Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Logging
It is very important for programmers to have logging enabled in their scripts as it will help in troubleshooting during unexpected behavior of the script. Logging is the mechanism of capturing the error message or exception, but it is also helpful in identifying the point until the script has been executed. Sometimes, if a script is working only for a few values and not working for others, then if logging is enabled, it will be easy for the programmer to narrow the issue and fix it. PowerShell provides various methods of logging, which will be covered in detail in this article. PowerShell provides three types of logging such as Module logging, Script block logging, and transcription logging.
Prerequisites to enable enhanced PowerShell Logging
For Windows 10, enhanced PowerShell logging is automatically supported.
For windows 7,8,2008,2012 with PowerShell v5.0, the following components are required
- .Net 4.5
- WMF (4.0/5.0)
For windows 7,8,2008,2012 with PowerShell v4.0, the following components are required
- .Net 4.5
- WMF (4.0)
1. Logging Configuration
Before trying to log errors in a script, it is important to enable them in the group policy. Below are the steps
Local Group Policy EditoràAdministrative TemplatesàWindows ComponentsàWindows PowerShell. In that, we need to enable Turn on Module Logging, turn on PowerShell Script Block Logging and Turn on PowerShell Transcription.
2. Module Logging
Module logging records pipeline details such as variable initialization and command invocations as the script executes. It will record samples of script and data that is formatted to be sent as output. In addition, it will capture the logging that may be missed by other types but may fail to capture certain commands. This type of logging event is written under the 4103-event id.
3. Script Block Logging
This is used to capture logs for all the scripts and commands. This is used to determine the mode of attack from an external attacker. Even the decoded commands are also captured and logged. This logging events are recorded under the event id-4104. If the logs exceed the specified limit, it is fragmented into multiple files and captured. From PowerShell 5.0, script blocking is automatically enabled if the script contains certain pre-defined commands or scripting techniques that may be prone to attack. These are logged under the warning level unless script blocking logging is disabled purposefully. This will capture all activity and not just suspicious activity. The non-suspicious activities will be logged under event id 4104 but either as verbose or as information levels.
4. Transcription Logging
If transaction logging is enabled, a record is created for each session, including each input and output command that is present in that session. These are written to a text file along with timestamp and metadata. They are automatically named, starting with PowerShell_transcript. The default location to which the files are written is the user’s document folder; this can be changed if needed. The best place to store them is to a network drive so that the attackers can’t access them easily. The size of the file is very less and then can be reviewed using any standard tool. The appropriate logging mechanism has to be enabled in the Local Group Policy editor or by setting their value in the registry.
5. Splitting huge log files to smaller files
Sometimes, the log file generated may be huge in size. This may hamper the debugging process. In this scenario, it will be helpful if we can split the single log file into smaller files. The below script will help in achieving this. The script first identifies the source file that needs to be split. It then asks for the destination folder where the new split log files are to be saved. Next, the script prompts the user for the number of lines that should be present in each log file. Once that is done, the new log files are generated.
Input:
Write-Host "Welcome to the demo of Split a large log file into smaller files"
$lc = 0
$fn = 1
# Getting the source log file
$source = Read-Host "Enter the log file path"
# Getting the destination where the smaller log files will be saved
$destination = Read-Host "Enter the destination path"
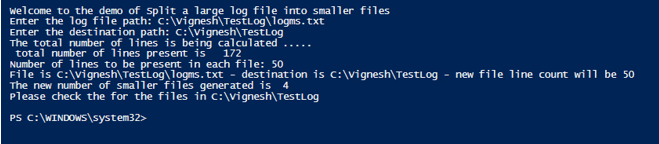
Write-Host "The total number of lines is being calculated ..... "
Get-Content $source | Measure-Object | ForEach-Object { $sourcelc = $_.Count }
#total number of lines in source file
Write-Host " total number of lines present is " $sourcelc
# size of each destination file
$destfilesize = Read-Host "Number of lines to be present in each file"
$maxsize = [int]$destfilesize
Write-Host File is $source - destination is $destination - new file line count will be $destfilesize
$content = get-content $source | % {
Add-Content $destination\splitlog$fn.txt "$_"
$lc ++
If ($lc -eq $maxsize) {
$fn++
$lc = 0
}
}
Write-Host "The new number of smaller files generated is " $fn
Write-Host "Please check the for the files in" $destination
Before running the script, the number of files in the source directory
Output:
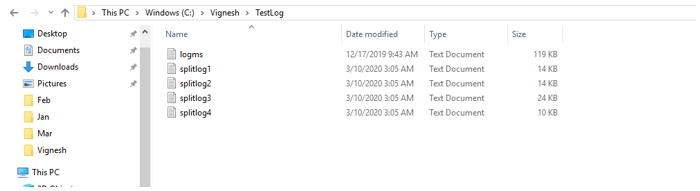
After running the script, the number of files in the directory
Input:
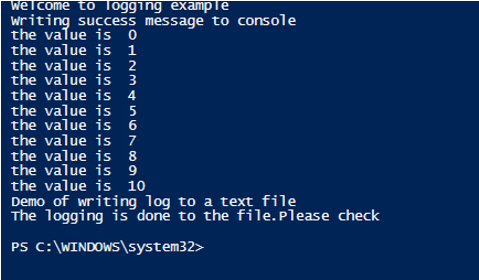
Write-Host "Welcome to logging example"
Write-Host "Writing success message to console"
for($i=0; $i -le 10; $i++)
{
Write-Host "the value is "$i
}
Write-Host "Demo of writing log to a text file"
for($i=0; $i -le 10; $i++)
{
$i |Out-File -FilePath C:\Vignesh\TestLog\test.txt -Append
}
Write-Host "The logging is done to the file.Please check"
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail about logging in PowerShell. It explained in detail the various types of logging available and the use of each logging mechanism. The article has explained with an example on how a large log file can be split into smaller log files. It also explained how logging can be done to a file or a console. Logging is one of the best practices to be followed during scripting, as it makes life easier whenever something unusual happens. The best way to learn more about this is to write sample scripts and execute them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Logging. Here we discuss the various types of PowerShell Logging that are available and the use of each logging mechanism. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –