Updated July 1, 2023
Difference Between R and Python
A comparison between statistical programming package R and programming language Python, so as to understand on a particular parameter in which one of the two programming languages excels, so as to enable the user to make the right selection for the given situation, and that parameters of comparison can be various ranging right from the objective of designing the language, user base, flexibility of usage, role of the language to provide good job opportunities to the learner, technical dimensions, along with some of the shortcomings of pitfalls also, thus assisting the user by providing a complete idea with respect to selection of a tool, is termed as R vs Python.
What is R?
R is a statistical language. It is used for developing statistical software and data analysis. Ever since data mining and study of data have become popular, R has also gained its popularity. Along with statistical techniques, R also provides a wide variety of libraries for graphical techniques. It can produce static graphs, which are used for publication-quality graphs. Dynamic and interactive graphs are also available. R has a package archive network (CRAN- Comprehensive R Archive Network) for all the packages that it supports. It contains more than 10,000 packages. R is a command-line language, but several interfaces provide interactive GUI to ease developers’ tasks.
What is Python?
Python is a multi-paradigm language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. It can be used in web development, software development, system scripting, etc. It works on different platforms. Python was designed for better readability; hence it has some similarities with the English language. Python focuses on simple, less cluttered syntax and grammar. For example, in python, white spaces mark the indentations to limit the block. It uses dynamic typing and late binding, which bind the methods and variables at the runtime. With a large number of libraries, Python can be used for many purposes. It has been ranked in the top ten most popular programming languages.
Real scenarios – Machine Learning has given us self-driven cars, effective web search, and a vastly improved understanding of the human genome over the years. But the question is, how this works?
You might have remembered some situations where you thanked the technology you were using but could not relate exactly why those things happen. Almost all of us nowadays spend most of our time on e-commerce websites or browsing through Google.
It happened often when you make a typo, for instance, while searching in Google, and it gives us the message that “did you mean this…….” This is nothing but Google Machine learning algorithms, a system that detects what searches you made a couple of times ago after making a specific search.
Let’s take one more scenario to make it clearer; Amazon is a world know e-commerce platform. People look for products that they need. Say Mr. Paul is looking for a Motorola mobile set, he does a search and finds the cell phone (of Motorola), but the website also suggests some relevant product details along with the cell phone, like screen guard, headphones which are best compatible with that particular cell phone. This is again the machine learning algorithm used by Amazon. The intention is to clear these companies are working on this technology to easy application usage with customer satisfaction by reducing the complexity.
Head to Head Comparison between R and Python (Infographics)
Below are the top 11 differences between R vs Python.
Key Differences between R and Python
Although R vs Python is popular for a similar purpose, i.e. data analysis and machine learning, both languages have different features. Moreover, each language offers different advantages and disadvantages. Nevertheless, both R Programming vs Python are popular choices in the market; let us discuss the Top key Differences Between R Programming vs Python to know which is the best:
R was created by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman in 1995, whereas Guido Van Rossum created Python in 1991. In addition, r is focused on coding language built solely for statistics and data analysis, whereas Python has flexibility with packages to tailor the data.
R is great when it comes to complex visuals with easy customization, whereas Python is not as good for press-ready visualization. In addition, r is hard to integrate with the production workflow. Mostly a statistical analysis and graphics tool, whereas Python integrates easily in a production workflow and can become an actual part of the product.
R has a stable release (current) of 3.5.0 as of April 23, 2018, whereas Python 3.6.5 (current) as of March 28, 2018. R has .r, .R, .R Data, .rds and .rda filename extensions whereas Python has .py, .pyc, .pyd, .pyo, .pwy, .pyz filename extensions.
Let’s have a look at some more key differences.
- Speed and Performance: Although both languages are used for big data analytics. But performance-wise, Python is a better option for building critical yet fast applications. R is a bit slower than Python but still fast enough to handle big data operations.
- Graphics and Visualization: Data can be understood easily if it can be visualized. R provides various packages for the graphical interpretation of data. Ggplot2 gives customized graphs. Python also has libraries for visualization, but it is a bit complex than R. R has a pretty-printed library which helps in building publication-quality graphs.
- Deep Learning: Both r vs python languages have got their popularity with the rising popularity of data science and machine learning. While python offers a lot of finely tuned libraries, R got KerasR, an interface of Python’s deep learning package. Thus, both languages now have a very good collection of packages for deep learning. But python stands out in the case of deep learning and AI.
- Statistical Correctness: Since R is developed for data statistics, it provides better support and library libraries. Python is best used for application development and deployment. But R and its libraries implement a wide variety of statistical and graphical techniques for data analysis.
- Unstructured Data: 80% of the world’s data is unstructured. Data generated from social media is mostly unstructured. Python offers packages like NLTK, scikit-image, PyPI to analyze unstructured data. R also offers libraries for analyzing unstructured data, but the support is not as good as Python. Yet, both languages can be used for unstructured data analysis.
- Community Support: Both R vs Python has good community support. Both languages have a user mailing list, StackOverflow groups, user-contributed documents, and codes. So here is a tie between both languages. But both languages do not have customer service support. This means users have just online communities and developer’s documents for help.
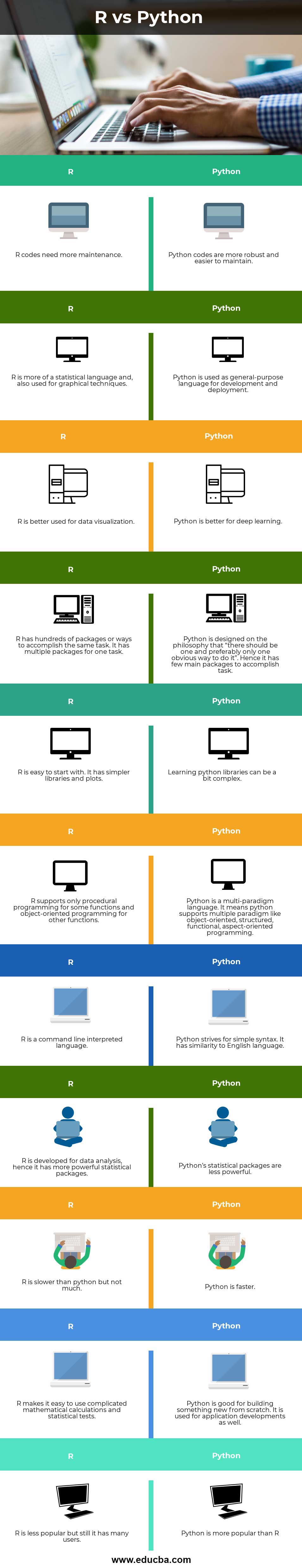
R vs Python Comparison Table
Let us discuss the topmost differences between R vs Python.
| R | Python |
| R codes need more maintenance. | Python codes are more robust and easier to maintain. |
| R is more of a statistical language and, also used for graphical techniques. | Python is used as a general-purpose language for development and deployment. |
| R is better used for data visualization. | Python is better for deep learning. |
| R has hundreds of packages or ways to accomplish the same task. It has multiple packages for one task. | Python is designed on the philosophy that “there should be one and preferably only one obvious way to do it”. Hence it has few main packages to accomplish the task. |
| R is easy to start with. It has simpler libraries and plots. | Learning python libraries can be a bit complex. |
| R supports only procedural programming for some functions and object-oriented programming for other functions. | Python is a multi-paradigm language. It means python supports multiple paradigms like object-oriented, structured, functional, aspect-oriented programming. |
| R is a command line interpreted language. | Python strives for simple syntax. It has a similarity to the English language. |
| R is developed for data analysis; hence it has more powerful statistical packages. | Python’s statistical packages are less powerful. |
| R is slower than python but not much. | Python is faster. |
| R makes it easy to use complicated mathematical calculations and statistical tests. | Python is good for building something new from scratch. It is used for application development as well. |
| R is less popular, but still, it has many users. | Python is more popular than R |
Conclusion:
Both r vs python languages have their pros and cons; it’s a tough fight between the two. Python seems to be a little more popular among data scientists, but R is also not a complete failure. R is developed for statistical analysis and is very good at that. Whereas Python is a general-purpose language for application development. Both languages provide a wide range of libraries and packages; cross-library support is also available in some cases. Hence it totally depends on the user’s requirements which one to choose.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to R vs Python. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –