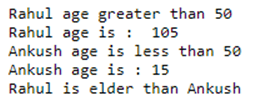Updated April 10, 2023
Introduction to Pseudocode Algorithm
Pseudocode algorithm is used while programming or is associated with writing algorithms. Pseudocode is a method that helps the programmer to define an algorithm’s implementation. We can also say that pseudocode is a cooked-up representation of a basic algorithm. In pseudocode algorithms, the algorithms are represented using pseudo codes as it is easier for anyone to interpret the pseudo-codes even if they do not have any programming background or are used to a different programming language. As the name explains itself, pseudo-codes is a false code that can be understood by a layman with a basic knowledge of programming.
How does Pseudocode Algorithm Work?
Writing an algorithm using pseudocodes is quite similar to writing in a coding language. Writing an algorithm is done on its own line in sequence. Generally, uppercase is used for writing the instructions and lowercase is used for writing the variables and the messages are written is sentence case. In pseudocode, the question is asked in INPUT and the message is printed by the OUTPUT.
Examples of Pseudocode Algorithm
Following are the examples as given below:
Example #1
In this example, we will check if the user has age below 50 years or more.
Step 1
- Put the input value
- The input is stored in the respective variable ‘age’
INPUT user inputs their age
STORE the user’s input in the age variable
Step 2
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the age variable value is less than 50. If the value is less than 50 then print the output comment. Otherwise, the else comment will be printed.
IF age<50 THEN
OUTPUT ‘My age is less than 50’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘My age greater than 50’
OUTPUT ‘My age is:’ age
Actual Code:
Age = 5;
if( Age< 50 )
then
print("My age is less than 50" )
else
print("My age greater than 50" )
end
print("My age is :", Age)
Output:
Example #2
Step 1
- Put the input value
- The input is stored in the respective variable ‘age’
INPUT user inputs their age
STORE the user’s input in the age variable
Step 2
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the age variable value is less then 50. If the value is less than 50 then print the output comment. Otherwise, the else comment will be printed. In this example the age variable has the value 5 which is less than 50 so the else statement is printed.
Code:
IF age<50 THEN
OUTPUT ‘My age is less than 50’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘My age greater than 50’
OUTPUT ‘My age is:’ age
Code:
Age = 105;
if( Age< 50 )
then
print("My age is less than 50" )
else
print("My age greater than 50" )
end
print("My age is :", Age)
Output:
Example #3
Step 1
- Put the input value of Rahul’s age
- The input is stored in the respective variable ‘Rahul’
INPUT user inputs their Rahul’s age
STORE the user’s input in the Rahul variable
Step 2
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the Rahul variable value is less then 50. If the value is less than 50 then print the output comment. Otherwise, the else comment will be printed.
IF rahul< 50 THEN
OUTPUT ‘Rahul age is less than 50’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘Rahul age greater than 50’
OUTPUT ‘Rahul age is:’ Rahul
Step 3
- Put the input value of Ankush’s age
- The input is stored in the respective variable ‘Ankush’
INPUT user inputs their Ankush’s age
STORE the user’s input in the ankushvariable
Step 4
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the Ankush variable value is less then 50. If the value is less than 50 then print the output comment. Otherwise, the else comment will be printed.
IF ankush<50 THEN
OUTPUT ‘Ankush age is less than 50’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘Ankush age greater than 50’
OUTPUT ‘Ankush age is:’ Ankush
Step 5
- Another condition is used here, where the values under the variables ‘Rahul’ and ‘Ankush’. If the condition fulfils then print the output statement otherwise print the else statement.
IF rahul>ankush THEN
OUTPUT ‘Rahul is elder than Ankush’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘Ankush is elder than Rahul’
Actual Code:
Rahul = 105;
if( Rahul< 50 )
then
print("Rahul age is less than 50" )
else
print("Rahul age greater than 50" )
end
print("Rahul age is :", Rahul)
Ankush = 15;
if( Ankush< 50 )
then
print("Ankush age is less than 50" )
else
print("Ankush age greater than 50" )
end
print("Ankush age is :", Ankush)
if (Rahul > Ankush)
then
print("Rahul is elder than Ankush" )
else
print("Ankush is elder than Rahul" )
end
Output:
Example #4
Step 1
- Put the input value of age
- The input is stored in the respective variable ‘age’
INPUT user inputs their age
STORE the user’s input in the age variable
OUTPUT ‘Actually I am:’ age
Step 2
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the age variable value is equal to 60. If the value is equal to 60 then print the output comment.
IF age == 60 THEN
OUTPUT ‘Got to know that, your age is 60’
Step 3
- Insert the condition, here the second condition is to check if the age variable value is equal to 5. If the value is equal to 5 then print the output comment.
IF age==5 THEN
OUTPUT ‘Got to know that, your age is 5’
Step 4
- Insert the condition, here the first condition is to check if the age variable value is equal to 0. If the value is equal to 0 then print the output comment.
ELSEIF age==0 THEN
OUTPUT ‘Got to know that, you are not born :P’
ELSE
OUTPUT ‘Sorry! I guess we are unable to determine your age’
OUTPUT ‘Told you man! my age is:’ age
Actual Code:
Age = 150
print("Actually I am: ", Age, "years old" )
if( Age == 60 )
then
print("Got to know that, your age is 60" )
elseif( Age == 5 )
then
print("Got to know that, your age is 5" )
elseif( Age == 0 )
then
print("Got to know that, you are not born :P" )
else
print("Sorry! I guess we are unable to determine your age" )
end
print("Told you man! my age is: ", Age )
Output:
Advantages
Following are the major advantages of pseudocodes:
- Pseudo codes help the codes to majorly focus on the logic which is to be used in the program rather than the syntax of the programming language.
- Pseudo codes are independent of any programming language which makes it easier to translate it into various languages.
- The coders are given the liberty to express their logic in plain English language without any restraints of major syntaxes.
- Writing actual codes become easier for the coder if they use pseudo-codes for writing the algorithm initially. As basic algorithms are not so concise and pseudo codes make the algorithm concise enough to make it more readable and easier for modification.
- If we compare flow charts to pseudo-codes, flow charts are lengthier to write and difficult to represent. On the other hand, pseudo-codes are easier to write and programs can be easily translated. The coders just have to focus on the meaning underlined. The major line of focus is to solve the problem with logic rather than being stuck at using the language perfectly.
- Using pseudo-code words and phrases while writing an algorithm eases the process of translation of algos into actual programming codes.
Conclusion
On the basis of the above article, we understood the concept of pseudo-codes algorithms. This article explains the pseudo-codes algorithm and how it works. The article covers the major advantages of using a pseudo-codes algorithm. Several examples are explained above which will help the coders in the understanding pseudo-codes algorithm for easing their program writing process.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Pseudocode Algorithm. Here we also discuss the definition and how the pseudocode algorithm works along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –