Updated March 4, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Like Operator
Like operator in PowerShell is a type of match operator. The match operators are used to find elements based on a condition using regular expressions. Like and not like both are the type of match operators. These operators are mainly used to identify whether a string is contained within another string. For comparing non-identical strings, they are used along with wildcards. When the input is a single scalar object, the $Matches variable is automatically populated. For scalar input, both like and not like operators return a Boolean value and the value of the $Matches is set to the corresponding matched component. This article will cover in detail about like and not like an operator. It will also cover other string comparison operators like the match, contains, etc.
Syntax:
The syntax of like and notlike cmdlet is as follows.
<string[]> -match <regular-expression>
<string[]> -notmatch <regular-expression>
Examples of PowerShell Like Operator
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1
Input:
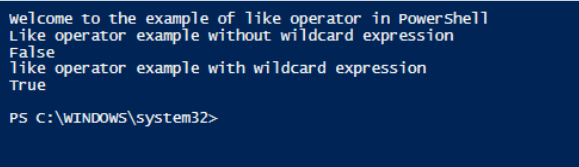
Write-Host "Welcome to the example of like operator in PowerShell"
Write-Host "Like operator example without wildcard expression"
$input="My name is vignesh"
$input -like "sh"
Write-Host "like operator example with wildcard expression"
$input="My name is vignesh"
$input -like "*sh"
Output:
In the above example, without wild card expression produces a false result as it searched for exact match. With wild card expression it searches only for a match.
Example #2
Input:
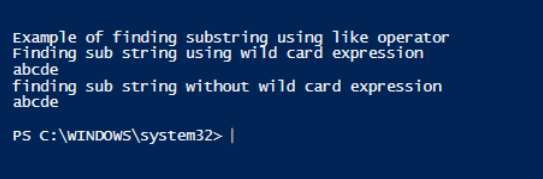
Write-Host "Example of finding substring using like operator"
Write-Host "Finding sub string using wild card expression"
"abcde", "fghijk", "lmnop", "qrstuv", "wxyz" -like "abcd*"
Write-Host "finding sub string without wild card expression"
"abcde", "fghijk", "lmnop", "qrstuv", "wxyz" -like "abcde"
Output:
Example #3
Input:
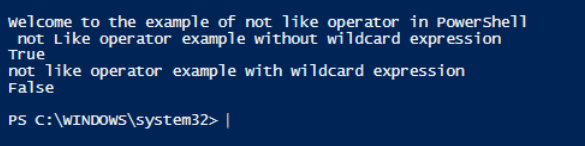
Write-Host "Welcome to the example of not like operator in PowerShell"
Write-Host " not Like operator example without wildcard expression"
$input="test input string"
$input -notlike "te"
Write-Host "not like operator example with wildcard expression"
$input="test input string"
$input -notlike "te*"
Output:
Example #4
Input:
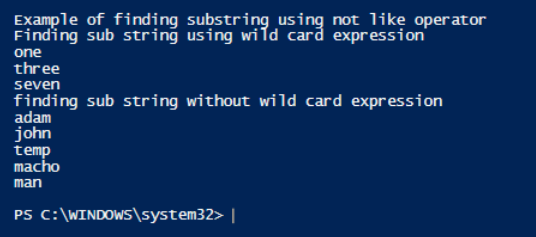
Write-Host "Example of finding substring using not like operator"
Write-Host "Finding sub string using wild card expression"
"one", "three", "seven", "ten", "tenth" -notlike "ten*"
Write-Host "finding sub string without wild card expression"
"adam", "john", "temp", "macho", "man" -notlike "ad"
Output:
-Match and not Match:
Match operator is used to match strings using regular expressions. The $matches variable is populated automatically for scalar input. This can be used only for strings and not for integers or any other data objects. In case if the input is a collection then only the matching members from the input is returned and the $matches variable is not populated. If the input is a single string, then the $matches variable is populated.
Example #5
Input:
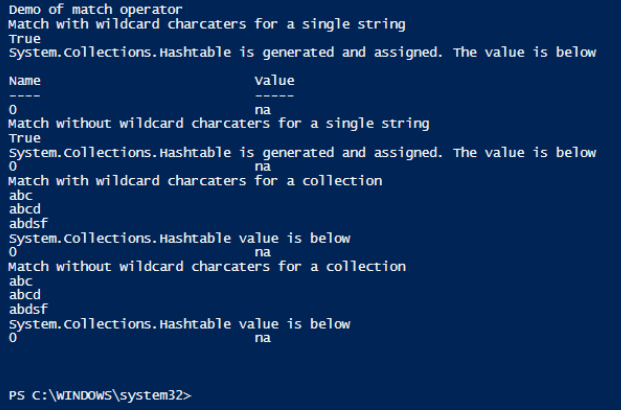
write-host "Demo of match operator"
Write-Host "Match with wildcard charcaters for a single string"
$input="My name is vignesh"
$input -match "na*"
Write-Host "$matches is generated and assigned. The value is below"
$Matches
Write-Host "Match without wildcard charcaters for a single string"
$input -match "na"
Write-Host "$matches is generated and assigned. The value is below"
$Matches
Write-Host "Match with wildcard charcaters for a collection"
$input="abc", "abcd", "abdsf","erert"
$input -match "ab*"
Write-Host "$matches value is below"
$matches
Write-Host "Match without wildcard charcaters for a collection"
$input="abc", "abcd", "abdsf","erert"
$input -match "ab"
Write-Host "$matches value is below"
$matches
Output:
In the above example as you can see the $matches is not generated for collection of strings and is only generated for a single string input.
Example #6
Input:
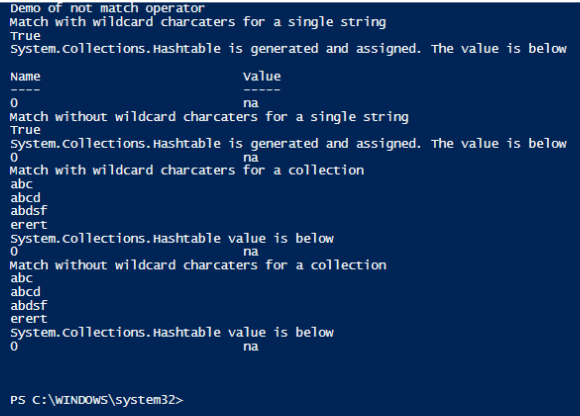
write-host "Demo of not match operator"
Write-Host "Not Match with wildcard charcaters for a single string"
$input="My name is vignesh"
$input -notmatch "za*"
Write-Host "$matches is generated and assigned. The value is below"
$Matches
Write-Host "Not Match without wildcard charcaters for a single string"
$input -notmatch "za"
Write-Host "$matches is generated and assigned. The value is below"
$Matches
Write-Host "Not Match with wildcard charcaters for a collection"
$input="abc", "abcd", "abdsf","erert"
$input -notmatch "za*"
Write-Host "$matches value is below"
$matches
Write-Host "Not Match without wildcard charcaters for a collection"
$input="abc", "abcd", "abdsf","erert"
$input -notmatch "za"
Write-Host "$matches value is below"
$matches
Output:
Contains and not contains:
These are same as like and not like operators. This is used to identify whether a value is present inside a collection of values. This always generates a Boolean value output. Only when the test value matches exactly with at least one of the values, then only a true is returned.
Syntax:
<Reference-values> -contains <Test-value>
-notcontains:
This is the opposite of contains operator. A true is returned when there is no exact match.
Syntax:
<Reference-values> -notcontains <Test-value>
Example #7
Input:
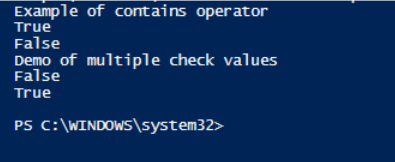
Write-Host "Example of contains operator"
$input= "sdfsdfdsf","adsadsad","test","test1"
$input -contains "test"
$input= "sdfsdfdsf","adsadsad","test","test1"
$input -contains "dfsdf"
Write-Host "Demo of multiple check values"
$input="one","two","three","four","five"
$input -contains "one","two"
$input="one","two"
$input, "three","four" -ccontains $input
Output:
Example #8
Input:
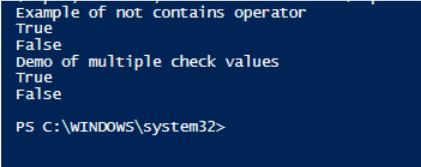
Write-Host "Example of not contains operator"
$input= "sdfsdfdsf","adsadsad","dfdf","sdf"
$input -notcontains "test"
$input= "sdfsdfdsf","adsadsad","test","test1"
$input -notcontains "test"
Write-Host "Demo of multiple check values"
$input="one","two","three","four","five"
$input -notcontains "one","two"
$input="one","two"
$input, "three","four" -notcontains $input
Output:
Example #9
Input:
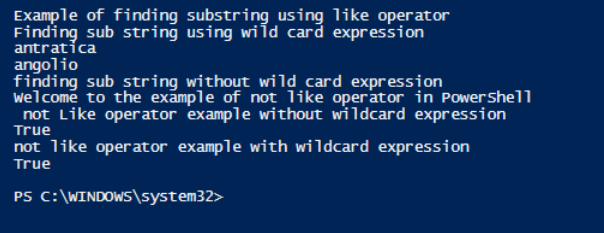
Write-Host "Example of finding substring using like operator"
Write-Host "Finding sub string using wild card expression"
"america", "australia", "antratica", "amesterdam", "angolio" -like "an*"
Write-Host "finding sub string without wild card expression"
"america", "australia", "antratica", "amesterdam", "angolio" -like "abcde"
Write-Host "Welcome to the example of not like operator in PowerShell"
Write-Host " not Like operator example without wildcard expression"
$input="one two three"
$input -notlike "te"
Write-Host "not like operator example with wildcard expression"
$input="my name is vignesh krishnakumar"
$input -notlike "te*"
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article explained in detail the like operator, its syntax and its usage with appropriate examples. The article also covered in detail about the, not like operator, match and not match operator, contains and not operator along with detailed explanation and examples. The differences between each of the type is shown using sample programs and necessary explanation was provided. The best way to learn more about this would be to practice sample programs and explore each operator in detail so as to know better on when to use which operator as most of the above operators discussed are similar in nature.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Like Operator. Here we discuss the Examples of PowerShell Like Operator along with the other string comparison operators. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –