Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expenditure refers to expenses incurred in the day-to-day running of the business. These are recurring in nature and are allocated to the profit and loss account of the same year.
Unlike capital expenditures, these are not carried forward to future years. The benefit of the revenue expenditures is received in the same accounting year itself. The expenses vary from the costs of producing a commodity to the cost of selling or any expenses incurred in paying the rent or regular expenses of the entity. It also includes costs incurred to maintain the capital expenditures i.e. maintenance cost of machinery every year.
Examples of Revenue Expenditure
Examples of Revenue Expenditure are as follows:
Example #1 – Depreciation on a Machinery
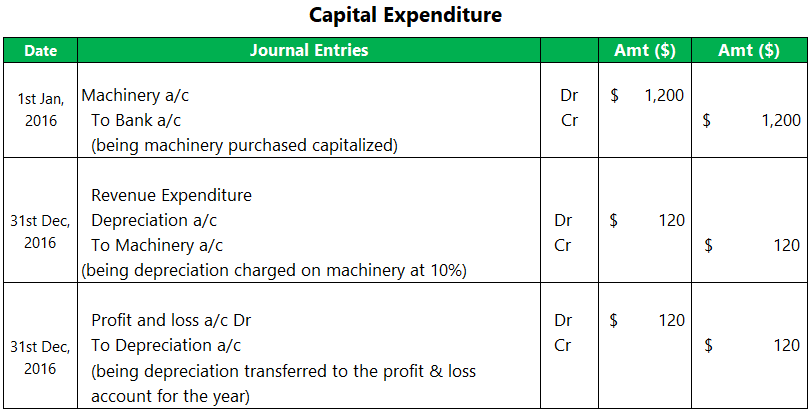
One of the examples of revenue expenditure that could serve as a contrast to capital expenditures is that of depreciation done on an annual basis on a capitalized asset. The initial expenditure on the machinery would be a capital expenditure and would be reported on the balance sheet as the amount paid to acquire it. On an annual basis, there would be depreciation charged on the machinery at 10%. This depreciation charged would be revenue and form part of the profit and loss account at the year-end. Below is an example of one of the machinery purchases and the consequent depreciation at the year-end.
- Company A bought machinery on 1st Jan 2016 for $1200
- The concern is supposed to depreciate the asset at 10% per annum
- Below are the journal entries that would be passed for the accounting of the machinery during the course of the year 2016
Example #2 – Cost of Labor
Revenue expenditures can be classified into two forms. Direct and indirect. Example 1 in the form of expenditures required to maintain a piece of machinery, equipment, or the business generally has already covered the indirect form.
The direct form of revenue expenditures includes the costs incurred in raw materials, labor, or other forms of production that are mandatory for establishing the product or service. Unless these occur, there are no direct factors available to get the finished product or services for the purpose of selling and conducting the prime business.
The cost of labor in this regard becomes an important component. These wages are paid to the factory workers to carry on the production. These might be calculated on a daily, hourly, or weekly rate and paid to them weekly or as of a month-end. Again, it is important to establish the important factors around the wages like overtime payment and bonuses. These have to be paid in addition to the regular rates.
A concern could calculate the gross profit in its working if it reduces the direct material and labor costs from the sales that have taken place.
Example #3 – Rent paid
Every business establishment obtains a physical location to conduct its operations through a rental agreement. Rent is a fixed amount that needs to be paid regularly, either monthly or quarterly, based on the terms of the rental agreement. It is important to note that the business must pay rent even if the premises are not utilized for any reason.
The rental agreement may also include provisions for additional payments if the occupier makes any modifications or alterations to the property. Typically, the rental agreement is for a specific period and must be renewed upon expiration. Additionally, a clause might specify a fixed percentage increase in rent annually.
Regarding recognition, it is crucial to highlight that rent is considered a revenue expenditure, and the business recognizes it on an accrual basis, regardless of the payment timing. For instance, if rent is paid in advance, it is proportioned over the time of occupying the property. Similarly, if rent remains unpaid until the end of the year, it is still recognized on an accrual basis, irrespective of the actual payment status.
Conclusion
To determine whether an expense qualifies as a revenue expenditure, certain features can be considered:
- It is not for the capitalization of an asset but rather for the maintenance of an existing asset, such as repair expenses.
- It is recurring in nature, requiring regular or need-based expenditure.
- The benefits of revenue expenditure are limited to the current accounting year and do not carry forward to subsequent years.
If a revenue expenditure is mistakenly recorded, it must be reversed within the current year or through pre-period adjustments in the following accounting year.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Revenue Expenditure. Here we discuss examples of Depreciation on Machinery, Rent paid, Cost of Labor, etc. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –