Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SAS Join
The SAS join is the kind of operation that is mainly helpful for performing the query operation or combination of one or more tables that can be viewed under the relationships. It may affect the data on those specific tables across the n number of tables which is listed on the FROM and SELECT statement for processing the result from one set to another data set.
Overview of SAS join
A SAS join operation is the main type of query that combines the n number of datas from more than one tables and it is mainly viewed among the data tables. When multiple number of table specifications on the keyword classes like FROM and SELECT that processed the data result from one form into another form. If the datas are stored in the separate result set it will contribute the tables that may be already saved on the most type of join operations and its satisfies the user condition. Most part of joined tables are performed and stored it on the result set variable the other sql like FedSQL data supports will use the several join operations such as mainly combined with the joins, equijoins, cross joins, qualified joins and natural joins.
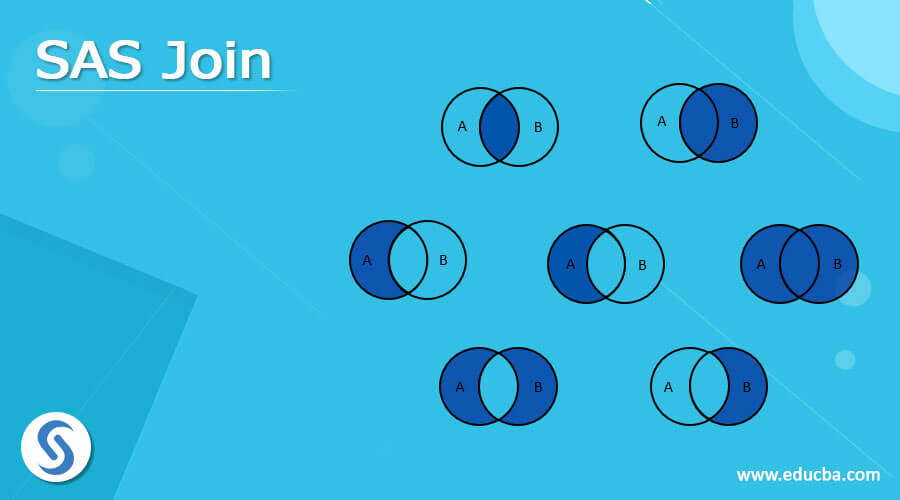
SAS Join Operations
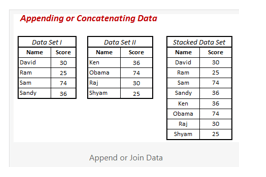
Generally SAS joins supports two types like vertical and horizontal joins. Vertical joining is the type and it is appended from one data set to another data set with sequence of time. Whereas horizontal joining is the one or more number of keys and variables are combined with the data observations. It will varied from one joins to another joins if the sql query will be used as vertical join then it follow the steps for to adding the vertical joining datas.
Vertical Joining:
It is the sequence of data and the time sequence that providing both data sets which have the some type of variables and attributes at the data type, length and labels. Here one data set is combined at least one variable that should practice for identifying the data source at the data sets with observation originated form. There is no need to sort the data sets if the source data sets would be restored by the date if would vertically joining the data sets if the issue is vertical compatibility. More ever corresponding data variables in each data set have the same attributes at the datas present in the other variable. We used proc datasets and append command will use the vertical joining utility procedure PROC DATASETS with APPEND statement. The vertical compatibility may be overridden by using the FORCE option if one data set will created the same attributes in the resulting data set.
If the values are missing at the each observation from one data set to the other variables with shorter and variable length are different at the numeric type of the characters. So that the data labels are different from the PROC DATASETS and APPEND commands also with UNION corresponding ALL variables common data sets.
Horizontal Joining:
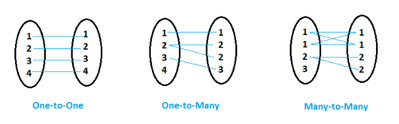
Whenever we combined the data sets through via horizontal join from the multiple data sets into the single data observation in the new data set. Mainly it is combine with data sets through horizontal way for to understand the data relationship between the input data sets like one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many or other related datas. Its combine with merging set of datas and it is observed from two or more number of data sets into the single data observation in the new data set.
Match-merging is mainly merged with the input values based on one or more number of common variables.
SAS left join:
It is one of the characteristics of SAS joins and it is performed only with the left set of joins with two datasets. In proc sql is mainly call it as the procedure sql which helps to create table, select table which referred as the left join. It helps to select the items from all the data observations in the first or left set of data set which combine with the key-values pairs. But its mainly observed with matching set of key and values from the right data set.
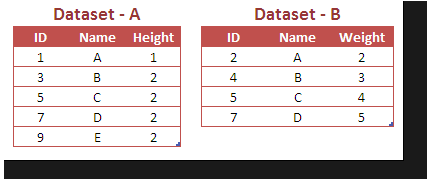
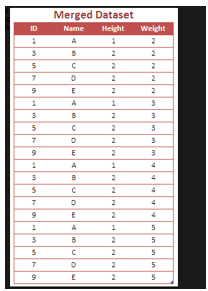
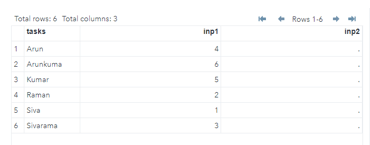
The above diagrams shows the example for the left join on the SAS datasets. It has two different data sets stored on the separate table and each if them will join using the id or other primary identifiers.
Example
data first;
input tasks $ inp1;
datalines;
Siva 01
Raman 02
Sivaraman 03
Arun 04
Kumar 05
Arunkumar 06
;
run;
data second;
input tasks $ inp2;
datalines;
January 1
February 2
March 3
April 4
May 5
June 6
July 7
August 8
September 9
October 10
November 11
December 12
;
run;
proc print data=first;
proc print data=second;
proc sql;
create table results as
select * from first as a left join second as b
on a.tasks = b.tasks;
quit;
proc print data=results;
Sample Outputs:
- The above example we used two different datasets like first and second.
- Next each data sets have the separate rows and columns along with the fields and attributes columns.
3. Next the data sets contains the inputs like inp1 and inp2 along with $ dollar sign for to assign the values on the variables.
’
- Then we need to pass the real inputs like String and integer formats with separate attributes. The first data set lines are to be achieved using the Name with rollnumbers its in integer format. Next datasets will operate the datas in the month formats finally it will print the datas using proc and print statements.
- Finally the new results table is created and perform the let join operations on the SAS data sets.
Conclusion
The SAS datasets are generally performed with sql operations along with different categories and data zones. Left join is the most frequent used operations in the huge and normal set of live SAS data sets for performing the complex set of user data operations. Its used and sorted with the statistical set of data in the application.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SAS Join. Here we discuss the introduction, overviews, SAS Join Operations and example, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –