Updated October 7, 2023
Introduction to String Operators in Python
A Python String is a sequence of characters. Python Strings are immutable, meaning we can’t modify a string once we declare a string. Python provides a built-in class “str” for handling text, as the text is the most common form of data a Python program handles. Following are the common string operations that can be performed in Python:
- Concatenation of two or more strings.
- Extracting or slicing partial strings from string values.
- Adding or removing spaces.
- Converting to lower or upper case.
- Formatting strings using string formatters.
- Finding and/or replacing a text in the given string with another text.
And the list of operations is countless. Python provides several built-in methods that let us perform operations on a string in a flexible way.
- Assignment operator: “=”
- Concatenate operator: “+”
- String repetition operator: “*”
- String slicing operator: “[]”
- String comparison operator: “==” & “!=”
- Membership operator: “in” & “not in”
- Escape sequence operator: “\”
- String formatting operator: “%” & “{}”
Table of Contents
Importance of String Operators
String operators are crucial in Python for several reasons:
- Text Manipulation: They enable you to perform essential text operations like concatenation, repetition, and slicing, making it easier to manipulate strings.
- Data Processing: String operators are fundamental for parsing and processing textual data, which is prevalent in many real-world applications.
- Code Efficiency: Using string operators reduces the need for writing complex code, making programs more concise and readable.
- User Input Handling: They are essential for validating and processing user input ensuring data integrity in applications.
- String Comparison: Operators like == and != are vital for comparing and evaluating strings, allowing for conditional logic in code.
- Formatting: String operators aid in formatting text, making creating user-friendly outputs and reports easier.
- Versatility: Python’s string operators provide flexibility, allowing developers to adapt and manipulate text data as needed for diverse tasks.
Examples of String Operators in Python
In the following article, with examples, we will learn how to perform operations on a string in Python.
Example #1 – Assignment Operator “=”
Python string can be assigned to any variable with an assignment operator “= “. Python string can be defined with either single quotes [”], double quotes[“”], or triple quotes[‘””‘]. var_name = “string” assigns “string” to variable var_name.
Code:
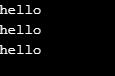
string1 = "hello"
string2 = 'hello'
string3 = '''hello'''
print(string1)
print(string2)
print(string3)Output:
Example #2 – Concatenate Operator “+”
Two strings can be concatenated or joined using the “+” operator in Python, as explained in the below example code:
Code:
string1 = "hello"
string2 = "world "
string_combined = string1+string2
print(string_combined)Output:
Example #3 – String Repetition Operator “*”
The same string can be repeated in Python by n times using string*n, as explained in the below example.
Code:
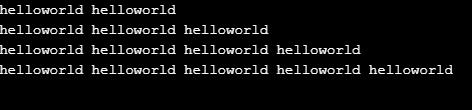
string1 = "helloworld "
print(string1*2)
print(string1*3)
print(string1*4)
print(string1*5)Output:
Example #4 – String slicing operator “[]”
Characters from a specific string index can be accessed with the string[index] operator. The index is interpreted as a positive index starting from 0 from the left side and a negative index starting from -1 from the right side.
| String | H | E | L | L | O | W | O | R | L | D |
| Positive index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Negative index | -10 | -9 | -8 | -7 | -6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 |
- string[a]: Returns a character from a positive index a of the string from the left side, as displayed in the index graph above.
- string[-a]: Returns a character from a negative index a of the string from the right side, as displayed in the index graph above.
- string[a:b]: Returns characters from positive index a to positive index b as displayed in the index graph above.
- string[a:-b]: Returns characters from positive index a to the negative index b of the string as displayed in the index graph above.
- string[a:]: Returns characters from positive index a to the end of the string.
- string[:b] Returns characters from the start of the string to the positive index b.
- string[-a:]: Returns characters from negative index a to the end of the string.
- string[:-b]: Returns characters from the start of the string to the negative index b.
- string[::-1]: Returns a string with reverse order.
Code:
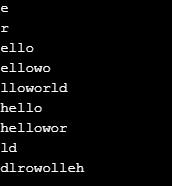
string1 = "helloworld"
print(string1[1])
print(string1[-3])
print(string1[1:5])
print(string1[1:-3])
print(string1[2:])
print(string1[:5])
print(string1[:-2])
print(string1[-2:])
print(string1[::-1])Output:
Example #5 – String Comparison Operator “==” & “!=”
The string comparison operator in Python is used to compare two strings.
- The “==” operator returns Boolean True if two strings are the same and Boolean False if two strings are different.
- The “!=” operator returns Boolean True if two strings are not the same and returns Boolean False if two strings are the same.
These operators are mainly used along with the if condition to compare two strings where the decision will be taken based on string comparison.
Code:
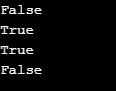
string1 = "hello"
string2 = "hello, world"
string3 = "hello, world"
string4 = "world"
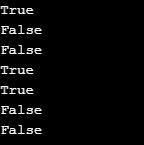
print(string1==string4)
print(string2==string3)
print(string1!=string4)
print(string2!=string3)Output:
Example #6 – Membership Operator “in” & “not in”
The membership operator searches whether the specific character is part/member of a given input Python string.
- “a” in the string: Returns boolean True if “a” is in the string and returns False if “a” is not in the string.
- “a” not in the string: Returns boolean True if “a” is not in the string and returns False if “a” is in the string.
A membership operator is also useful to find whether a specific substring is part of a given string.
Code:
string1 = "helloworld"
print("w" in string1)
print("W" in string1)
print("t" in string1)
print("t" not in string1)
print("hello" in string1)
print("Hello" in string1)
print("hello" not in string1)Output:
Example #7 – Escape Sequence Operator “\”
An escape character is used to insert a non-allowed character in the given input string. An escape character is a “\” or “backslash” operator followed by a non-allowed character. An example of a non-allowed character in a Python string is inserting double quotes in the string surrounded by double quotes.
1. Example of non-allowed double quotes in Python string:
Code:
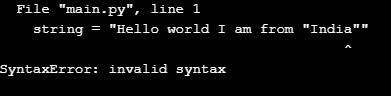
string = "Hello world I am from "India""
print(string)Output:
2. Example of non-allowed double quotes with escape sequence operator:
Code:
string = "Hello world I am from \"India\""
print(string)Output:
Example #8 – String Formatting Operator “%”
The string formatting operator is used to format a string as per requirement. To insert another type of variable along with string, the “%” operator is used along with Python string. “%” is prefixed to another character, indicating the type of value we want to insert along with the Python string. Please refer to the table below for some of the commonly used different string formatting specifiers:
| Operator | Description |
| %d | Signed decimal integer |
| %u | unsigned decimal integer |
| %c | Character |
| %s | String |
| %f | Floating-point real number |
Code:
name = "india"
age = 19
marks = 20.56
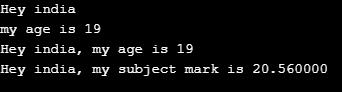
string1 = 'Hey %s' % (name)
print(string1)
string2 = 'my age is %d' % (age)
print(string2)
string3= 'Hey %s, my age is %d' % (name, age)
print(string3)
string3= 'Hey %s, my subject mark is %f' % (name, marks)
print(string3)Output:
Example #9
Code:
# String formatting using f-strings
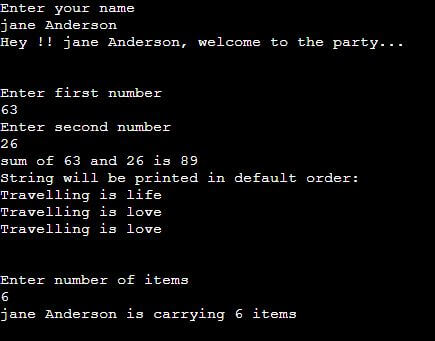
print("Enter your name")
name = input()
print(f"Hey !! {name}, welcome to the party...")
print('\n')
print("Enter first number")
a = int(input())
print("Enter second number")
b = int(input())
print(f"sum of {a} and {b} is {a+b}")
# String formatting using format() method
str1 = "{} {} {}".format("Travelling", 'is', 'life')
print("String will be printed in default order:")
print(str1)
str2 = "{1} {2} {0}".format("love", "Travelling", "is")
print(str2)
str3 = "{T} {i} {l}".format(T='Travelling', l='love', i='is')
print(str3)
# String formatting using % operator
print('\n')
print("Enter number of items")
item = int(input())
print("%s is carrying %d items"%(name, item))Output:
Explanation:
1. f-string: The letter “f” is placed before the beginning of the string, and the variables mentioned in curly braces will refer to the variables declared above. For example, {name} refers to the name variable defined above. Similarly, {a} and {b} refers to variable a and b, respectively.
2. format() method: format() method is called on a string object. We use curly braces {} that will refer to the format() method arguments inside the string. The number of {} should match the number of arguments inside format()
- In default formatting, {} will refer to the format() arguments in the order in which they are placed.
- In positional formatting, order is indicated inside {}. The above example “{1} {2} {0}” .format(“love”, “Travelling”, “is”) states that the argument positioned at index 1 (“travelling”) inside format() will come first, argument position at 2 index(“is”) will come second, and argument positioned at index 0(“love”) will come last.
- In keyword formatting, specific keywords are used inside {}, which will be mapped to corresponding format() arguments.
3. % operator: The “%” operator will be replaced by variables defined in parenthesis/in tuple. %s means a string variable will come to this place, %d is an integer, and %f is a floating-point value.
Example #10
Code:
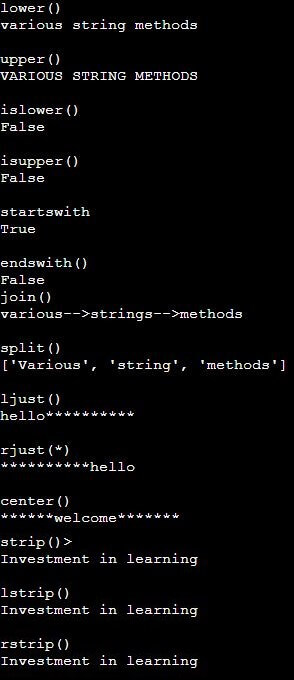
string = "Various string methods"
string2 = "Investment in learning "
print("lower()")
print(string.lower())
print("\nupper()")
print(string.upper())
print("\nislower()")
print(string.islower())
print("\nisupper()")
print(string.isupper())
print("\nstartswith")
print(string.startswith("Var"))
print("\nendswith()")
print(string.endswith("el"))
print("join()")
print('-->'.join(['various', 'strings', 'methods']))
print("\nsplit()")
print(string.split())
print("\nljust()")
print("hello".ljust(15, '*'))
print("\nrjust(*)")
print("hello".rjust(15, '*'))
print("\ncenter()")
print("welcome".center(20, '*'))
print("\nstrip()>")
print(string2.strip())
print("\nlstrip()")
print(string2.lstrip())
print("\nrstrip()")
print(string2.rstrip())Output:
Explanation:
- lower(): Converts a string to the lowercase letter.
- upper(): Converts a string to the uppercase letter.
- islower() / isupper(): Checks if the whole string is in lower case or upper case and returns bool value, respectively.
- startswith(): Returns a bool value. Check if the given string starts with a particular text.
- endswith(): Returns a bool value. Check if the given string ends with a particular text.
- join(): Join different strings to make a single concatenated string. A list of strings is joined together into a single string.
- split(): Reverse of join(). It splits a large string into smaller strings. By default, a string is split wherever characters such as space, tab or newline characters are found. However, a delimiter can be passed inside the split(). The string then will split when this delimiter is encountered.
- ljust()/ rjust()/ center(): These three methods are for justifying text. The first argument is an integer length for the justified string, and the second argument is the fill character. ljust() fills the fill char on the left side, rjust() fills the fill char on the right side, and center() justifies the text at the center, filling the fill char at both the left and right sides.
- strip()/ lstrip()/ strip(): Removes whitespaces(space, tab and newline) from left side(lstrip()), right side(rstrip()) and from both sides(strip()).
Example #11
Code:
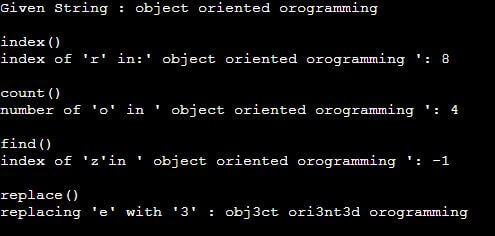
string = "object oriented orogramming"
print("Given String :", string)
print('\nindex()')
print("index of 'r' in:'", string, "':", string.index('r'))
print('\ncount()')
print("number of 'o' in '", string, "':", string.count('o'))
print('\nfind()')
print("index of 'z'in '", string, "':", string.find('z'))
print('\nreplace()')
print("replacing 'e' with '3' :", string.replace('e', '3'))Output:
Explanation:
- index(): The index() method finds the first occurrence of a particular character or text in the given string. In this example, the index position for the first occurrence of ‘r’ is printed.
- count(): counts the total number of occurrences of a character in the given string. Character ‘o’ occurs thrice in the string “object-oriented programming.”
- find(): find() method is similar to index() method. It also returns the index for the first occurrence. But the major difference is that if a character whose index is to find is not present, index() will throw an error while find() returns -1 (as shown in the output)
- replace(): It replaces a text with another text in the given string. In this example, ‘e’ is being replaced by ‘3’.
Conclusion
This tutorial delves into Python’s versatile string operators, encompassing string assignment, repetition, slicing, concatenation, comparison, formatting, membership, and escape sequences. These concepts are invaluable for handling text data in Python applications. With a rich array of string methods, Python simplifies text manipulation, streamlining operations and reducing the need for extensive code. Textual data is ubiquitous in Python, making these string operators indispensable for real-world projects.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “String Operators in Python” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.