Updated July 4, 2023

Introduction to Python Sys Module
Python is a very popular and powerful scripting language these days. From developing applications to developing websites, making analytical products to production-level codes, python is getting so much popularity. One of the reasons behind this is its flexibility and easy-to-use modules. Let’s see one of the widely used modules in Python known as “Sys”. “Sys” module is defined for the system. It defines, basically, the environment. In order to import the sys module, one can simply type in “import sys.”
Functions of Python Sys Module
Given below are the functions of the Python Sys Module:
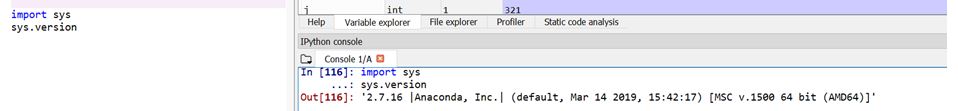
Let’s import the sys module in our IDE and check the version of Python.
1. version
It helps you understand the version of Python being in use.
Code:
import sys
sys.versionOutput:
2. executable
It’s a string that tells you where your filesystem or your Python interpreter exists.
Code:
import sys
sys.executableOutput:

3. sys.builtin_module_names
This helps you understand which are the built-in modules available in Python. One need not download these modules, and hence can be used directly environment after importing.
Code:
sys.builtin_module_namesOutput:

Like shown here:

However, the modules which are not part of sys need to be first downloaded and then imported into the Python environment.
Examples:
dateutil, git, etc.
4. sys.platform
This helps you know about the platform. Everyone wants their program to run irrespective of the platform. And that’s where this command is mostly used.
Code:
sys.platformOutput:

If one needs to make code in aligned with the platform, here is what one can do.
Code:
if sys.platform.startswith('win'):
# win-specific code ...
elif sys.platform.startswith('aix'):
# AIX-specific code...
elif sys.platform.startswith('darwin'):
# MAC-specific code ..
elif sys.platform.startswith('linux'):
# Linux-specific code ..
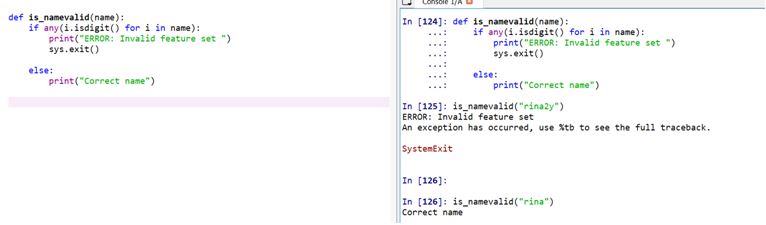
5. sys.exit
In case of any exceptions in the program, the need for a safe exit from the program occurs. Sys.exit helps there.
Code:
def is_namevalid(name):
if any(i.isdigit() for i in name):
print("ERROR: Invalid feature set ")
sys.exit()
else:
print("Correct name")
Output:
6. sys.argv
This refers to a Python list containing arguments(command line) passed to the script. If someone types len(sys.argv), it will fetch you the count of the number of arguments. Someone working with command line arguments will use sys.argv. Sys.argv[0] refers to the name of the script.
Code:
import sys
print(sys.argv[0])
print 'Number of arguments:', len(sys.argv), 'arguments.'
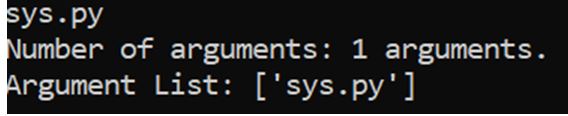
print 'Argument List:', str(sys.argv)Say this Python code is saved with the name “sys.py” at a certain location.
Now, go to the command line and type “python sys.py”.
Output:
However, if you type “python sys.py arg1”.
Output:
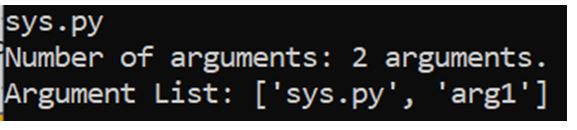
The thing to note here is that the first argument will always be the script name, which in itself will be counted in counting the number of arguments.
7. sys.exitfunc
This is a parameter-less function, which the user can use to perform cleanup actions at the program’s exit. This function no more exists in Python 3.x. However, one can use “atexit” instead.
8. sys.stdin, sys.stdout, sys.stderr
These functions refer to file objects used by the interpreter for the standard input, output, and errors.
- Stdin is for interactive input, like we use input(), and raw_input(). Input is taken through stdin.
- Stdout is used for output like print(); output is printed actually through stdout.
- Stderr is to prompt the error message.
Code:
import sys
for j in (sys.stdin, sys.stdout, sys.stderr):
print (j)
Output:

As one can notice stdin, is printed with mode ‘r’ which means reading, while stdout and stderr are writing mode.
9. sys. setrecursionlimit(limit)
This function can help you limit the maximum depth of the Python interpreter. It helps you keep a stopover infinite recursion that can be a cause of overflow. However, the highest possible limit depends on the platform to platform. If someone keeps the limit higher, he/she should be aware of risks that can lead to crashes in Python.
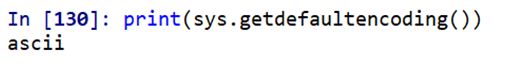
10.sys.getdefaultencoding()
It returns the default string encoding.
Let me show you in Python environment.
Code:
print(sys.getdefaultencoding())Output:
11. sys.setdefaultencoding()
This function helps you change the default encoding for strings in the Python environment.
Example:
Code:
import sys
sys.setdefaultencoding('UTF8')12. sys.exc_clear()
This function helps you clear all information about current or previous exceptions. This function is great to use when you need to free the allocated resources and have to do object finalization.
Conclusion
All the above we saw are important sets of functions available in the sys module. Sys module helps you to know about your working environment e.g. where your code is running, which platform it is running on, which Python version, and which interpreter is in use, etc. One needs to go through these functions and start playing with them in order to get a good grip over these functions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python Sys Module” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


