Updated March 3, 2023
Introduction to Filtering in PowerShell
Filtering refers to the process of restricting the output of a cmdlet or a statement based on certain conditions. This helps in optimizing the results and the user will be able to see what he wants from the cornucopia of results. This is achieved in PowerShell with the help of the Where-object cmdlet. Where the object will select the objects in the collection that matches the condition. The where objects can be used in two ways, either using script block or using conditional statements. This article will cover in detail the various filters that are available in PowerShell.
Syntax
The following is the syntax of the script block where the condition
Where-Object[-InputObject <PSObject>][-FilterScript] <ScriptBlock>[<CommonParameters>]
OR
Get-Process | Where-Object {$_.Id -eq 5940}
The following is the syntax of the condition operator:
Where-Object[-InputObject <PSObject>][-Property] <String>[[-Value] <Object>][-Comparison Operator][<CommonParameters>]
OR
Get-Process | Where-Object ID -eq 5940
To get the list of properties that are available for a cmdlet, the Format-List cmdlet can be piped to the respective cmdlet to list the available properties.
To select only a handful of objects from the collection the Select-Object cmdlet can be used.
OR
Get-Process | Select-Object -First 5
The above cmdlet will only display the first five processes.
Different Types of Filter
Different types and their use:
Contains
Demonstrates that this gets objects if anything within the property esteem of the question is an exact coordinate for the desired value. If the property esteem contains a single question, PowerShell changes over it to a collection of one object. This parameter was presented in Windows PowerShell 3.0. The data type is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias It Contains. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
Eq
This will return objects from the collection whose property value is the same as the given value. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias IEQ. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
FilterScript
This denotes the script block that should be used for filtering. The script block is enclosed within ({}). Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
GE
This will return objects from the collection whose property value is greater than or equal to the given value. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias IGE. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
GT
This will return objects from the collection whose property value is greater than the given value. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias IGT. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
In
This will return the objects whose values are one of the specified values. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias IIn.Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
Is
This will return objects whose datatype is the same as the value mentioned. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
IsNot
This is the opposite of Is. This will return objects that don’t match the specified type. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
LE
This will return objects from the collection whose property value is less than or equal to the given value. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias ILE. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
LT
This will return objects from the collection whose property value is less than the given value. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias ILT. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
Like
This returns objects that satisfy the wildcard condition. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias ILike. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
Match
This returns objects that satisfy the regular expression. The data type of the parameter is the switch parameter. None is the default esteem. It is referred by the alias IMatch. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
Example to Implement PowerShell Filter
Below is the example mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
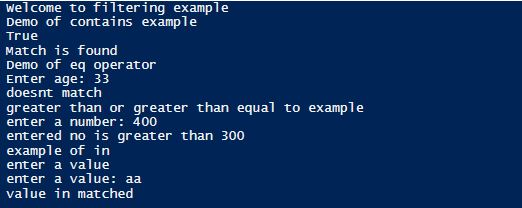
Write-Host "Welcome to filtering example"
Write-Host "Demo of contains example"
$names = 'vignesh','nandhini','vyapini','vijay','sethu'
$names -contains 'vignesh'
Write-Host "Match is found"
$age=19
Write-Host "Demo of eq operator"
$ee= Read-Host "Enter age"
if($ee -eq $age)
{
Write-Host "age matches"
}
else
{
Write-Host "doesnt match"
}
Write-Host "greater than or greater than equal to example"
$ee= Read-Host "enter a number"
if(($ee -ge 100) -and ($ee -le 200))
{
Write-Host "entered no is greater than or equal to 100 and less than or equal to 200"
}
elseif(($ee -gt 200) -and ($ee -lt 300))
{
Write-Host "entered no is greater than 200 and less than 300"
}
else
{
Write-Host "entered no is greater than 300"
}
Write-Host "example of in"
$val= "aa","bb","cc"
Write-Host "enter a value"
$tt= Read-Host "enter a value"
if($tt -in $val)
{
Write-Host "value in matched"
}
else
{
Write-Host "no match"
}
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail about the filtering operations in PowerShell. It covered with appropriate examples of the various operators that are available for filtering. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample scripts and practice them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Filter. Here we discuss an introduction to PowerShell Filter, syntax, different types, and example with sample code. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –