Difference Between React State vs Props
In this article React State vs Props, we will figure out major differences between two very important react components, state and props. We will cover some basic examples to figure out the differences between both state and props. Also, we will see situations where state or props can be used.
What is React, State?
State: State can be considered an instance of react component class and is majorly used to communicate with a component. The state of a react a component is an object that contains information that may or may not change over the lifecycle of a component. State object stores values of properties related to a component. Whenever there is a change in properties related to a component, the value associated with the state object changes and the component will re-render itself, which means it will change itself by the new values. Here is an example that will explain react state:
Code:
class Bike extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
Company: "Yamaha",
Modelnumber : "R15",
color: "blue",
launch-year: 2001
};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Name {this.state. Company}</h1>
<p>
This is a {this.state.color}
{this.state. Modelnumber}
from {this.state. launch-year}.
</p>
</div>
);
}
}Output:

Now let us consider we want to change component properties. To achieve this, there exists a method called setState(). Note that you should always use the setState() method to change the state of a component; it will make sure that the component will re-render its state.
Code:
class Car extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
Company: "Ford",
Modelnumber : "Mustang",
color: "red",
launch-year: 1964
};
}
changeColor = () => {
this.setState({color: "green"});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My {this.state.Company}</h1>
<p>
It is a {this.state.color}
{this.state.Modelnumber}
from {this.state.launch-year}.
</p>
<button
type="button"
onClick={this.changeColor}
>Change Bike color</button>
</div>
);
}
}In the above code, we have added a button to click on which new changes will be rendered on the component. The above code will produce the following output on the button click.
Output:

What is Props?
Props: Props in ReactJs are used to send data to components. Props are equivalent to javascript pure function parameters. Since pure function parameters cannot be changed once assigned, we cannot change their values. The below example will show how props are used:
Code:
class Bike extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h3>This is {this.props.Companyname}</h3>
}
}
const component = <Bike Companyname="Yamaha" />;Output:
![]()
If the component has a constructor, then the props object should be necessary passed to the constructor using super. Here is an example:
Code:
class Bike extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <h2>This is a Bike</h2>;
}
}Output:
![]()
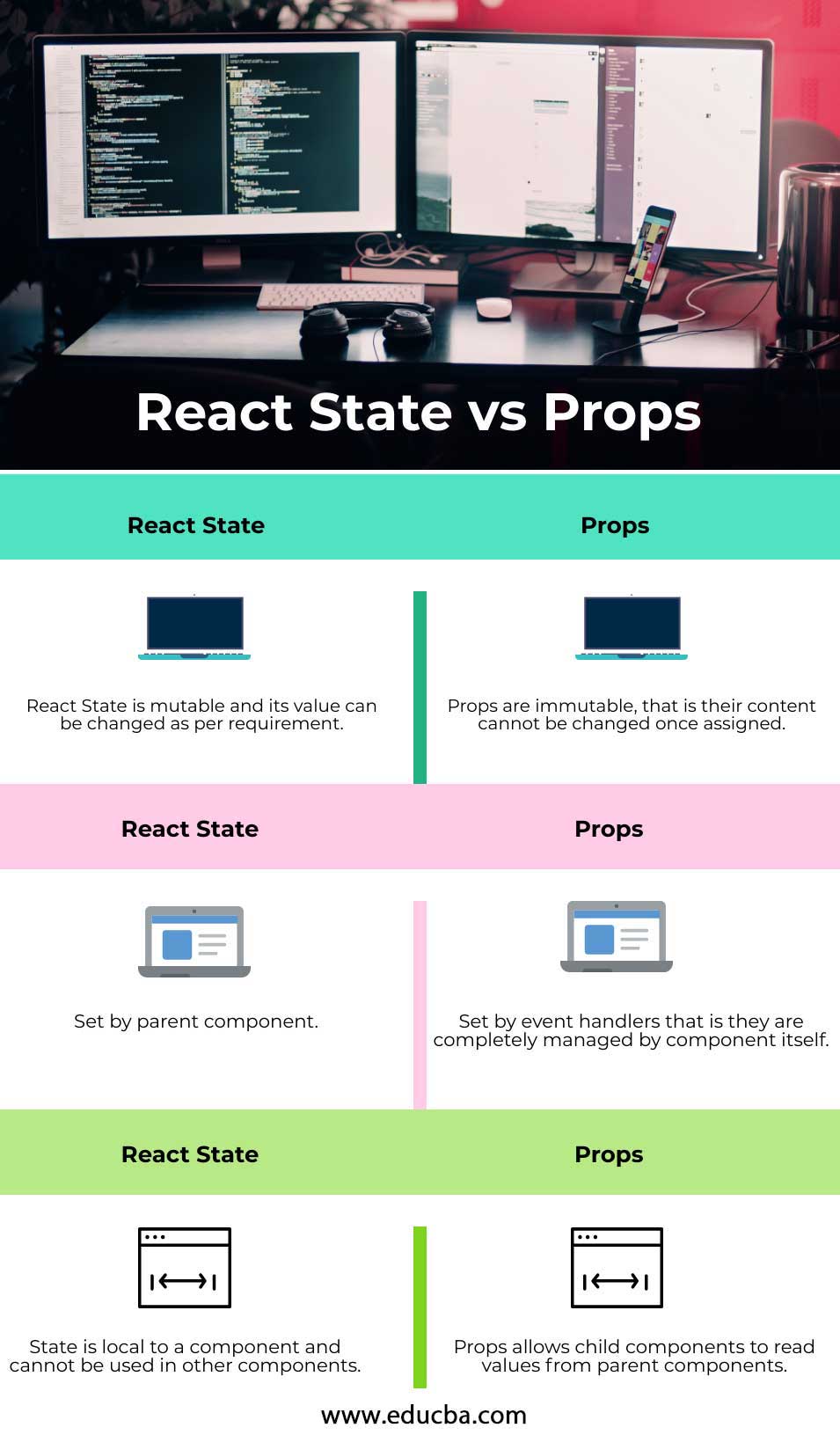
Head to Head Comparison between React State vs Props (Infographics)
Below are the Top 4 comparisons between React State vs Props:
Key Differences Between React State vs Props
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between React State vs Props:
- Props are immutable; that is, their content cannot be changed once assigned, but a state is an object that is used to hold data that can change in the future; also state controls the behavior of the component after the change is made.
- Both Props and states are used for storing data related to a component.
- States can only be used in Class components, whereas props do not have such restrictions.
- Props are generally set by the parent component, whereas event handlers govern the state; the component itself manages them.
- The state is local to a component and cannot be used in other components, whereas Props allow child components to read values from parent components.
Comparison Table of React State vs Props
The table below summarizes the comparisons between React State vs Props:
| React State | Props |
| React State is mutable, and its value can be changed as per requirement. | Props are immutable; that is, their content cannot be changed once assigned. |
| States can only be used by class components. | Props can be used by class as well as other components. |
| Set by the parent component. | Set by event handlers, that is, they are completely managed by the component itself. |
| The state is local to a component and cannot be used in other components. | Props allow child components to read values from parent components. |
Conclusion
After covering both state and props features, we have concluded that whenever there is a possibility of property changes related to a component, then we should prefer state as it allows the re-rendering of properties. On the other hand, props allow child components to access methods that are defined in parent components; this minimizes a need in child components to have their state. Props are read-only in child components. It is worth noting that state and props are very important components of react architecture.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to React State vs Props. Here we also discuss the React State vs Props key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

