Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Remotesigned
PowerShell has some policy that determines the situation in which PowerShell can run configuration files and scripts. This prevents PowerShell from running or executing malicious code or software. An execution policy in a windows machine can be set for a user, for the machine, or a session. A group policy can also be created for a specific set of users. Execution policies for the system and the current user are maintained in the registry. The execution policy of a session is maintained in the memory and is lost as soon as the session is closed. The available execution policies are All signed, Bypass, Default, Remote signed, restricted, undefined, and unrestricted. The default policy is Remote signed. This article will cover in detail the remote signed execution policy in PowerShell. In this topic, we are going to learn about Powershell Remotesigned.
Remotesigned Execution Policy Features
Remote signed execution policy is the default. Under this execution policy, scripts can be run. It needs digital signatures to run scripts and config files that are downloaded from the internet. It doesn’t require digital signatures to run files that are developed on the local machine. To run files without a digital signature, an unlock-File cmdlet must be used. Running scripts without a digital signature can be fatal.
The execution policy is set using the Set-ExecutionPolicy cmdlet.
Syntax:
NAME
Set-ExecutionPolicy
SYNTAX
Set-ExecutionPolicy [-ExecutionPolicy] {Unrestricted | RemoteSigned | AllSigned | Restricted | Default | Bypass | Undefined} [[-Scope] {Process | CurrentUser |
LocalMachine | UserPolicy | MachinePolicy}] [-Force] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
None
To set the policy as remote signed, the following cmdlet is used
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
To see the execution policy settings the following cmdlet can be used.
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy Undefined
Process Undefined
CurrentUser Undefined
LocalMachine Unrestricted
1. Execution Policy scope
It is possible to set policies for a certain scope. The permitted values of scope are Machine policy, User policy, Process, local machine, and current user. The default execution policy is the local machine.
2. Machine Policy
It is used to apply the policy for all users of th system.
3. User Policy
It creates a group policy for the current user.
4. Process
This is applicable only for the current session, its value is stored in the environment variable and not in the registry. The variable and the corresponding value are deleted once the PowerShell session is closed.
5. Current User
This applies only to the current user. It’s available in the HKEY_CURRENT_USER key in the registry.
6. Local machine:
It is used to set the policy for all the users in the system. It’s available in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE in the registry.
Setting a policy for one session
It is possible to set an execution policy for a session and its child sessions. For that pwsh.exe can be used. This is stored in the environment variable,” $env: PSExecutionPolicyPreference”. This value is erased once the session is closed. Inside the session, this execution policy is given a higher priority than the one set in the registry. It can never take precedence above the group execution policy.
Example:
pwsh.exe -ExecutionPolicy LocalMachine
Input:
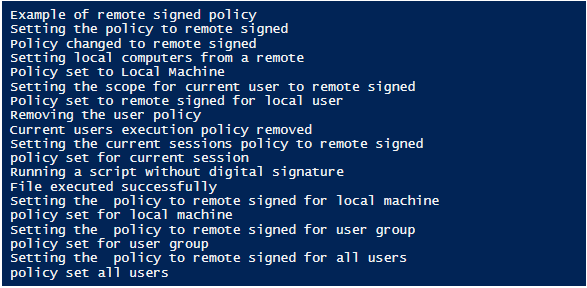
Write-Host "Example of remote signed policy"
Write-Host "Setting the policy to remote signed"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Write-Host "Policy changed to remote signed"
write-host "Setting local computers from a remote"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName testserver1 -ScriptBlock { Get-ExecutionPolicy } | Set-ExecutionPolicy
Write-Host "Policy set to Local Machine"
Write-Host "Setting the scope for current user to remote signed"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
Write-Host "Policy set to remote signed for local user"
Write-Host "Removing the user policy"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy Undefined -Scope CurrentUser
Write-Host "Current users execution policy removed"
Write-Host "Setting the current sessions policy to remote signed"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
Write-Host "policy set for current session"
Write-Host "Running a script without digital signature"
Unblock-File c:\vignesh\test.ps1
Write-Host "File executed successfully"
Write-Host "Setting the policy to remote signed for local machine"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope LocalMachine
Write-Host "policy set for local machine"
Write-Host "Setting the policy to remote signed for user group"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope UserPolicy
Write-Host "policy set for user group"
Write-Host "Setting the policy to remote signed for all users"
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope MachinePolicy
Write-Host "policy set all users"
Output:
Other Powershell Remotesigned Execution Policies Features
1. All signed
This allows the execution of all the scripts but requires a digital signature for all the scripts even the ones developed in the local machine. A prompt will be asked before running the scripts.
2. By Pass
There is no warning or prompts shown for executing scripts.
3. Default
The default policy for windows clients is restricted and for windows, servers are remote signed
4. Restricted
It allows only commands and not the execution of scripts. None of the config files, ps files, or module scripts are allowed.
5. Unrestricted
The policy for non-windows computers can’t be changed. All unsigned scripts can be run.
Group Policy Features
If the turn-on script execution is disabled, then scripts will not be run. This is like a restricted execution policy. To enable execution policy, turn on script execution group policy must be enabled. To allow all scripts then policy should be set as unrestricted. To allow execution of scripts with digital signatures, then it must be Remote signed, if only signed scripts are to be executed then the policy must be All signed.
The policies are executed in the following order. The highest priority is given to Machine policy, then user policy followed by process, then-current user, and finally local machine.
Conclusion – Powershell Remotesigned
Thus, the article covered in detail the remote signed execution policy in PowerShell. It explained the features of the remote signed policy along with syntax. The article showed various examples of how to set the policy to remote signed for various scope. It also gave a brief introduction to other available execution policies. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample programs and practice them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Powershell Remotesigned. Here we discuss the Remotesigned Execution Policy Features along with the Other Execution Policies Features. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

