Updated February 17, 2023
Introduction to Redis Replication
Redis replication contains the leader follower which is simple to configure and use. It will allow the redis replica instances which are exact copies of the master instances. When the redis replica server disconnects from the master server, it automatically reconnects to it. When connecting the master and replica servers, the master will keep the replica up to date by sending the stream command to the replica for replication.
Key Takeaways
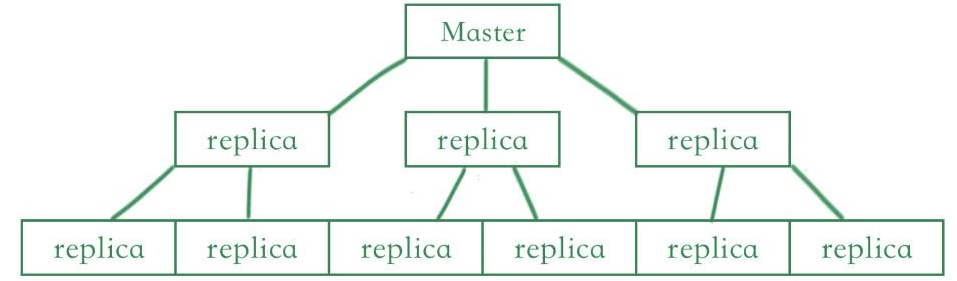
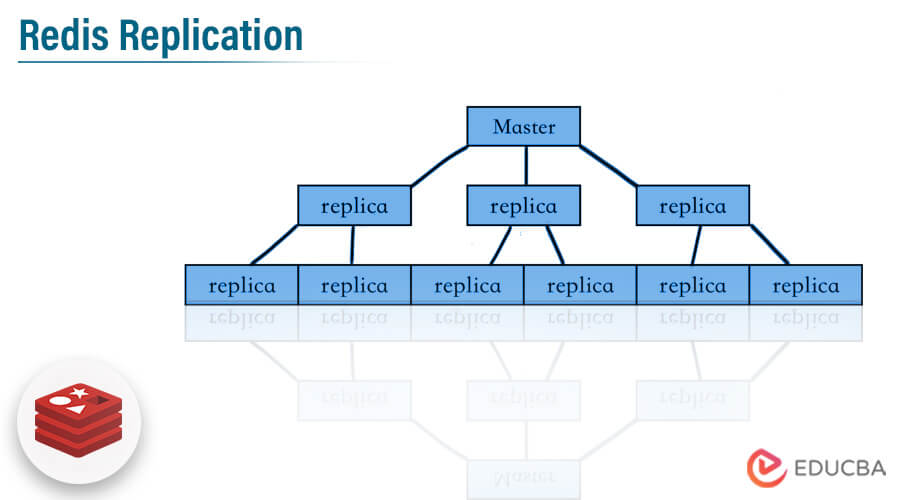
- One master will contain multiple slave nodes in redis replication. The replica server is accepting connections from other replicas that are linked to the master server.
- Basically, it is non-blocking from the master server side, so we can say that master will handle the query when the replica performs partial synchronization.
What is Redis Replication?
Redis will implement the replication by using two ways. The first is a single shard that contains the all-cluster data in every node, and the second is partitioned replication across 500 shards. Each shard into the redis replication contains the single read and write primary node, we can connect a maximum of five replica read-only nodes. We can create our redis replication cluster with a high number of shards and less number of replicas.
We can do the redis replication configuration with 90 shards and zero number of replicas. We can increase the replication node or shard limit up to 500 per cluster. It supports high availability. The redis replication contains non-blocking of query on the master as well as slave side, also it will allow the exact copy of the instances.
How to Setup Redis Replication?
We are using the ubuntu system for the setup of redis replication.
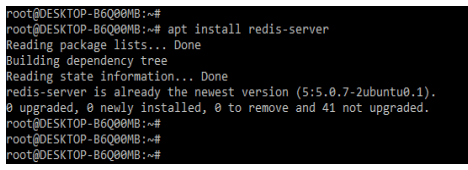
1. Now in this step we will first install the redis server by using apt command. In the below example, we have already installed the redis server.
Code:
apt install redis-serverOutput:
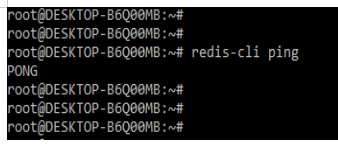
2. After installing the redis server, now we are checking the installation by login into the redis-cli as follows.
Code:
redis-cli pingOutput:
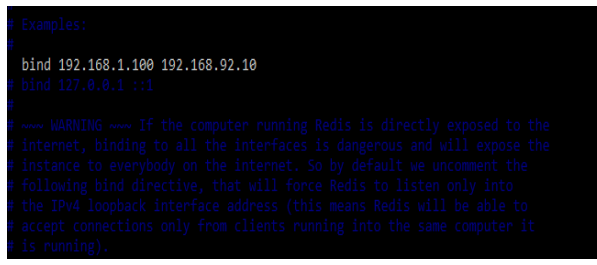
3. After checking the installation of redis server now we are securing the traffic of two servers. We are opening the redis configuration file and editing the bind address as follows.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
bind 192.168.1.100 192.168.92.10Output:
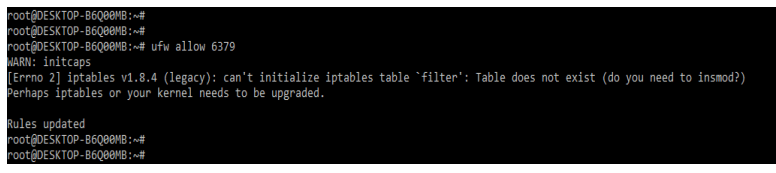
4. After securing the traffic of the server now in this step we are opening the access of the redis port by using ufw command as follows.
Code:
ufw allow 6379Output:
How does Redis Replication Work?
The redis replication will work on three mechanisms. The below figure shows how redis replication will work as follows:
When the master and replica servers are properly linked, the master will keep the read replica in sync while sending stream commands to the replica to replicate the dataset that was happening on the master side because the client is writing changes to the master dataset.
When the link between the master and replica is broken due to a network issue or a timeout detected by the master replica, the replication will reconnect and attempt to continue the partial resynchronization, which means it will try to obtain the stream portion that was lost during the disconnection.
It is not possible for replica to request resynchronization during partial resynchronization. It will provide a more complex process in which the master must create a snapshot of all the data that we are sending to the replica for sending stream commands for changes to the dataset.
Redis Replication ID
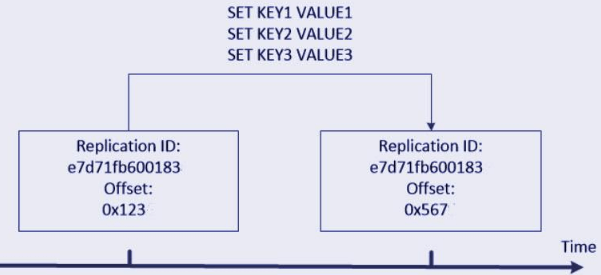
The replication ID will be present in every master replication. The replication ID identifies the given history as belonging to the specified data set. When the instance restarts the master from scratch or a replica is promoted to the master, a new replication ID is generated for the specified master. After handshaking, the replica that was connected to the master inherits the replication ID. The same replication instance ID will contain the same data at different times.
In the below example, we have two instances i.e. A and B containing the same replication ID but they will contain different offsets.
The replication will contain the two replication IDs because replicas will connect as a master. After failover the replica which was promoted which requires remembering a replication ID that contains in past. In the same way another replica will sync with the master, which was newly promoted, they are performing the partial resynchronization by using the replication ID which was old.
If we don’t know why the replica was promoted to master, and we need to change the replication ID after failover, it’s possible that the old master will continue to work as master by using network partition. Using the same replication ID violates the fact that it contains the same offset and replication ID that contains two random instances with the same data set.
Redis Replication Configuration
After installing the redis server now we are configuring the master and slave server as follows. First, we are configuring the master server as follows. To configure the master server we are opening the redis configuration file. We are changing the below parameter value in the configuration file.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
tcp-keepalive 30
requirepass 192.168.92.101
maxmemory-policy noeviction
appendonly yes
appendfilename "redis-staging-ao.aof"Output:
After changing the parameter values in the configuration file now we need to restart the redis server as follows.
Code:
systemctl restart redis-server.serviceOutput:
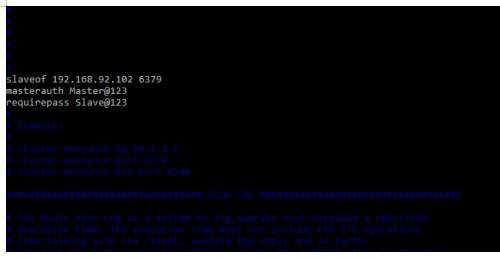
Now we are configuring the slave server as follows. To configure the slave server we are opening the redis configuration file. We are changing the below parameter value in the configuration file.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
slaveof 192.168.92.102 6379
masterauth Master@123
requirepass Slave@123Output:
After changing the parameter values in the configuration file now we need to restart the redis slave server as follows.
Code:
systemctl restart redis-server.serviceOutput:
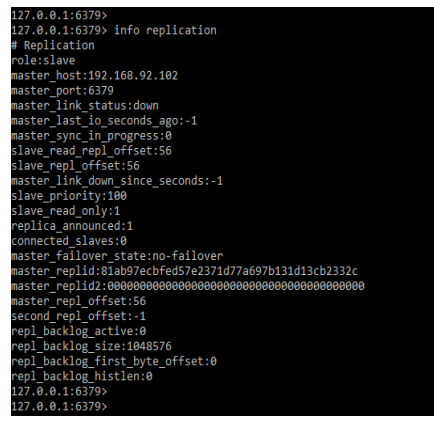
After restarting both servers we can check the status of replication by using the below command as follows.
Code:
info replicationOutput:
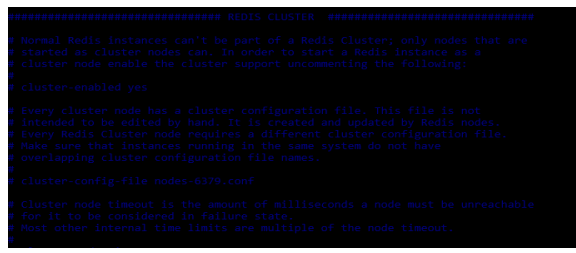
Redis Replication – Disabled and Enabled
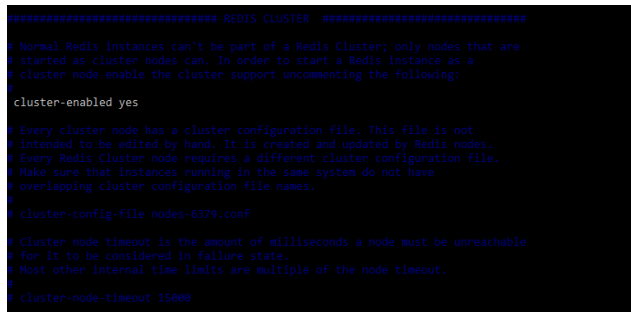
There are two modes available in redis replication i.e. enable and disable. Redis feature will contain the redis feature which was enabling the cluster without impacting the performance of the cluster. While instantiating a scale-out operation for adding the new node to the replication we can also instantiate scale-down and scale up the operation by specifying the node type. To enable the redis replication mode we need to enable the below parameter in the configuration file as follows.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
cluster-enabled yesOutput:
For disabling the same we can hash the line which we have enabled. The below example shows how we can disable the redis replication cluster mode as follows.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
# cluster-enabled yesOutput:
Redis Replication Setting Up
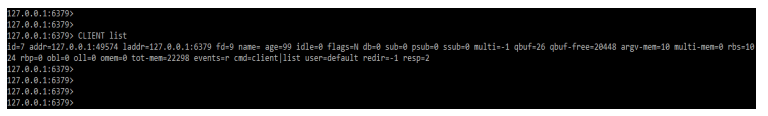
To set up the replication we need to install the redis server. We have already installed the redis server so we have no need to install it again. In the below example, we are executing the client list command to define all flags as follows.
Code:
CLIENT listOutput:
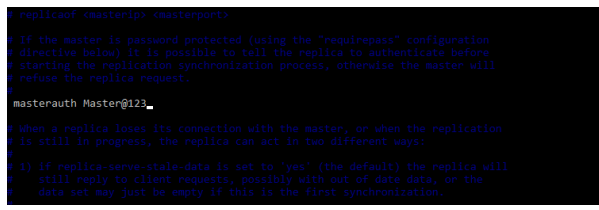
We also need to set the master parameter, in the below example, we are setting the master password.
Code:
# vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
masterauth Master@123Output:
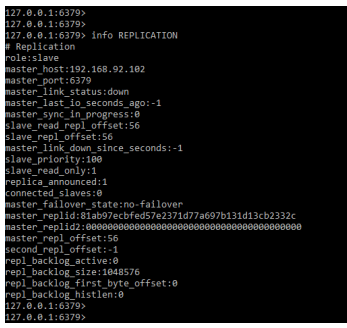
We can also check the replication info by using the info replication command as follows. It will show all the details related to master and slave server.
Code:
info REPLICATIONOutput:
Conclusion
Redis will use two methods to implement replication. The first is a single shard that contains all cluster data in each node. Redis replication includes a leader follower that is simple to set up and use. It will permit redis replica instances that are exact copies of the master instances.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Redis Replication. Here we discuss the introduction, how to Setup redis replication. working, configuring, disabling, and enabling. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –