Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of PowerShell ZIP
PowerShell ZIP module allows to compress the files and the folders on the local computer or the remote machine without installing any third party or inbuilt software and zip module (Microsoft.PowerShell.ZIP) ships with the two cmdlets Compress-Archive and Expand-Archive among them, the Compress-Archive cmdlet is used to compress the files and folders and there is also System.IO.Compression class of the .Net Framework is used for compressing the data on the windows systems.
Syntax:
Compress-Archive Syntax:
Syntax 1:
Compress-Archive
[-Path] <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Syntax 2:
Compress-Archive
[-Path] <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
-Update
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Syntax 3:
Compress-Archive
[-Path] <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
-Force
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Syntax 4:
Compress-Archive
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
-Update
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Syntax 5:
Compress-Archive
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
-Force
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Syntax 6:
Compress-Archive
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-DestinationPath] <String>
[-CompressionLevel <String>]
[-PassThru]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]
Among the given syntaxes sets, we can use only one syntax combination at a time. For example, a Combination of Syntax4 and Syntax5 cannot be used together that is we can’t use -Force and -Update parameters together.
System.IO.Compression Syntax:
ZipFile.CreateFromDirectory: This class methods create a Zip archive from the Directory.
ZipArchive.CreateEntry: This class methods add new files to an existing Zip archive.
How does the ZIP function work in PowerShell?
The easy way to zipping the files and folders is by using the Compress-Archive cmdlet. This cmdlet was introduced in the PowerShell module Microsoft.PowerShell.Archive in PS version 5. It uses the Source path and the destination to compress the data and also uses the different compression levels.
Compression Levels specify how much compression we to apply to create a ZIP file. A faster compression level compresses the file faster but leads to larger file size. There are three types of compressions.
a. Fastest: Uses the fastest compression method to compress a file and it reduces the processing time but the file size will be larger.
b. NoCompression: Doesn’t apply any compression method and it doesn’t compress the source file. The destination archive file will be larger than the Optimal compression.
c. Optimal: This is the moderate level and default for this command. The processing time depends on the size of the file.
When we use the .NET compression API System.IO.Compression.ZipArchive, it supports the below overload constructors to create a Zip file.
a. CreateFromDirectory(String, String): Creates a Zip archive that contains the files and the folders from the specified directory.
b. CreateFromDirectory(String, String, CompressionLevel, Boolean): It creates a ZIP archive that contains the files and folders from the specified directory, uses the compression level, and optionally includes the base directory.
c. CreateFromDirectory(String, String, CompressionLevel, Boolean, Encoding): It creates a zip archive that contains the files and folders from the specified directory, uses the compression level, optionally includes the base directory, and uses the character encoding for the entry name.
We will understand more about the above methods when we see the examples.
Examples
Let us discuss examples of PowerShell ZIP.
Example #1: Using Compress-Archive to create an archive file.
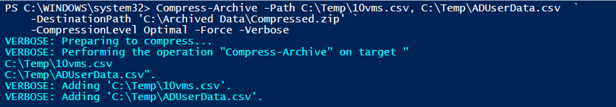
In this example, we are archiving two files at the destination location ‘C:\Archived Data’ with the default compression level (Although specified) and it creates a destination file name Compressed.Zip.
Compress-Archive -Path C:\Temp\10vms.csv, C:\Temp\ADUserData.csv `
-DestinationPath 'C:\Archived Data\Compressed.zip' `
-CompressionLevel Optimal -Force -Verbose
Output:
Example #2: Compress-Archive with Splatting.
We can also use the first example with splatting, which gathers requires input into a single hashtable and pass it to the command as shown below.
$data = @{
Path = 'C:\Temp\10vms.csv','C:\Temp\ADUserData.csv'
DestinationPath = 'C:\Archived Data\Compressed.zip'
CompressionLevel = 'Optimal'
Force = $true
Verbose = $true
}
Compress-Archive @data
The above command is similar to Example 1.
Example #3: Compress-Archive to create a source folder archive.
To zip the specific folder, we need to use the wildcard character (*) so the entire folder and files will be archived as shown below. We will use the fastest compression level here.
$data = @{
Path = 'C:\Temp\*'
DestinationPath = 'C:\Archived Data\temparchive.zip'
CompressionLevel = 'Fastest'
Force = $true
Verbose = $true
}
Compress-Archive @data
We can also use the wildcard (*) for the specific file name that starts with a specific word. For example, we can use C:\temp\ts* so it will take all the files starting with TS and C:\temp\*.csv to compress only CSV files from the C:\temp folder.
Example #4: Compress-Archive with the NoCompression level.
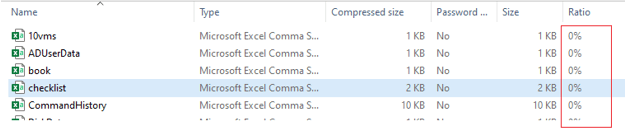
When we use the NoCompression level to create an archive, its compression ratio would be 0 and results in increasing destination folder size. For example,
$data = @{
Path = 'C:\Temp\*.csv'
DestinationPath = 'C:\Archived Data\CSVarchive1.zip'
CompressionLevel = 'NoCompression'
Force = $true
Verbose = $true
}
Compress-Archive @data
When we check the compression ratio it would be 0. See the output below.
Example #5: Update an Existing file.
The below command will add new files and folders from the C:\temp and also add the C:\Test1\7z1900-x64.msi to the existing archive temparchive.zip.
$data = @{
Path = 'C:\Temp\*', 'C:\Test1\7z1900-x64.msi'
DestinationPath = 'C:\Archived Data\temparchive.zip'
Update = $true
Verbose = $true
}
Compress-Archive @Data
Example #6: Using .Net Namespace method.
With the System.IO.Compression.ZipFile class and CreateFromDirectory method, we can create the compressed file as shown below. It creates an archive of the C:\temp to the destination path “C:\Archived Data\DotNetCompression.Zip”.
[System.IO.Compression.ZipFile]::CreateFromDirectory('C:\temp\', 'C:\Archived data\Dotnetcompression.zip')
We can also add the CompressionLevel from its syntax CreateFromDirectory(String, String, CompressionLevel, Boolean).
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IO.Compression.FileSystem
$CompressionLevel = [System.IO.Compression.CompressionLevel]::Fastest
[System.IO.Compression.ZipFile]::CreateFromDirectory('C:\temp','C:\Archived Data\Dotnetcompression.zip',$CompressionLevel,$true)
In the above example, we are using the Compression Level faster and $true the last argument mentions the includeBaseDirectory property which mentions $true means Include the directory name from the source directory from the root of the archive, and $false means to include only the content of the directory.
Conclusion
PowerShell provides a great way to compress the data without using any software, and we just need PowerShell modules. This helps us greatly when we can’t install ZIP software in restricted systems. There is also third-party software like 7ZIP which offers the PowerShell module to ZIP and unzip files.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell ZIP. Here we discuss the Definition, syntax, How does the ZIP function work in PowerShell? examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –