Updated March 16, 2023
Overview of Reverse Number in Java
Java has been a versatile, general-purpose, robust, class-based, and object-oriented programming language that has as few dependencies as possible. Before we talk about reversing a particular number in java, let us first understand what reversing a number in any language means and why it is relevant and its uses and applications. Reversing a number implies that the value of the unit of a particular number will become the nth digit value if the number is n digits long and tens digit number will become (n-1)th place value number on and so forth. In this article will see a detailed explanation of reverse number in java.
Understanding Reverse Number Logic in Java
To understand the concept further, we are required to take the help of an example. Let us say the number is 120, then the number is 3 digits long and contains the place value of units, tens and hundreds. Now when we apply the logic of reversing a number in java, then the units digit, i.e. 0, will become our hundreds digit, and 1 will become our units digit, and 2 will remain as is. Therefore the new number obtained will be 021, and this will be the reverse number of 120. The logic or the program to write is more or less similar in every programming language, and therefore reading this logic in java should not be a problem.
Now, let us discuss the relevance of a reverse number and why do we actually need it. Sometimes there becomes a need to take out the palindrome of a number. If you are new to programming and are unfamiliar with the concept of palindrome, then palindrome is the number that is the same even upon reversal. For example, number 5885 is a palindrome of 5885. So it becomes mandatory to fetch all those values or records which contain palindrome numbers, and there becomes a need to make use of reversing a number in java.
Finding Reverse Number
Let us understand below with the help of various examples for the reverse numbers in java.
But first, let us understand the algorithm behind the reversing of numbers.
Algorithm
- Input a value number.
- Take another variable and initialize it as 0.
- Put the condition of a while loop until the value number > 0.
- Multiply another variable by 10
- Take out the remainder of the value number
- Add the results of steps 4 and 5 and store them in the another variable
- Divide the actual value number by 10
- Close the loop and return the value
Examples
Following are the different examples:
while loop
In this case, to find out the reverse of a number in java, we are using a while loop, a pre-conditioned loop. The condition here is related to the use of > operator where the check is related to the number if it has a value greater than 0.
Code:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num=569;
int r_num=0;
while(num>0)
{
r_num=(r_num*10)+(num%10);
num=num/10;
}
System.out.println(r_num);
}
}Output:

Do-while loop
In this program, the compiler will scan the code at least once and iterates once the condition matches. This is the basic difference between the do-while loop and the while loop. This is a post-condition loop, whereas the while loop is a preconditioned loop.
Code:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num=569;
int r_num=0;
do
{
r_num=(r_num*10)+(num%10);
num=num/10;
} while(num>0);
System.out.println(r_num);
}
}Output:

Recursion Method
Code:
class main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
int num, c = 0, n1;
num = 569
n1 = num;
while(n1 > 0)
{
c++;
n1 = n1 / 10;
}
Rev_Rec obj = new Rev_Rec();
int x = obj.reverse(num, c);
System.out.println("Reversal of a number is:"+x);
}
int reverse(int a, int len)
{
if(len == 1)
{
return a;
}
else
{
int b = a % 10;
a = a / 10;
return (int) ((b * pow(10, len - 1)) + reverse(a, --len));
}
}
}Output:

While loop
In this case, to find out the reverse of a number in java, we are using a while loop, a pre-conditioned loop. The condition here is related to the use of != operator where the check is related to the number if it has the value not equal to 0.
Code:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num=569;
int r_num=0;
while(num!=0)
{
r_num=(r_num*10)+(num%10);
num=num/10;
}
System.out.println(r_num);
}
}Output:

How to Find the Reverse Number in Java?
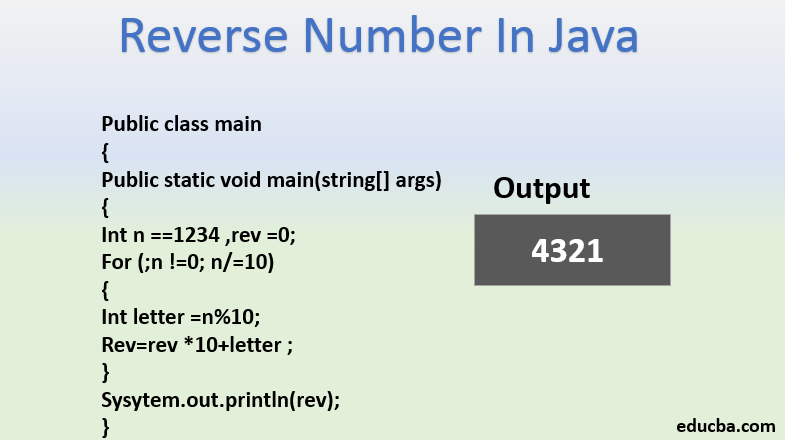
Here in this section, we are going to read about the alternative way of finding the reverse of a number in Java to the one explained above. This will be done with the help of for loop, which is another kind of a looping construct just like the while loop which we studied above. The for loop is generally used at places where we know the number of iterations to be done.
Code:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 123, rev = 0;
for(;n != 0; n /= 10) {
int letter = n % 10;
rev = rev * 10 + letter;
}
System.out.println(rev);
}
}Output:

Here, in this blog post, we have read about the reverse number in Java and how to find the reversal of a number. We also studied the various applications and usages of finding the reverse number. This can be put to many uses based upon the requirement. There can be other ways of writing the same code of code, explained in this post. This is the most optimal and widely used approach for finding the reverse of a number. The approach for reversing a number is almost the same in every programming language; therefore, once you know the logic of the program, it will be very easy for you to implement this solution in other languages as well. I hope you liked our article. Stay tuned to our blog for more articles.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Reverse Number in Java. Here we discuss the basic concept of finding the Reverse Number in Java with the various examples and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


