Updated June 14, 2023
Introduction to Python Slice String
The string is a sequence of characters. The character can be any letter, digit, whitespace, or special symbol. Strings in Python are immutable, meaning they cannot be modified once created. We can only extract a part called a substring from the original string, but the original string remains unchanged.
Python provides two ways in which a text can be accessed from a given string:
- Index: only a single character is extracted from the string.
- Slicing: a range of characters can be extracted from the original string. The process of extracting a sequence of characters (a substring) from the original string is called slicing.
Syntax:
Slicing in Python can be done in two ways:
1. Using Python slice() function
slice(start, stop, step)2. Slicing using indexing
String_object[start: stop: step]Parameters:
- start: Starting index from where slicing is to begin. This index is inclusive and is an optional parameter.
- stop: Ending index where to stop slicing. This index is exclusive, which means slicing will be stopped at the (stop-1) index and is a mandatory parameter.
- step: Number of indexes to be skipped. This, again, is an optional parameter.
Why do we use Python slice string?
To understand Python slicing, a basic understanding of indexing is required.
Indexing: As Strings are a sequential data type, they can be indexed as other sequential data types like lists, tuples, etc. Indexing begins at 0.
Python supports both positive and negative indexing, as illustrated below:
| P | Y | T | H | O | N | S | T | R | I | N | G | ||
| Positive Indexing | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Negative Indexing | -13 | -12 | -11 | -10 | -9 | -8 | -7 | -6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 |
But with indexing, we can extract a single character at one time.
Example:
string = "PYTHON STRING"
string[2]
'T'But there are situations when we require a range of characters. In this situation, slicing comes handy as slicing allows us to extract a substring from the original string.
Example:
string[0:6]
'PYTHON'Python Slicing Examples
The Python slicing examples are given below:
Example #1
Python String Slicing using slice() function
Code:
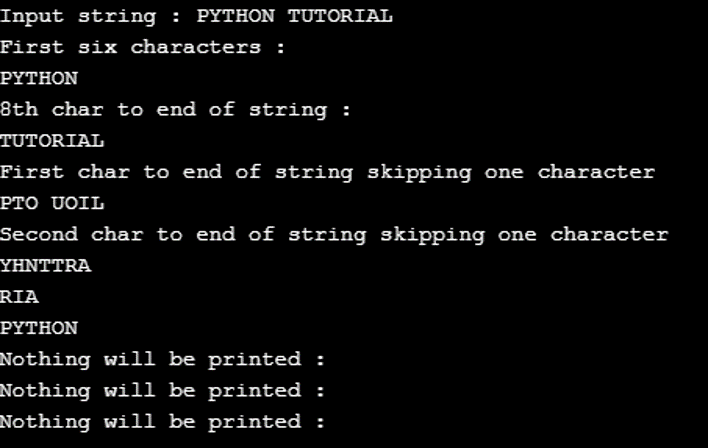
string = "PYTHON TUTORIAL"
print("Input string :",string)
# Positive indexing
print("First six characters :")
print(string[slice(6)])
print("8th char to end of string :")
print(string[slice(7, len(string))])
# Extracting alternate odd chars using step parameter
print("First char to end of string skipping one character")
print(string[slice(0,len(string),2)])
# Extracting alternate even chars using step parameter
print("Second char to end of string skipping one character")
print(string[slice(1, len(string), 2)])
# Negative indexing
print(string[slice(-4,-1)])
print(string[slice(-8)])
# Stop parameter should be greater than start parameter
print("Nothing will be printed :",string[slice(-4,0)])
print("Nothing will be printed :",string[slice(-1,-1)])
print("Nothing will be printed :",string[slice(-2,-4)])Output:
Explanation:
Input String:
| P | Y | T | H | O | N | T | U | T | O | R | I | A | L | ||
| Positive Indexing | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| Negative Indexing | -15 | -14 | -13 | -12 | -11 | -10 | -9 | -8 | -7 | -6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 |
Positive indexing:
- string[slice(6)] → start index: 0, stop index: 6, step value: 1
The first 6 chars (“PYTHON”) will be printed
- string[slice(7, len(string))] → start index: 7, stop index: 15 (len(string)), step value: 1
char indexed at 7 positions to the end of the string will be printed, i.e., TUTORIAL
- string[slice(0,len(string),2)] → start index: 0, stop index: 15, step value: 2
alternate characters will be printed starting from the first character
- string[slice(1,len(string),2)] → start index: 1, stop index: 15, step value: 2
alternate characters will be printed starting from the second character
Negative indexing:
- string[slice(-4,-1)] → start index: -4, stop index: -1, step value: 1
| R | I | A |
| -4 | -3 | -2 |
- string[slice(-8)] → start index: 0, stop index: -8, step value: 1
Example #2
Python Slice String using indexing
Code:
# Python slicing using indexing
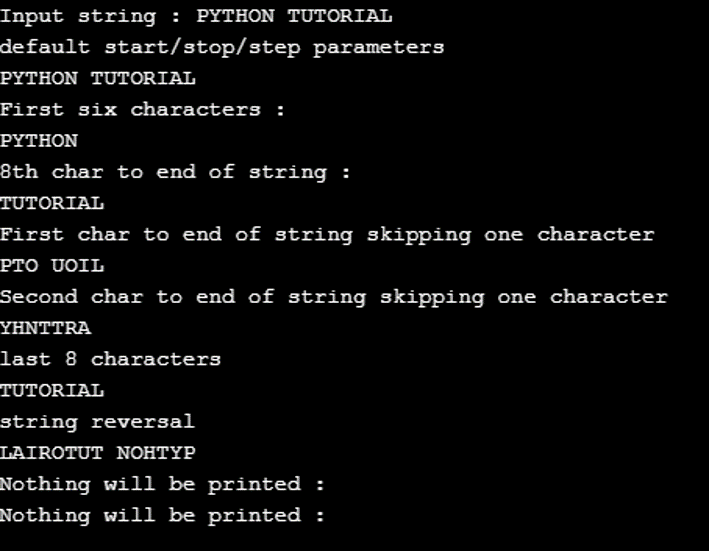
string = "PYTHON TUTORIAL"
print("Input string :",string)
print("default start/stop/step parameters")
print(string[::])
# Positive indexing
print("First six characters :")
print(string[:6])
print("8th char to end of string :")
print(string[7:])
# Extracting alternate odd chars using step parameter
print("First char to end of string skipping one character")
print(string[::2])
# Extracting alternate even chars using step parameter
print("Second char to end of string skipping one character")
print(string[1::2])
# Negative indexing
print("last 8 characters")
print(string[-8:])
print("string reversal")
print(string[::-1])
# Stop parameter should be greater than start parameter
print("Nothing will be printed :",string[3:1])
print("Nothing will be printed :",string[-1:-8:1])Output:
Example #3
Creating Username using Python Substrings
Code:
# creating username from user's first and last name
# list containing users name
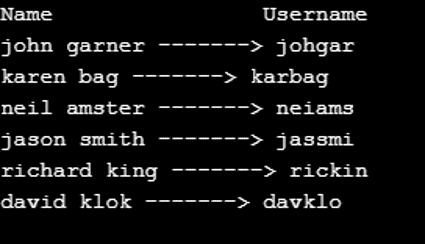
names = ['john garner', 'karen bag', 'neil amster', 'jason smith', 'richard king', 'david klok']
# empty list which will contain usernames
username = []
# defining function for creating username
def uname(names):
for i in names:
full_name=i.split() # split the name on occurrence of whitespace chars
fname = full_name[0]
lname = full_name[1]
#concatenating first 3 chars of first name with first 3 chars of last name to create username
uname = fname[:3]+lname[:3] # extracting substrings from fname and lname
username.append(uname)
# calling function uname() taking list “names” as input argument
uname(names)
# printing name of the user along with username
print("Name Username")
for name,uname in zip(names, username):
print(name, '------->', uname)Output:
Conclusion
The string is a sequence-based data type, and slicing a string gives more flexibility to work on string data as indexing only facilitates a single char extraction, whereas, with slicing, a sequence/ range of characters or substring can be accessed.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python Slice String. Here we discuss the Introduction, Why we use Python slice string and Parameters, along with syntax, examples, and outputs. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –