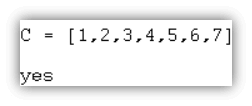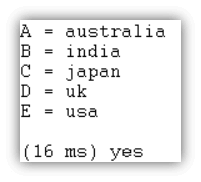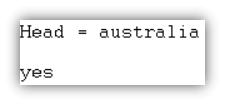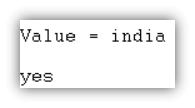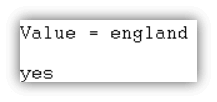Updated April 6, 2023
Introduction to Prolog list
The prolog list is a function for collecting several values to operate on large-size data.The list is a data structure for grouping the entity to handle the application’s data.The list is a collection to store multiple data items using brackets.The list is a data structure to create groups of the different values using square brackets.The prolog list is functional to store various data items, and it differs by using comma symbols.The prolog list is used to insert, delete, update, and append operations of the large values.The list is a function to handle and operate different entities in similar or different categories.
Syntax
- The prolog list uses square brackets [prolog list] to store data.
- The data list differs by a comma after a single value.
- The list syntax is shown below.
- [Value1, Value2, Value3, …, Value ]
- Description
- The prolog list contains values of a similar category.
- The square bracket contains values and differentiates these values using commas.
- The prolog empty list syntax is shown below.
- [ ]
- Description
- The prolog list is either empty or non-empty.
- If the list is empty, then the bracket does not contain any value.
- The prolog list works with the head.
- [Head | value1, value2, value3]
- The list works with a tail.
- [Head| tail1, tail2, tail3]
- Description
- The vertical bar separates the head and tail of the list.
- The first value is called the head of the list.
- The other values except the first are called tail values.
- The list works with variables using the head.
[Head|_] = [Head| value1, value2, value].- The list works with variables using a tail.
Tail = [value1, value2, value]
Prolist = [value| Tail].- Description
- The prolog creates variables and contains lists with values.
- If this variable list is required in the main list, then include it in the head or tail part.
- Some prolog list syntaxes are given below.
[v1, v2 | [v3] ]
[v1, v2| [v3] ]
[v1, v2, v3| [ ] ]How does the list work in Prolog?
Prolog comment works in the “pl” file
- Create a file with the “pl” extension.
Example: main. pl
- Create a list with list multiple entities.
Plist([Australia, india, japan, UK, USA]).Prolog comment works in the console
- Open console or interpreter.
- Set the directory path of the “pl” file.
- Use the given prolog file.
[main].- Use the list in the console.
Plist([Australia, india, japan, UK, USA]).- Directly use the list in the prolog console.
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].Prolog comment works in the console.
- Method1: use with multiple variables.
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].- The “1” number is assigned for Australia.
Australia = 1- The “2” number is assigned for India.
India = 2- The “3” number is assigned for Japan.
Japan = 3- The “4” number is Assigned for the Uk.
UK = 4- The “5” number is assigned for the USA.
USA = 5- Method2: use with a single variable.
A = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].Examples
Here are the following examples mentioned below
Example 1
The basic list with a single variable example and output are below.
- Prolog console
| ?- A = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].Output
- Prolog console
| ?- C = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7].Output
- Prolog console
| ?- D = [India, 1, USA, uk].Output
- Description:
- The list contains a value in number, lowercase, and uppercase format.
- The list assigns a single variable and displays the same as a program.
Example 2
The basic prolog list with multiple variables examples and output is below.
-
- Prolog console
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].Output
- Prolog console
[A, B, C, D, E] = [Australia, India, Japan, UK, USA].Output
- Prolog console
[A, B, C, D, E] = [australia, india, japan, uk, usa].Output
- Description:
- The list contains a value in number, lowercase, and uppercase format.
- The list assigns multiple variables and displays values with variables.
Example 3
The list with tail example and the output shown below.
-
- Prolog console
| ?- Tail = [australia, india, japan, england, america],
C = [ countries | Tail].Output
- Description:
- The prolog list specifies head and tail using a vertical bar.
- The other values except the first value are called a tail of the list.
Example 4
The list with a head example with a single variable.
-
- Prolog console
| ?- [Head|_] = [australia, india, japan, england, america].Output
- Description:
- The list specifies head and tail using a vertical bar.
- The first value is called the head of the list.
- Example5: the list with the required entity example and the output shows below.
- Prolog console
| ?- [_,Value|_] = [australia, india, japan, england, america].Output
- Prolog console
| ?- [_,_,Value|_] = [australia, india, japan, england, america].Output
- Prolog console
| ?- [_,_,_,Value|_] = [australia, india, japan, england, america].Output
- Description:
- The list displays the required value using variable and underscores symbols.
- You specify the position of the value using a comma and underscore symbol.
Example 6
The basic list example and the output shows below.
-
- pl file
cntry([australia, india, japan, england, america]).- Prolog console
| ?- cntry(List).Output
- Description:
- The file contains a list with the required value.
- You assign a list name with the required variable name.
- The output displays a list with the variable name.
- Prolog console
| ?- [Head|Tail] = [Countries, australia, india, japan, england, america].Output
- Description:
- The list specifies head and tail using a vertical bar.
- The first value is called the head of the list.
- The other value is called the tail of the list.
Conclusion
- The list maintains a collection of the values in the applications.
- The prolog list operates on large size data of the database.
- The list creates applications that are user-friendly, fast, and lightweight.
- The list operates efficiently.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Prolog list” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.