Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SAS INTCK
The SAS INTCK is one of the default functions. It returns the number of interval boundaries between the two dates or times. The function’s return value is integer even though we used default discrete methods at the number of times. This is because the start and beginning of the time interval are reaches at the first and second dates of the complete intervals between the two important dates and times.
Key Takeaways
It has some key points to follow and perform the SAS operation:
- It specifies the character constant, variable, and expression that can be the same as the Interval name.
- Then the Interval may be either upper or lower characters.
- We can use Multipliers and shift indexes in the basic Interval names to reconstruct the data.
- The Start-date and End-date expressions are required as the function parameters.
- We can use default methods like continuous and discrete.
What is SAS INTCK?
Even though we have used some default discrete methods on the SAS language, the most important date function is at the intck(). It helps to calculate the number of times it starts and begins the time interval, and it may reach the first and second date of the complete intervals between the two important dates and times. The SAS intck returns the number of interval boundaries between the two dates or times and counts the datetime feature. It always returns the value of the function may be the integer, because the count is applicable for all the areas, including the date, time, and years. Mainly the date9 format is specified and used for the SAS modules to calculate the date difference like day, week, month, and year.
SAS INTCK Function
We know that the INTCK is the default date function, and it helps in different real-world scenarios like calculating the individual’s age difference. Then we may use it to perform the employee tenure in the specific companies in which they worked over the years. The same organization is also used to calculate the customer tenure, which is based on the product that will be applied to the company and released with the Live project. Several working days will be the the main theme, and employee welfare growth organization employees also benefit the same in the all big and small organizations.
In the course section, the number of hours will calculate the syllabus coverage and covered topics for the examination and carrier growth of the students and the employees in the organization sectors. Whenever we learn new technologies like courses, we need to pay the amount, so sometimes, we can calculate the payments quarterly, half-yearly, and annually. The amount will vary depending upon the courses. Other, the date and time will be the the main role of the sections so that it will track the datas in the software application.
Steps to Create SAS INTCK Function
Given below are the steps mentioned:
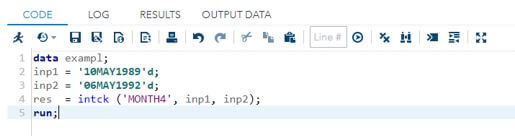
1. Navigate to the below link.
3. Paste the below code as the sample to perform the intck() function.
4. data exampl;
5. inp1 = ’10MAY1989’d;
6. inp2 = ’06MAY1992’d;
7. res = intck (‘MONTH4’, inp1, inp2);
8. run;
9. In the above code, the intck() function is used and performed the operations with different parameters like MONTH4, inp1, and inp2.
SAS INTCK Date and Intervals
The SAS intck function computes the date and time intervals for the two different dates, while the INTCK function varies on the time units. It may support the years, months, weeks, days, etc. So that we can call and refer to the INTCK as INTerval ChecK, everyone knows the INTCK function, which helps to return the integer count of the numbers in the two different datetime intervals. Some operations like changing formats to perform the dates with the dataset in SAS of the date variables. We can use and perform the continuous operation on the INTCK function along with the SAME data option on the interval boundaries.
The start date and end date will vary based on the user’s request that the parameters or arguments are changed due to the new datasets. Datepart() and Timepart() are the additional functions that help to calculate the result counts, days, events, and hours coverage. Interval names and values of each datas include the interval at the the date and time intervals with multipliers and shift indexes options for using the basic intervals on the constructed datas with more complex interval specifications.
We can also create our Intervals, Multipliers, and other Shifting Intervals depending on the types like Interval, Multiple, and Shift index. These three parts are used to perform the interval name operations on the SAS, that is, an interval that helps to denote the basic interval type. The algorithm helps compute the number of years and days between the two dates in the SAS.
The Multiple represents the optional multipliers that helps to sets the basic interval types, and finally, the shift index helps to start the index period at the specific time duration. That will be included the calendar date and time intervals.
Example of SAS INTCK
Given below is the example mentioned:
Code:
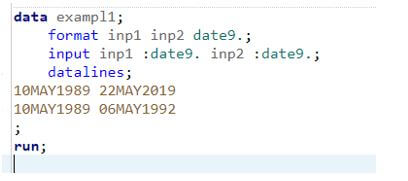
data exampl1;
format inp1 inp2 date9.;
input inp1 :date9. inp2 :date9.;
datalines;
10MAY1989 22MAY2019
10MAY1989 06MAY1992
;
run;
data exampl2;
set exampl1;
a = intck('day', inp1, inp2);
b = intck('weeks', inp1, inp2);
c = intck('months', inp1, inp2);
run;
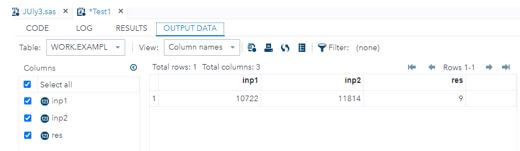
proc print data=exampl2;Output:
1. In the above example, first we need to create the dataset along with required inputs, variables and other dependencies.
2. Then we need to perform the intck() function of the above datasets. Here I can add the different dateofbirths.
3. So, by using the intck() function, calculate the differences from days, weeks, months and years, etc.
FAQ
Given below is the FAQ mentioned:
Q1. What is SAS intck?
Answer:
It is mainly used to return the number of days difference time intervals between the two dates that including times, date, and datetime values.
Q2. How will use the intck function in SAS?
Answer:
It is the function for to perform the date calculation between the two dates like example syntax: intck(‘YEAR,’’10MAY1989’d, ‘06MAY1992’d ).
Q3. How do you find the date difference in the SAS intck?
Answer:
Mainly we used the Interval parameter so we can call the method in the intck(day, week, month, year, time,..)
Q4. What are the two-parameter methods in the SAS intck?
Answer:
- Continuous
- Discrete
Q5. What are the types of Intervals?
Answer:
- Calendar Interval Calculations
- Date and Datetime Intervals
- Retail Calendar Intervals
- Custom Time Intervals
Conclusion
The SAS intck() function helps to perform the date operations from the different areas like that it helps to calculate the date and time intervals. Mainly it will calculate the days, weeks, months, and years from more than one resource based on the requirement it may vary and return the results in integer format.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SAS INTCK. Here we discuss the introduction, steps to create SAS INTCK function, date and intervals, example, and FAQ. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –