Updated February 18, 2023
Introduction to Redis TTL
Redis TTL command is one of the default key commands and can be primarily used to calculate the remaining expired time with seconds and format return with the data key in order to enable the Redis database client to check with the dataset in the future keys which are typically set forever and there is no default TTL along with keys that have no expiration date, so its value must be set.
Key Takeaways
- TTL command helps to return the key remaining time.
- It focuses to calculate the time-to-live for each key mentioned by the user.
- The calculated time is -1 or -2 time seconds.
- If the key does not have any time out then it will return -1.
- If the key does not exist in the redis then it will return -2.
What is Redis TTL?
Redis TTL command is used for calculating the remaining time and retrieving the time expired seconds. The timeout session’s integer value expired the key, which is -1, and another set of keys, -2, do not exist. Its time-to-live designates the time window for sending the data in the packet, and its validity on the topology of the computer network should be checked before it is discarded. In general, the maximum TTL for Redis is 9223372036854775807, not the 2147483647 session expiration time. Using the commands expire, Set key value and go to the pattern session, timeout will be cleared.
Why Use Redis TTL?
Returning the time of the keys is helpful because it verifies whether the user session is active or has timed out. Redis client will assist in comparing the supplied set of dataset keys to the time in seconds. Redis older or newer versions have commands that return values such as -1 for keys that are supplied but do not yet exist or will exist on the associated dataset. The memory data format for data storage used on database memory cache and message brokers for transmitting and receiving the data records was designed by the open source and BSD licensed redis.
Redis allows users to specify the number of seconds until the key expires in millions. Navigation session is the data pattern that helps to find the web services and validate the user pages which is recently used on the user’s session and attempted page views. It contains the user information which recommends the products for each user’s session and validates the session whether it is ideal for more than 60 seconds if so the key will be deleted automatically and view the subsequent pages which are already less than that of 60 seconds time events.
On each attempt further, it will throw an exception like the key is not found. Database is the set of SQL queries tables and records each contains a collection of rows and columns the queried data will cache up the existing datas.
Steps to Create Redis TTL
Given below are the steps to create Redis TTL:
1. Navigate to the Ubuntu desktop command terminal.
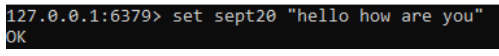
2. Create the key by using the Set command with the following syntax.
Command:
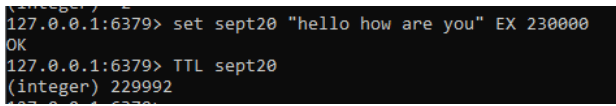
Set sept20 “hello how are you”Output:
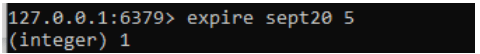
3. Then we need to calculate and set the expired time for the specific key like below.
Command:
Expire sept20 5Output:
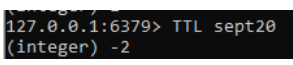
4. Further we need to set the TTL for the specific key.
Command:
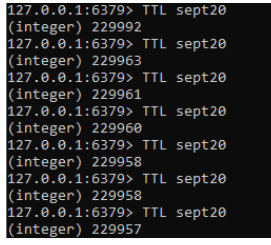
TTL sept20Output:
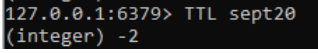
5. Then we need to calculate and set the expired time for the specific key like below.
Command:
Expire sept20 56. Further we need to set the TTL for the specific key.
Command:
TTL sept20Output:
Redis TTL Command
We are aware that the redis TTL command is used to determine the key’s remaining time with a seconds-based expiration time. When a deleted key associated with a volatile timeout milliseconds has been deleted, the key’s time-to-live will expire and a timeout will be set. The timeout instructions, along with the data contents for the default keys like SET, GET, GETSET, and DEL commands, cause the state to be volatile and cleared. Data operations that can be used to compute the timeout seconds include operations to insert, alter, and replace data. creating the data instance for the INCR command to increase the key value or the LPUSH command to push the values into a list. Using collection operations and techniques like HSET to turn the key back to the continuation using PERSIST command.
The command RENAME for the existing key is overwritten on the timeout session and can be used if the key has to be overwritten. If the original key is returned with a timeout exception, a new key will be associated with all of its properties. The non-volatile key TTL limitless purpose of GT, LT, and NX options is another name for it.
Redis’s TTL command returns the time-to-live values for the specified key in seconds. If the key does not have a session timeout, an integer value of -1 is returned, and response of -2 is given on the PTTL command if the key does not exist.
Below is the syntax for the TTL command:
TTL KeyWhereas key is the key for time-to-live seconds.
Every time we can calculate the time on TTL seconds for executing the TTL key code on the terminals.
Non-volatile keys are the redis database timeout if the key is with a timeout then considered volatile. If we run the TTL command against a non-volatile key that is key without a timeout for integer value -1.
Example of Redis TTL
Given below is the example mentioned:
Code:
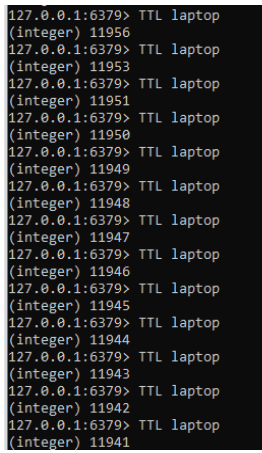
set laptop "Dell" ex 12000
TTL laptopOutput:
- In the above example, we can perform the TTL operations on the given keys.
- First, we need to set the key by using the set command along with double quotes values.
- Then we need to specify the time with expired keywords like ex.
- For each time the key is executed then the timeout count is decreased to -1 or -2.
FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. Define Redis TTL.
Answer: It is one of the commands that can be used to calculate the key remaining time in seconds.
Q2. Define the syntax for TTL.
Answer: TTL key is the syntax for calculating the time.
Q3. Define Volatile and Non-Volatile keys.
Answer:
A key with timeout is considered as volatile and without timeout is called non-volatile.
Conclusion
Redis TTL is one of the concepts and is mostly used to determine how long the keys’ expiration dates are. And using the set command in conjunction with values and a given time limit on the ex keyword, we may set the key. The maximum range is not past the TTL limit, and there is no default TTL key value.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Redis TTL. Here we discuss the introduction, steps to create Redis TTL, example, and FAQ respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –