Updated May 19, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL User Password
PostgreSQL provides a user management facility in which we can create a user, create a password for the user, and change the user’s password. Also, we can update the user’s role and delete the user’s passworduser. User password is essential in PostgreSQL because it maintains the security of the database management system. The user management plays an important role in the database administration of systems. Under user management, we can change the role of the user as well as change the password of the user to maintain a safe environment.
How does Sort Function work in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge about PostgreSQL.
- We must require users to perform different operations.
- To manage users effectively, we must have a foundational understanding of how it works.
- We can perform different operations on users with the help of psql and pgAdmin.
How to Create a Password for Users in PostgreSQL?
First, we see how to create users in PostgreSQL.
Following statement is used to create a password for the user.
Syntax:
create user user name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax where create a user or role statement is used to generate a user or role in PostgreSQL, and user name means specified user name or role name. Here we create users without any privilege. Second syntax is also used to create user through the psql terminal.
Example:
Code:
create user sam;In the above example, we use a create statement to create a user, and sam is a new user that we need to create.
Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
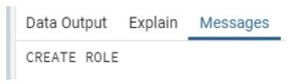
Now we have the same user, so we create a password for the sam user using the following syntax.
Syntax:
alter user user name password 'XXXXXXXX';Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use an alter user or role statement to create a password for the user, where the user name is the specified user name which we need to assign a password by using the password keyword.
Example:
Code:
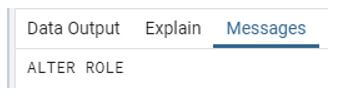
alter user sam password '123456';Explanation:
- In the above example, we use an alter user statement, where sam is a specified user name, and we assign a password to sam user by using the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
How to Change a Password for the User in PostgreSQL?
If we change the password time to time, it is convenient to protect data, and a safe environment can be maintained for users. In this type, suppose we need to change the user password. At that time, we used the following syntax, and it was an easy method to change passwords.
Syntax:
alter user user name with password 'xxxxxxx';Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use alter user or role statement, where name is the specified user name and with and password is a keyword to change user password, where user name means specified user name and new password for that user.
Example:
Suppose we need to change the password of a sam user at that time we use the following statement.
Code:
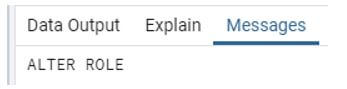
alter user sam with password 'sam123';Explanation:
- In the above statement, we used to alter the user statement, where sam is the specified user name and with password is a keywords used to change the password of sam user.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Suppose after some days, we want to change the user’s password or update the user’s password at that time, we provide a valid date to the user password. Now see how we can provide validity to the password of the specified user.
Syntax:
alter user user name with password 'xxxxxxx' valid until timestamp;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use alter user or role statement where user name means specified user name with, password and valid until is a keyword to assign password and timestamp to the user.
- Timestamp means assigning a valid date of password to a specific user.
Example:
Code:
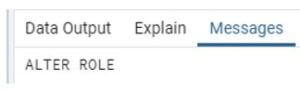
alter user sam with password 'sam123' valid until '1 August 2020';Explanation:
- In the above example, we use alter user statement, where sam is the specified user name, and we assign a password to a sam user with a valid date of password. Here the assigned password is sma123, and valid until 1 August 2020.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
How to Delete a Password for the User in PostgreSQL?
In this type, suppose we need to delete the password of the user. But when we delete the password, it cannot protect data as well as the safe environment of the user at that time, we use the following syntax.
Syntax:
alter user user name with password null;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use an alter user or role statement.
- Where user name means specified user name, with and password is the keywords used to assign a password to a specific user in the above syntax, we use the null keyword to assign a null password.
Example:
Code:
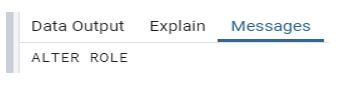
alter user sam with password null;Explanation:
- In the above statement where we use the alter user statement, sam is specified user name, where with and password is the keywords, and null indicates the password is null for sam user.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw the basic syntax of create a user, create a password, change a password, and delete a password. We also saw how we can implement them in PostgreSQL with different examples of each type. In this article, we saw how we can maintain the security of data and how we can maintain a safe environment. From this article, we saw how we can handle User Passwords in PostgreSQL on the server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL User Password” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

