Updated November 23, 2023
Difference Between Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
The repo rate is an interest rate in a repo or repurchase agreement. A repurchase agreement involves borrowing money against some security posted with the lender. It involves two transactions: the first one being an outright sale of the specified securities and a simultaneous agreement to repurchase the same securities from the purchaser at an agreed price at a selected future date. The reverse repo rate is the interest rate in a reverse repo or reverse repurchase transaction.
A reverse repurchase agreement involves lending money against some security posted as collateral with the lender. It involves an outright purchase of the collateral with a simultaneous agreement to sell the same collateral at a future specified date at a price agreed with the borrower of money.
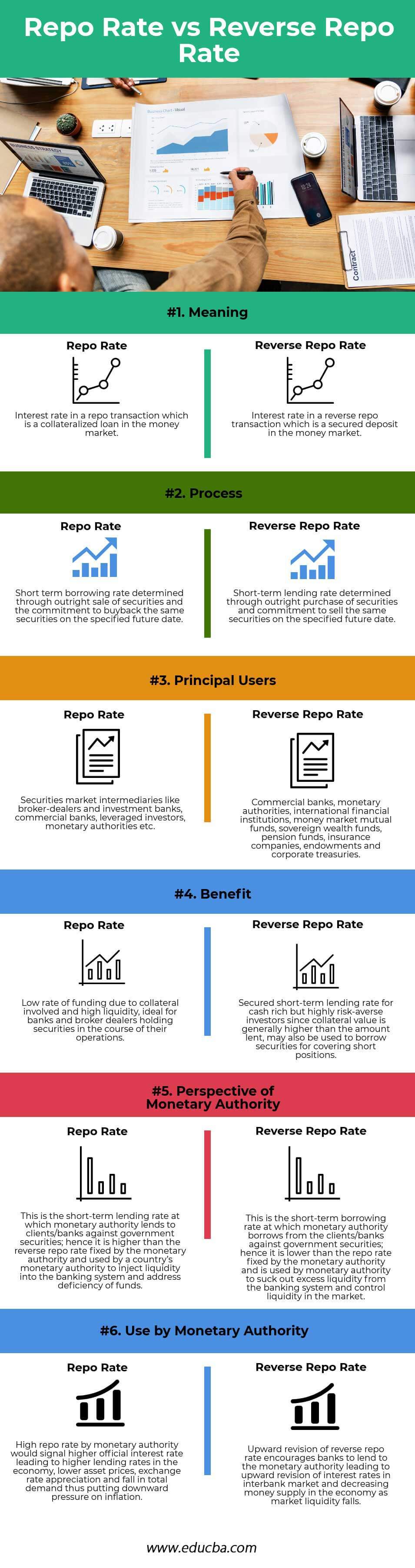
Head To Head Comparison Between Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate:
Key Differences Between Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
Both Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the significant differences:
- Repo rate is the interest rate in a repo transaction that involves the outright selling of securities with a commitment to buy back at a specified future date in the money market. In contrast, the reverse repo rate is the interest rate in a reverse repo transaction involving the outright purchase of securities with a commitment to sell at a specified future date in the money market.
- Principle users of repo rate transactions are securities market intermediaries, commercial banks, leveraged investors, and monetary authorities. In contrast, principal users of reverse repo transactions are commercial banks, monetary authorities, international financial institutions, money market mutual funds, sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, insurance companies, endowments, and corporate treasuries.
- Repo rates offer the benefits of low short-term funding and high liquidity. They are most suitable for securities market intermediaries who can free up funds using the securities held during their business. Reverse repo offers a short-term secured lending opportunity to cash-rich but highly risk-averse investors and may also be used for borrowing securities to cover short positions previously undertaken by the investors.
- Monetary authority uses the repo rate to lend to the banking system and inject liquidity into the system to control inflation in the economy. Monetary authority uses the reverse repo rate to borrow from the banking system and simultaneously suck out excess liquidity from the system to control the money supply in the economy.
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
| Basis of comparison | Repo Rate | Reverse Repo Rate |
| Meaning | The interest rate in a repo transaction which is a collateralized loan in the money market | The interest rate in a reverse repo transaction which is a secured deposit in the money market |
| Process | Short-term borrowing rate determined through outright sale of securities and the commitment to buy back the same securities on the specified future date | Short-term lending rate determined through outright purchase of securities and commitment to selling the same securities on the specified future date |
| Principal users | Securities market intermediaries include broker-dealers, investment banks, commercial banks, leveraged investors, monetary authorities, etc. | Commercial banks, monetary authorities, international financial institutions, money market mutual funds, sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, insurance companies, endowments, and corporate treasuries |
| Benefit | A low funding rate due to the collateral involved and high liquidity is ideal for banks and broker-dealers holding securities during their operations. | Secured short-term lending rate for cash-rich but highly risk-averse investors since a collateral value is generally higher than the amount lent may also be used to borrow securities for covering short positions. |
| The Perspective of the Monetary Authority | This is the short-term lending rate at which monetary authority lends to clients/banks against government securities; hence it is higher than the reverse repo rate fixed by the monetary authority and used by a country’s monetary authority to inject liquidity into the banking system and address the deficiency of funds. | This is the short-term borrowing rate at which the monetary authority borrows from the clients/banks against government securities; hence it is lower than the repo rate fixed by the monetary authority and is used by the monetary authority to suck out excess liquidity from the banking system and control liquidity in the market. |
| Use by the monetary authority. | A high repo rate by the monetary authority would signal a higher official interest rate leading to higher lending rates in the economy, lower asset prices, exchange rate appreciation, and a fall in total demand, thus putting downward pressure on inflation. | An upward revision of the reverse repo rate encourages banks to lend to the monetary authority leading to an upward revision of interest rates in the interbank market and decreasing money supply in the economy as market liquidity falls. |
Conclusion
Repo rates are the rates connected with repurchase agreements identical to a collateralized loan. In contrast, reverse repo rates are those associated with reverse repurchase transactions similar to a secured deposit. Repurchase and reverse repurchase agreements are, in fact, two sides of the same agreement, the former being from the perspective of the short-term fund borrower and the latter being from the perspective of a short-term lender.
Usually, when referring to these transactions with monetary authorities, the dealer’s perspective is considered for distinguishing the trade between the Repo Rate and the Reverse Repo Rate. Hence, repo rates set by monetary authorities are always higher than corresponding reverse repo rates. The repo rate is like a collateralized loan and is usually attractive to the fund borrower owing to a low borrowing rate and high liquidity. The reverse repo is a security deposit for the lender of funds providing him with a short-term investment opportunity. It could also provide an avenue of borrowing security for covering short positions.
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate is the most effective and direct tool the monetary authority uses to signal its policy rate stance. Repo rates control inflation in the economy, while reverse repo rates control the money supply.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between the Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate. Here we also discuss the Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.