Updated May 30, 2023
Difference Between PostgreSQL union vs union all
PostgreSQL union: UNION operator in PostgreSQL combines the result of two or more SELECT statements and removes the duplicate rows. Before the final result of the UNION operation, DISTINCT is applied to the resultset, which removes the duplicate rows from it and displays only the relevant data to the user.
PostgreSQL union all: UNION ALL operator in PostgreSQL is also used to combine the result of two or more SELECT statements, but it does not perform any additional operation on the resultset. Instead, it returns the full table by concatenating the results of SELECT statements and displaying them to the user. It is somewhat faster than the UNION operator as no extra overhead of removing duplicates needs to be performed.
Head to Head Comparison Between PostgreSQL union vs union all (Infographics)
Below is the Top Comparison Between PostgreSQL union vs union all:
Key Differences
Some of the key differences between union and union all in PostgreSQL describing the detailed description are given below:
1. Both the UNION and UNION ALL operators are used in PostgreSQL to combine two tables by merging the rows returned by two or more SELECT statements. The only difference is that UNION does not return or removes the duplicate rows, whereas UNION returns all the rows returned after merging, either duplicate or not.
2. The UNION operator performs the DISTINCT operation on the resultset, removing the duplicate rows from it. So, in case of a large volume of data present in the tables, the UNION operator is considered to be slower than the UNION ALL operator as it hampers the overall speed by performing the additional overhead of the DISTINCT operation.
3. To perform both the UNION and UNION ALL operations for combining the tables, the same conditions need to be satisfied:
- The same number of columns should be retrieved from each SELECT statement that is to be combined.
- Columns retrieved from each SELECT statement must be of the same data type.
- Columns retrieved from each SELECT statement must be in the same order.
4. Let us understand the difference in the result set returned by the UNION and UNION ALL operators with the help of an example:
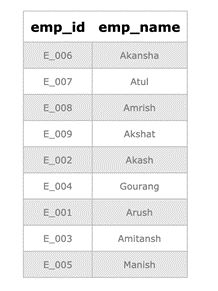
Consider the two tables with the name ‘ITDepartment’ and ‘OperationsDepartment’ having the fields ’emp_id’ and ’emp_name’
ITDepartment:
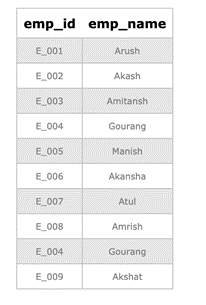
| emp_id | emp_name |
| E_001 | Arush |
| E_002 | Akash |
| E_003 | Amitansh |
| E_004 | Gourang |
| E_005 | Manish |
OperationsDepartment:
| emp_id | emp_name |
| E_006 | Akansha |
| E_007 | Atul |
| E_008 | Amrish |
| E_004 | Gourang |
| E_009 | Akshat |
Query using the UNION operator:
SELECT * from ITDepartment
UNION
SELECT * from OperationsDepartment;Result:
In the above tables, Employee ‘Gourang’ having emp_id ‘E_004’ is working in both IT and Operations Department, so present in both the tables, i.e., ‘ITDepartment’ and ‘OperationsDepartment’. Since the UNION operator on both tables’ SELECT statement returns a combined result set of both tables and removes the duplicate rows. So, performing the UNION on the resultset of both the tables, the results displaying the employee ‘Gourang’ only once.
Query using UNION ALL operator:
SELECT * from ITDepartment
UNION ALL
SELECT * from OperationsDepartment;Result:
In the above tables, Employee ‘Gourang’ having emp_id ‘E_004’ is working in both IT and Operations Department, so present in both the tables, i.e., ‘ITDepartment’ and ‘OperationsDepartment’. Since the UNION ALL operator on both tables’ SELECT statement returns a combined result set of both tables. Still, it does not remove the duplicate rows, it instead displays all the data resulting by concatenation. So
performing the UNION ALL on the resultset of both the tables, the results display the employee ‘Gourang’ two times. If it is present ‘n’ number of times, UNION ALL will return all of them.
Comparison Table
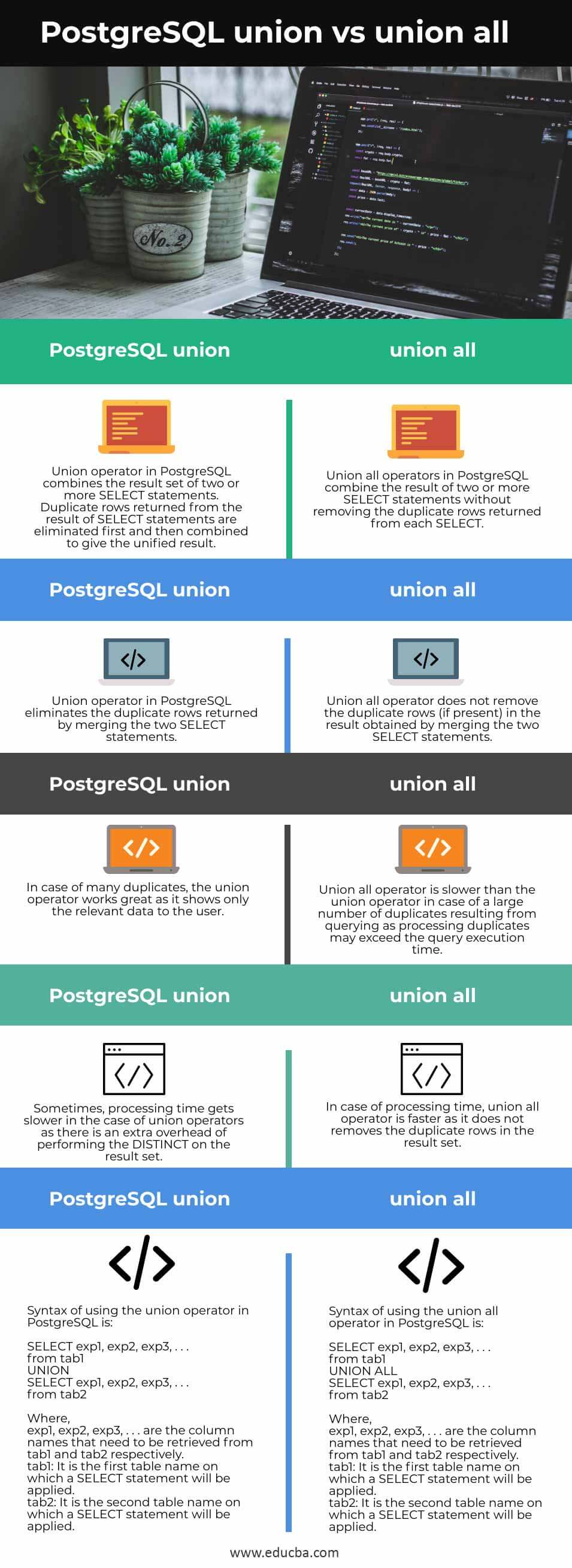
Below given is the comparison table showing the head to head comparison between union and union all in PostgreSQL:
| S.No. | PostgreSQL union | PostgreSQL union all |
| 1. | Union operator in PostgreSQL combines the result set of two or more SELECT statements. Duplicate rows returned from the result of SELECT statements are eliminated first and combined to give the unified result. | Union all operators in PostgreSQL combine the result of two or more SELECT statements without removing the duplicate rows returned from each SELECT. |
| 2. | Union operator in PostgreSQL eliminates the duplicate rows returned by merging the two SELECT statements. | Union all operator does not remove the duplicate rows (if present) in the result obtained by merging the two SELECT statements. |
| 3. | In case of many duplicates, the union operator works great, showing only the relevant data to the user. | Union all operator is slower than the union operator in case of a large number of duplicates resulting from querying, as processing duplicates may exceed the query execution time. |
| 4. | Sometimes, processing time gets slower in the case of union operators as there is an extra overhead of performing the DISTINCT on the result set. | In the case of processing time, the union all operator is faster as it does not remove the duplicate rows in the result set. |
| 5. | Syntax of using the union operator in PostgreSQL is:
SELECT exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . from tab1 UNION SELECT exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . from tab2
Where, exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . are the column names that need to be retrieved from tab1 and tab2 respectively. tab1: It is the first table name on which a SELECT statement will be applied. tab2: It is the second table name on which a SELECT statement will be applied. |
Syntax of using the union all operator in PostgreSQL is:
SELECT exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . from tab1 UNION ALL SELECT exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . from tab2
Where, exp1, exp2, exp3, . . . are the column names that need to be retrieved from tab1 and tab2 respectively. tab1: It is the first table name on which a SELECT statement will be applied. tab2: It is the second table name on which a SELECT statement will be applied. |
Conclusion
The above description clearly explains what the PostgreSQL union and union all is and the major differences between the two. Both the UNION and UNION ALL operators are used for the same purpose in PostgreSQL (though the output is different). It depends on the programmer’s choice, the data present in the tables, and the required output for the user to use any of them according to their requirements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL union vs union all” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.