greater security as compared to other hashing algorithms. Md5 is called a message digest, and sha1 stands for secure hash algorithms for the square measure.
The md5 hash function provides a 128-bit hash value; this algorithm is used to design the cryptography, but by using this algorithm, vulnerabilities are discovered as per the course time. The first version of the algorithm is known as sha1. The md5 algorithm is used for computing checksums and partitioning for validating the files to transfer. Sha1 is designed for cryptography applications, but by using this algorithm, we have found vulnerabilities.
The message digest algorithm is a hashing algorithm used to protect the data when files were conveyed by using insecure channels. Sha1 is a part of the cryptographic function which was created to keep the data safe. Sha1 is a functioning algorithm that makes compression functions and modular additions. The md5 function is used to provide data integrity where we have to alter the messages.
What is SHA1?
This is a cryptographic hash function that takes input and generates the message digest, which is a 160-bit hash value represented as a 40-digit hexadecimal integer value. This algorithm is a US federal information processing standard created by the NSA in the United States. PGP, TLS, and IPsec are security protocols that use sha1 algorithms.
To understand the initial message by using the sha1 algorithms, the attacker needs to perform 2^160 operations. If an attacker needs to look at two messages by using message digest, which was identical, then they need to perform 2^80 operations. So, we can say that the sha1 is secure as compared to the md5. Since the year 2005, sha1 is regarded as insecure by adversaries.
What is MD5?
The md5 is a hashing algorithm that produces a 128-bit hash value. The md5 algorithm is created with the intention of using a hash function that was cryptographic. The md5 algorithm is used for validating the integrity of data as a checksum. This algorithm is used in tasks that were non-cryptographic, such as finding the partition for a certain key in the partitioned database.
This algorithm is used in the software industry to ensure that the file which was transferred arrived in good condition. Sum programs of md5 algorithms are provided in a distribution package of operating systems which was UNIX based. Windows users are using the inbuilt function of PowerShell.
Head to Head Comparison between SHA1 vs MD5 (Infographics)
Below are the top 10 differences between SHA1 vs MD5:
Key Difference Between SHA1 vs MD5
Let us discuss some of the major differences between SHA1 vs MD5:
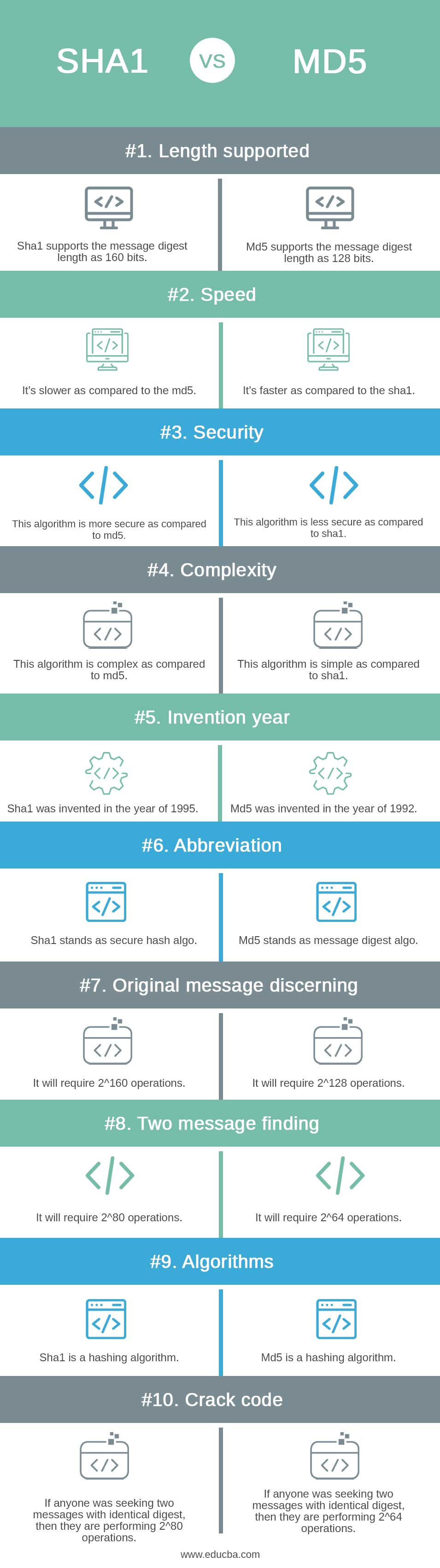
- Md5 creates the 128-bit message digest while the sha1 algorithm generates the 160 bits message digest.
- Using md5 algorithms, retrieving the original attacker’s message requires 2^128 operations. When using the sha1 algorithms, it takes 2^160 operations to retrieve the message that was originally sent by the attacker.
- If the attacker wants to find the two messages which contain the same digest, he will require 2^64 operations by using md5 algorithms, whereas by using the sha1 algorithm, it will require 2^80 operations.
- As a part of security, the sha1 algorithms are more secure as compared to the md5 algorithms. As a part of security, md5 algorithms are less secure as compared to the sha1 algorithms.
- MD5 is faster as compared to sha1, and sha1 is less fast as compared to md5. But sha1 is more complex as compared with the md5.
- The message digest algorithms are 168 bits in a length, while the sha1 algorithm is 160 bits in a length.
- Md5 algorithms are very simple compared with the sha1 algorithms. The sha1 algorithm is very complex compared with the md5 algorithms.
- Basically, we are not using md5 algorithms in security applications. We are using the sha1 algorithm in a security application.
- Sha1 algorithms have not reported any attacks yet, while md5 algorithms reported attacks in applications.
- Sha1 algorithms are suitable for sensitive applications, whereas md5 algorithms are not suitable for sensitive applications.
- Md5 algorithm is very simple compared to the sha1 algorithm. The sha1 algorithm is not simple as compared to the md5 algorithms.
SHA1 Requirement
This algorithm was cryptographically broken, but still, we are using the same in multiple applications. This function takes input and produces the 160-bit hash value, which was known as a message digest. This algorithm was typically rendered from the 40 digits of hexadecimal numbers. Sha1 produces the message digest, which was based on the principle similar to those who are using message digest algorithms, but it will generate the hash value, which was larger.
The original specification of the sha1 algorithm is published in 1993 under the title name as the standard of secure hash. The sha1 algorithm is a part of multiple security applications and protocols, including SSL and TLS. Sha1 algorithms are required as per law in the specific application of the US government. We are initializing the sha1 algorithms by using the method name as getInstance. This method is used in all hashing algorithms.
MD5 Requirement
Md5 algorithms is running mathematical files by using hashing algorithms to generate the signature, which was matched from the original file. By using the same way, the received file is authenticated by matching with the original file to ensure that the right files where will go. The md5 hashing algorithm is used to convert the data into 32-bit characters.
The md5 hashing algorithm is a cryptographic function which was accepting a message of any length and, in output, will provide a fixed-length digest value for authenticating the message which was sent by the sender. This algorithm was basically designed for authenticating digital signatures.
Comparison Table of SHA1 vs MD5
Below is the top comparison between SHA1 vs MD5:
| Sr. No | Key Points | MD5 | Sha1 |
| 1 | Length supported | Md5 supports the message digest length as 128 bits. | Sha1 supports the message digest length as 160 bits. |
| 2 | Speed | It’s faster as compared to the sha1. | It’s slower as compared to the md5. |
| 3 | Security | This algorithm is less secure as compared to sha1. | This algorithm is more secure as compared to md5. |
| 4 | Complexity | This algorithm is simple as compared to sha1. | This algorithm is complex as compared to md5. |
| 5 | Invention year | Md5 was invented in the year of 1992. | Sha1 was invented in the year of 1995. |
| 6 | Abbreviation | Md5 stands as message digest algo. | Sha1 stands as secure hash algo. |
| 7 | Original message discerning | It will require 2^128 operations. | It will require 2^160 operations. |
| 8 | Two message finding | It will require 2^64 operations. | It will require 2^80 operations. |
| 9 | Algorithms | Md5 is a hashing algorithm. | Sha1 is a hashing algorithm. |
| 10 | Crack code | If anyone was seeking two messages with identical digest, then they are performing 2^64 operations. | If anyone was seeking two messages with identical digest, then they are performing 2^80 operations. |
Purpose of SHA1
The sha1 is the hash function that was basically used to verify the files which were not altered. We can do the same by producing the checksum before we have transmitted the file, and after producing the checksum, then it will reach the destination. In the real world, sha1 is used at the time of entering the password into the login page of our website, it will happen in the background; this is the method that the website will use to securely check whether our password is correct or incorrect.
At the time of using the sha1 algorithm in the specified website, the same time our password will turn into the checksums after we are entering it. The same checksums are compared with the checksum, which we have stored in the websites where we are relating to the current password, where we have not changed the password.
Purpose of MD5
This message is originally designed for the message authentication purpose, which we are using on the internet. The md5 algorithms were not reliable as per using cryptographic checksums. The encryption collision is nothing but the two files will contain the same hash functions. We are using hash functions, password security, or message security, and also in cryptocurrency.
We are using md5 hashing in integrity protection; also, we are using the same for protecting against errors. We are accepting the md5 hash, which we are adding to any application or protocol which we are employing with the md5 for any purpose which we have stating the security.
Conclusion
The message digest algorithm is a hashing algorithms used to protect the data when files were conveyed by using insecure channels. Sha1 is a part of the cryptographic function which was created to keep the data safe. Sha1 vs md5 is used in hashing, both algorithms are hashing algorithms. Md5 is secured as compared to sha1, but it is not providing good security as compared to other hashing algorithms.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SHA1 vs MD5. Here we discuss the SHA1 vs MD5 key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –