Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a soft, light-weighted markup language like HTML that defines the set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable and used to store and transport data. This language is self-descriptive so PowerShell uses XML generally to retrieve the data from the webpage, modify the content and post it back on the site and even many application configurations are in the XML format that is easy for the application to process the data for machines and can easily be understood and modified by humans.
Syntax
XML Format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<child>
<subchild>.....</subchild>
</child>
</root>
Select-XML cmdlet syntax:
Select-Xml
[-Xml] <XmlNode[]>
[-Path] <String[]>
-LiteralPath <String[]>
-Content <String[]>
[-XPath] <String>
[-Namespace <Hashtable>]
[<CommonParameters>]
ConvertTo-XML syntax:
ConvertTo-Xml
[-Depth <Int32>]
[-InputObject] <PSObject>
[-NoTypeInformation]
[-As <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
XPath Syntax:
This is not only for the PowerShell but it is a global XPath syntax and XPath is a major element in the XSLT standard. XPath is very helpful in retrieving the data from the XML file.
| Expression | Description |
| NodeName | Selects all nodes with the name “NodeName” |
| / | Selects from the root node |
| // | Selects Nodes from the entire document with that tag |
| . | Selects the current node |
| .. | Select the parent of the current node |
| @ | Select Attribute |
How does XML in PowerShell Works?
PowerShell handles the XML files very efficiently. There are two ways that PowerShell retrieves the data from the XML file.
- XPath
- Dot Method.
And for converting a file to XML,
- ConvertTo-XML
Before we start further explanation, we will use a Sample file (Books.xml ) from Microsoft to read XML data throughout this article.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/desktop/ms762271(v=vs.85)?redirectedfrom=MSDN
1. Retrieving Data from the XML file
- Loading XML file
To load the XML file into PowerShell, we can use the First Get-Content command and then typecast into the XML as shown below.
$file = [XML](Get-Content C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml)
Or
[XML]$file = Get-Content C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml
You can also load XML by creating an XML object type and then loading an XML file. For example,
$xml = New-Object -TypeName XML
$xml.Load('C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml')
$xml.Load('C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml')
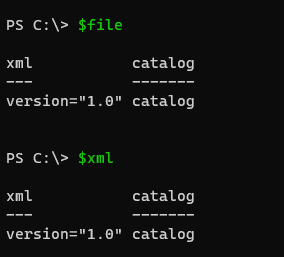
In the above cases, you will get the output as below,
Output:
To check which methods are supported in XML operation, you can check methods using the Get-Member command as shown below.
$xml | Get-Member
a. XPath method
To work with the XPath method, we can use the table shown in the Syntax section. First of all, to retrieve the data of the single node from the entire document, we can use the below command syntax.
$xml.SelectNodes("//NodeName")
In this example, we have nodes like Book, Author, Title, genre, etc. We can select any of them.
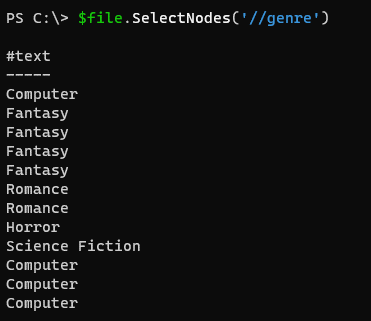
$file.SelectNodes('//genre')
Output:
Please note that the XML operation is case-sensitive.
To select single node, we can use SelectSingleNode() method.
$xml.SelectSingleNode('//title')
This will select the data from the first node. To select a different node, we need to provide the array number. In PowerShell, the array starts with [0] but in XML, it starts with numbers 1,2,3, and so on.
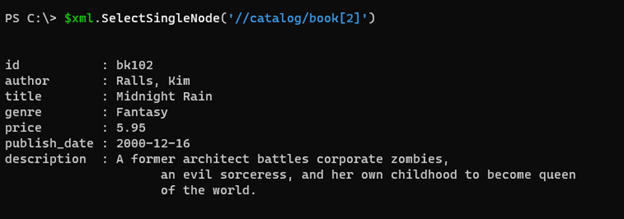
$xml.SelectSingleNode('//catalog/book[2]')
The above command will select book number 2 from the main catalog.
Output:
The below node is selected.
You can also directly use the command without specifying the parent node.
$xml.SelectSingleNode('//book[2]')
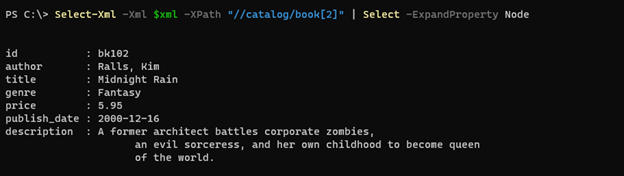
To use get the above output, we can also use the Select-XML command which works the same way as the above command. For example,
Select-Xml -Xml $xml -XPath "//catalog/book[2]" | Select -ExpandProperty Node
Output:
You can also further expand as shown below.
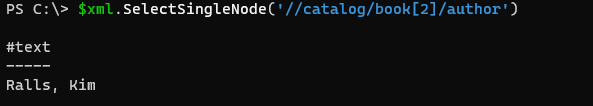
$xml.SelectSingleNode('//catalog/book[2]/author')
Output:
b. Dot method
This method is very well known that we are using on daily basis in PowerShell. We have already loaded the XML document at the beginning of this section. We will use now the Dot method for it.
The below command will retrieve book number 2 from the XML document.
This is our sample XML document.
PS C:\> $xml
xml catalog
--- -------
version="1.0" catalog
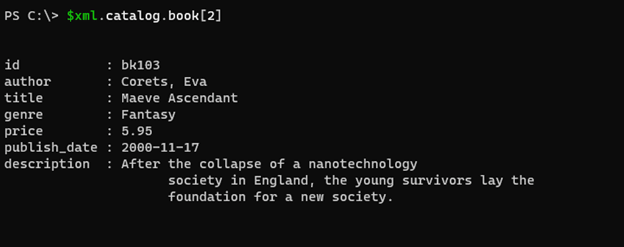
Command to retrieve book number:2
$xml.catalog.book[2]
Output:
2. ConvertTo the XML file
To convert any possible output to the XML, you can use the convertTo-XML command.
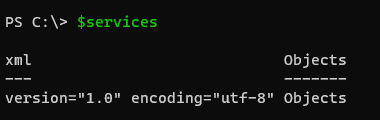
$services = Get-Service | ConvertTo-Xml
$services = Get-Service | ConvertTo-Xml
$services
Output:
To expand further, we can use any of the methods (Xpath or Dot method). For example,
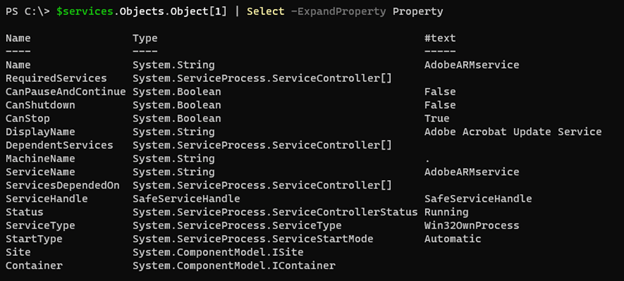
$services.Objects.Object[1] | Select -ExpandProperty Property
Output:
Examples
Here are the follwoing examples mention below
1. To load the entire content of the XML
To load the entire XML using
$xml = [xml](Get-Content C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml)
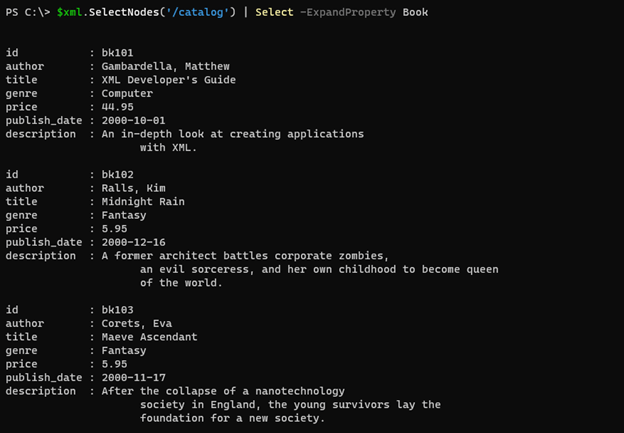
$xml.SelectNodes('/catalog') | Select -ExpandProperty Book
Output:
2. To search for the specific attribute
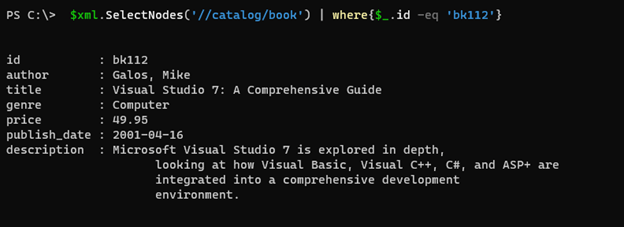
To search the specific attribute we can use the below command. It will search for the book id ‘bk112’.
$xml.SelectNodes('//catalog/book') | where{$_.id -eq 'bk112'}
Output:
3. Finding attribute using Dot Method
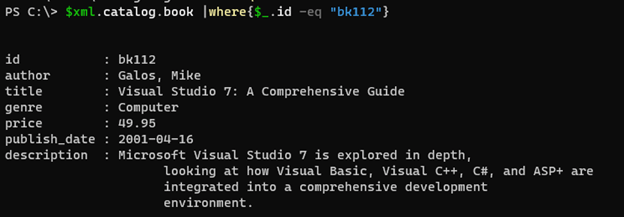
The example shown above can also be written through the Dot method as shown below.
$xml.catalog.book |where{$_.id -eq "bk112"}
Output:
4. To add a new element in the file
We will add the new element to the existing file.
$file = 'C:\Temp\SampleXML.xml'
$xml = [xml](Get-Content $file)
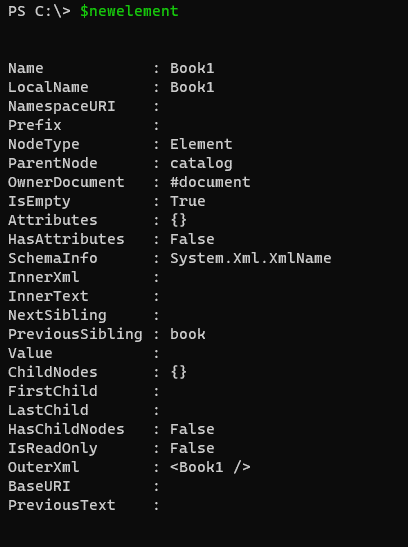
The below command will create a “Book1” named new element in the XML file.
$newelement = $xml.CreateElement("Book1")
$newelement
Output:
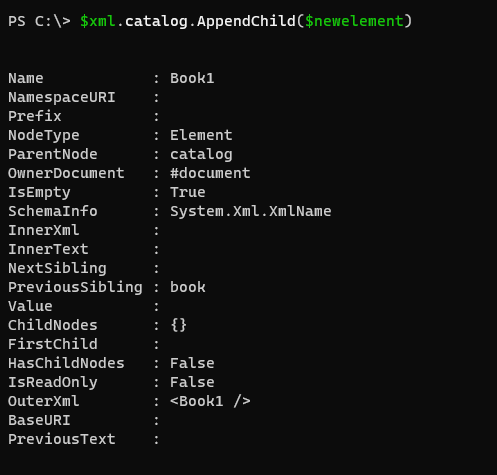
Once it is created, the second task is to append it to the existing document.
$xml.catalog.AppendChild($newelement)
Output:
Once you appended the element, next is to save the file using the below command.
$xml.Save($file)
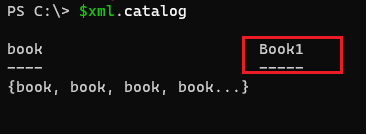
Now let’s test if the new element appears in the XML document or not.
$xml.catalog
Output:
5. Create a new node and set its attributes
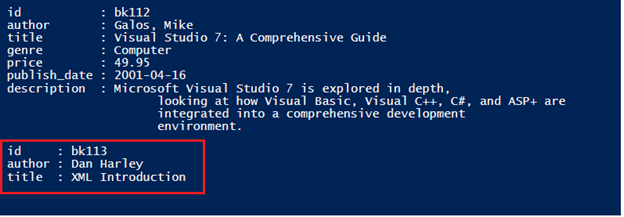
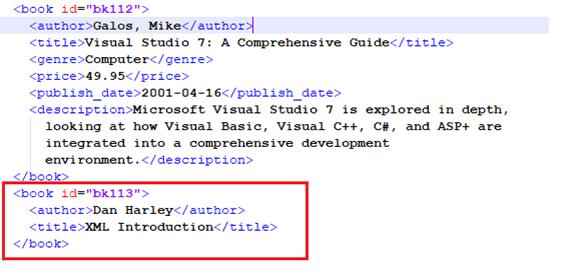
In this example, we will add a new book name “XML Introduction” with the code shown below.
$file = "C:\temp\SampleXML.xml"
$xml = [xml](Get-Content $file)
$newbookelement = $xml.catalog.AppendChild($xml.CreateElement("book"))
$newbookelement.SetAttribute("id","bk113")
$newAuthorelement = $newbookelement.AppendChild($xml.CreateElement("author"))
$newAuthorelement.AppendChild($xml.CreateTextNode("Dan Harley")) | Out-Null
$newtitleelement = $newbookelement.AppendChild($xml.CreateElement("title"))
$newtitleelement.AppendChild($xml.CreateTextNode("XML Introduction")) | Out-Null
$xml.Save(($file))
Output:
You can also check the same in the XML file.
Conclusion
XML files are the best way to provide the configuration data. Most applications use XML files for configuration and even to interact with the RestAPI methods, many websites have XML as the API output.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell XML. Here we discuss that XML files are the best way to provide the configuration data. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –