Introduction to PowerShell Registry
In windows operating systems, all the information related to all software and hardware such as settings, the value of software, and other options is stored in a database like called Registry. Whenever a program gets installed, a subkey with information related to the program like location or version is created and added to the registry. These settings can be found or modified in the Registry Editor. Fixing some errors related to software or operating system involves working with the registry to modify their values. Though the users can interact with the registry using Regedit or reg.exe, PowerShell has many cmdlets that can be used by the administrators to connect and work with the registry entries. This article will explain in detail how PowerShell can be used to interact with the registry.
Syntax
Below are the syntax of PowerShell Registry:
Syntax #1
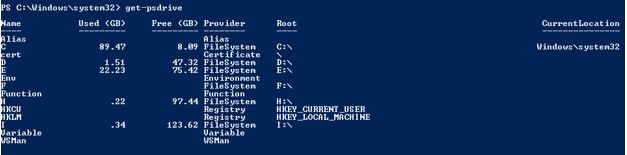
To find the path of the registry on a local machine, use the below cmdlet
Code:
get-psdrive
Output:
Syntax #2
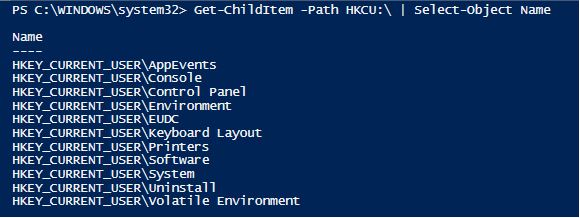
To get the registry keys that are available in the registry the following cmdlet can be used
Code:
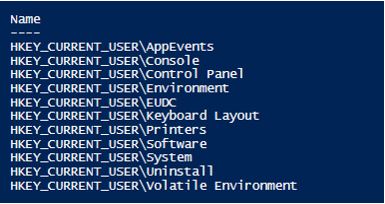
Get-ChildItem -Path HKCU:\ | Select-Object Name
Output:
Syntax #3
The following are the keys present in the HKCU registry
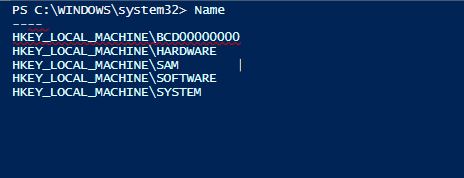
For HKLM registry keys
Code:
Get-ChildItem -Path HKLM:\ | Select-Object Name
Output:
Creating new Keys in the PowerShell Registry
The registry is like a folder or a file system and registry entries and their values are the properties of the registry.
To create a new key in the registry the following cmdlet can be used.
Code:
New-Item -Path HKCU:\TestRegistry
Or
New-Item -Path Registry::HKCU\TestRegistry
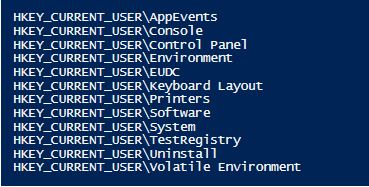
Output:
Explanation: In the above screenshot, the new key TestRegistry is added to the HKCU registry.
Deleting Keys
The below cmdlet can be used to delete the registry keys.
Code:
Remove-Item -Path HKCU:\TestRegistry
or
Remove-Item -Path 'HKCU:\TestRegistry'
Output:
Explanation: The specified entry is deleted from the registry. To remove the keys that are under a specific key, then the recurse parameter must be used in the remove cmdlet.
Navigating between Registry Entries
As discussed earlier, registry entries are keys to the registry and cant be accessed directly.
Code:
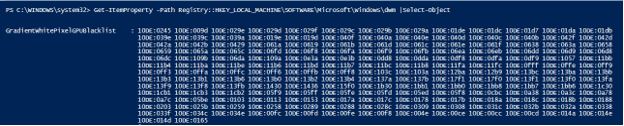
Get-Item -Path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\dwm |Select-Object -ExpandProperty Property
Or
Get-ItemProperty -Path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\dwm |Select-Object
Output:
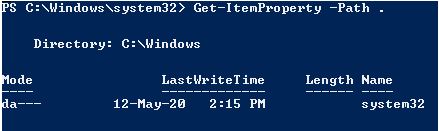
To get the properties of the current location, the below cmdlet can be used
Code:
Get-ItemProperty -Path
Output:
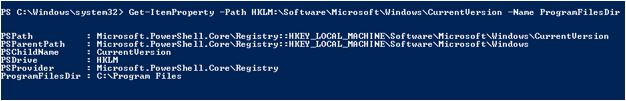
A specific entry can be retrieved directly by specifying the name along with Name parameter
Code:
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name ProgramFilesDir
Output:
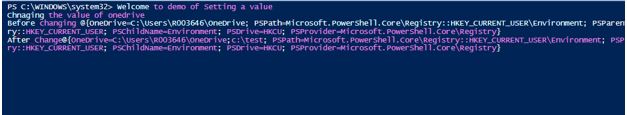
To change the value of a key
Code:
write-host "Welcome to demo of Setting a value"
Write-Host "Chnaging the value of onedrive"
$value = Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name OneDrive
Write-Host "Before changing" $value
$newvalue = $value.OneDrive += ";C:\test"
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name OneDrive -Value $newvalue
$value = Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment -Name OneDrive
write-host "After change" $value
Output:
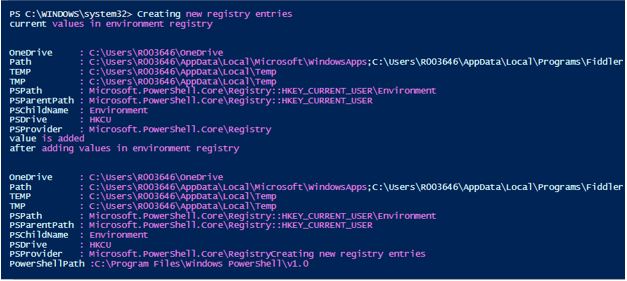
Creating new Registry Entries
A new entry can be created as follows.
Code:
Write-Host "Creating new registry entries"
write-host "current values in environment registry"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment
New-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Environment -Name PowerShellPath -PropertyType String -Value $PSHome
Write-Host "Value is added"
Write-Host "after adding values in environment registry"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKCU:\Environment
Output:
| Type | Value |
| Binary | Denotes Binary Data |
| DWord | Denotes int32 number |
| Expand String | String with environment variables |
| MultiString | Denotes Multiline string |
| String | Denotes a normal string |
| Qword | Denotes 8-byte binary data |
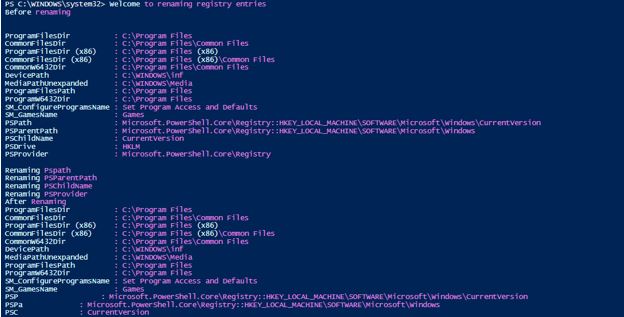
Renaming entries
Code:
write-host "Welcome to renaming registry entries"
write-host "Before renaming"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Write-Host "Renaming Pspath"
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSPath -NewName PSP
Write-Host "Renaming PSParentPath"
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSParentPath -NewNamePSPa
Write-Host "Renaming PSChildName"
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSChildName -NewName PSC
Write-Host "Renaming PSProvider"
Rename-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSProvider -NewNamePSPr
Write-Host "After Renaming"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Output:
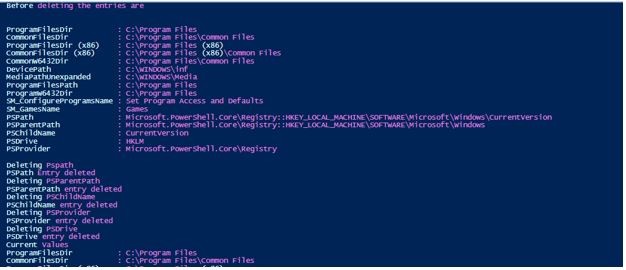
Deleting Multiple Entries from the registry
Code:
write-host "Welcome to delting registry entries"
write-host "Before deleting the entries are"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Write-Host "Deleting Pspath"
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PsPath
Write-Host "PSPath Entry deleted"
Write-Host "Deleting PSParentPath"
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSParentPath
Write-Host "PSParentPath entry deleted"
Write-Host "Deleting PSChildName"
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSChildName
Write-Host "PSChildName entry deleted"
Write-Host "Deleting PSProvider"
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSProvider
Write-Host "PSProvider entry deleted"
Write-Host "Deleting PSDrive"
Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion -Name PSDrive
Write-Host "PSDrive entry deleted"
Write-Host "Current Values"
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Output:
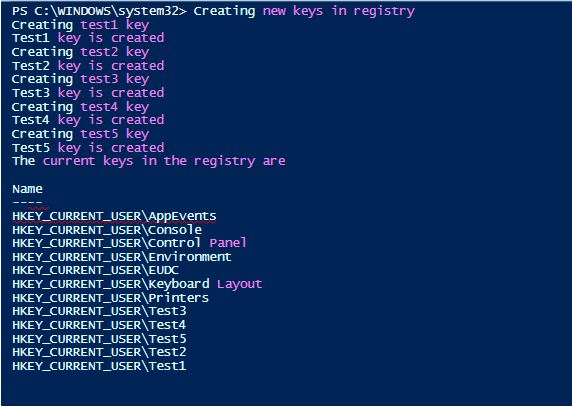
Creating multiple keys in the registry
Code:
Write-Host "Creating new keys in registry"
Write-Host "Creating test1 key"
New-Item -Path HKCU:\test1
Write-Host "Test1 key is created"
Write-Host "Creating test2 key"
New-Item -Path HKCU:\test2
Write-Host "Test2 key is created"
Write-Host "Creating test3 key"
New-Item -Path HKCU:\test3
Write-Host "Test3 key is created"
Write-Host "Creating test4 key"
New-Item -Path HKCU:\test4
Write-Host "Test4 key is created"
Write-Host "Creating test5 key"
New-Item -Path HKCU:\test5
Write-Host "Test5 key is created"
Write-Host "The current keys in the registry are"
Get-ChildItem -Path HKCU:\ | Select-Object Name
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail about how PowerShell can be used to work with the registry. It demonstrated with an example of how new keys are created, deleted and values are changed. It also showed how to add registry entries to keys, how a registry key value can be changed and deleted. All the operations are illustrated with an appropriate example. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample scripts and work on them. The article also demonstrated bulk-adding and deletion of keys and bulk addition and deletion of entries to the keys. The more the practice is done, the more the learning can be.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Registry. Here we discuss introduction to PowerShell Registry, syntax, creating keys, deleting multiple keys, and entries. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –