
Introduction to PostgreSQL Timestamp
PostgreSQL, or “Postgres,” is a highly advanced and powerful open-source relational database management system. It boasts a wide range of features and functionalities, making it a popular choice among developers and businesses. From small-scale projects to large-scale corporate solutions, Postgres is an ideal database system that can easily handle any project requirements. Its reliability, security, and scalability are key reasons it has gained so much popularity over the years.
Table of Contents:
Why are Timestamps Important in a Database Management System?
Timestamps are essential components within database management systems, vital in recording and monitoring time-related data. They store temporal information such as dates, times, and intervals. Timestamps are indispensable for various applications, including event tracking, data versioning, task scheduling, and time-based analysis.
PostgreSQL provides two main data types for storing timestamps:
- Timestamp: Stores date and time value without timezone information.
- Timestamptz: Stores date and time value along with the timezone information.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE events (
event_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_name VARCHAR(100),
event_timestamp TIMESTAMP, #Use_For_Timestamp
event_timestamptz TIMESTAMPTZ #Use_For_Timestamptz
);In this syntax:
- SERIAL PRIMARY KEY creates an auto-incrementing serial column and designates it as the primary key for the table.
- VARCHAR declares a column named event_name with a variable character type that can store upto 100 characters.
- TIMESTAMP is used to store date and time values without a timezone.
- TIMESTAMPTZ is used to store date and time values along with the timezone information.
Example:
Let’s Create a Table to show the difference between timestamp and timestamptz:
Code:
INSERT INTO events (event_name, event_timestamp, event_timestamptz)
VALUES ('Meeting', '2024-01-29 15:30:00', '2024-01-29 15:30:00');Let’s display the timestamp values:
SELECT event_id, event_name, event_timestamp FROM events;Output:

Here, We get the timestamp value output in the table without timezone information.
Now, let’s check for the timestamptz; we will insert data for the timestamptz:
Code:
INSERT INTO events (event_name, event_timestamp, event_timestamptz)
VALUES ('Conference', '2024-01-30 09:00:00', '2024-01-30 09:00:00+05:00');
(UTC+05:00 timezone)Let’s display the timestamptz output:
Code:
SELECT event_id, event_name, event_timestamptz FROM events;Output:
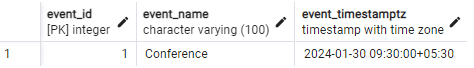
Here, Data stores the timestamp values with timezone information.
Some PostgreSQL Timestamp Syntax
1. Now(): In PostgreSQL, the function utilized to obtain the current date and time is known as “now.” This function is essential for selecting the current date and time within PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
SELECT now() :: timestamp;2. Date and Time: Any date and time can display the timestamp format. The format will automatically include the time if you only provide the date.
Syntax:
SELECT '2024-01-29 10:29' :: timestamp;3. Current Timestamp: The function in PostgreSQL that selects the current date and time is the “current timestamp” function. It’s essential to employ the “current timestamp” function in PostgreSQL to utilize the current date and time. This function holds greater significance for selecting the current date and time within PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :: timestamp;4. Interval: The INTERVAL data type in PostgreSQL stores time intervals, encompassing units like hours, minutes, seconds, and more.
Syntax:
SELECT TIMESTAMP '2024-01-29 12:00:00' + INTERVAL + '1 day' - INTERVAL '1 hour';This syntax will increase the interval day by one day and reduce the time by one hour.
How does the Timestamp Work?
Internal Representation: Timestamp values in PostgreSQL represent the count of microseconds elapsed since midnight on January 1, 2000, in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This methodology ensures high precision in storing date and time data.
Precision and Range: Timestamp values in PostgreSQL can possess up to microsecond precision, facilitating precise representation of time down to fractions of a second. The range of Timestamp values constrains the storage size and encompasses dates from 4713 BC to 294276 AD.
Manipulating Timestamp values: PostgreSQL offers various functions and operators dedicated to manipulating Timestamp values. These include functions for extracting specific parts of a Timestamp (such as year, month, and day), calculating differences between Timestamp values, and formatting Timestamp values for display purposes.
Automatic Timestamp Generation: In PostgreSQL, To create timestamp values, you can use the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP or NOW() functions, which generate the timestamp value automatically. These functions return the current date and time at the start of the ongoing transaction.
Let’s see some examples:
Code#1:
SELECT now();Output:
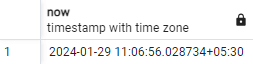
Explanation: This function provides the current date and time using ‘now()’.
Code#2:
SELECT Current_timestamp;Output:
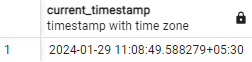
Explanation: This function holds the current date and time in PostgreSQL.
Code#3:
SELECT timeofday();Output:
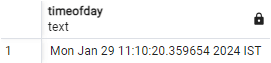
Explanation: This function selects the current day, date, and time format with the corresponding timezone.
Additional Information:
- The timestamp data type in PostgreSQL solely stores time and date information and does not include time zone data. Therefore, changes in the server’s time zone do not impact the stored data in the database.
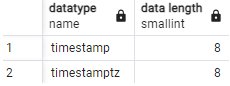
- The storage size for timestamp data in PostgreSQL is 8 bytes, making it efficient for storing date and time information.
- The timestamp data type in PostgreSQL can represent dates as far back as 4713 BC and as far forward as 294276 AD.
- Overall, with its 8-byte storage size, the timestamp data type proves crucial for accurately storing date and time data in PostgreSQL.
Code:
SELECT typname as "datatype", typlen as "data length"
FROM pg_type WHERE typname ~'^timestamp';Output:
Example
Step#1: Creating a table with Timestamp column
CREATE TABLE login (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(255),
last_login TIMESTAMP
);Step#2: Inserting Timestamp Values
INSERT INTO login (username, last_login) VALUES ('Rocky', '2019-01-14 08:45:00'),('Sarah', '2019-03-27 04:33:00');Step#3: Updating Timestamp Values
UPDATE login SET last_login = '2024-01-30 09:15:00' WHERE user_id = 1;Step#4: Querying Timestamp Values
SELECT * FROM user_activity WHERE last_login >= '2024-01-29 00:00:00';Output:
![]()
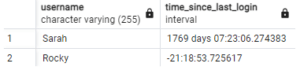
Step#5: Calculating Time Since last login
SELECT username, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP - last_login AS time_since_last_login FROM user_activity;Output:
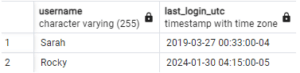
Step#6: Timezone Conversion
SET TIME ZONE 'America/New_York';
SELECT username, last_login AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AS last_login_utc FROM user_activity;Output:
Timezone Considerations
When dealing with Timestamp data in PostgreSQL, it’s vital to consider timezone implications to ensure accurate representation and consistency across diverse environments. PostgreSQL automatically converts Timestamp values to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) for storage, guaranteeing uniformity irrespective of the timezone during data insertion. When retrieving Timestamp values, PostgreSQL adjusts them to the session timezone, providing users with the correct local time representation.
Moreover, PostgreSQL furnishes functions like AT TIME ZONE for converting Timestamp values between different time zones as required. In distributed systems where users may span various time zones, meticulous timezone management is imperative to prevent inconsistencies and confusion. Adhering to best practices such as consistently storing Timestamp values, employing standardized time zone names, and rigorously testing timezone conversions is indispensable for upholding accuracy and reliability in managing temporal data within PostgreSQL databases.
Indexing Timestamp Columns
Indexing Timestamp columns in PostgreSQL is crucial for boosting query performance, particularly with extensive datasets. Efficient indexing significantly expedites data retrieval based on Timestamp conditions in WHERE clauses. By default, PostgreSQL employs B-tree indexes for Timestamp columns, effectively organizing and sorting Timestamp values for quicker range queries and equality conditions. Conditional indexing is advantageous, as it involves creating indexes based on specific conditions often used in queries, especially for filtering data based on Timestamp ranges or specific time intervals.
Expression indexes, which index a function of the Timestamp column, are also beneficial, particularly when querying based on derived values from Timestamps. Regular maintenance, For example, you can keep track of and manage indexes by rebuilding them and vacuuming tables, is essential for optimal performance. In summary, employing appropriate strategies to index Timestamp columns in PostgreSQL contributes to efficient data retrieval and enhances overall database performance.
Conclusion – PostgreSQL Timestamp
PostgreSQL Timestamps, essential for storing time-related data, offer precision and adaptability. With two primary data types, TIMESTAMP and TIMESTAMPTZ, they handle timestamps with or without timezone information. Functions like NOW() and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP simplify timestamp generation, facilitating temporal analysis. Efficient indexing, primarily via B-tree indexes, improves query performance, especially with extensive datasets. PostgreSQL automatically adjusts timestamps to UTC for storage and converts them to the session timezone for retrieval, ensuring consistency across environments. Functions like AT TIME ZONE aid in timezone conversion, which is vital for international systems. Regular maintenance, including index rebuilding and table vacuuming, is essential for optimal performance and reliability. In summary, PostgreSQL timestamps provide accuracy and flexibility in managing time-related data, supported by efficient indexing and maintenance practices.
FAQs
1. Why is efficient indexing important for Timestamp columns in PostgreSQL?
Answer: Efficient indexing, particularly utilizing B-tree indexes, is vital in optimizing query performance for Timestamp columns in PostgreSQL, particularly when managing extensive datasets. Indexing facilitates swift data retrieval based on Timestamp conditions specified in WHERE clauses, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the database.
2. Can I manipulate timestamp values in PostgreSQL?
Answer: Indeed, PostgreSQL offers a range of functions dedicated to manipulating timestamp values. These include extracting specific components of a timestamp and computing differences between timestamps.
3. Can PostgreSQL timestamps handle sub-second precision?
Answer: Absolutely; PostgreSQL timestamps support up to microsecond precision, enabling accurate representation of time down to fractions of a second.
4. What are some best practices for working with timestamp data in postgreSQL?
Answer: Following best practices involves consistently storing timestamp values, using standardized timezone names, and thoroughly testing timezone conversions to maintain accuracy and reliability when managing temporal data within PostgreSQL databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Timestamp” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

