Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Update
PostgreSQL update statement is used to update the existing data from the table; we use the update statement to update the existing data from the table. Update query is used to modify the existing data from the table; we have used the where clause with an update statement to modify or update the selected rows if we have not used an update statement, all rows will be updated from the table. The update statement is beneficial and important in PostgreSQL to modify the existing rows from the table. We must use an update statement if we have to update the existing row after table creation.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the update query in PostgreSQL.
1. Update the statement without using where clause
Update name_of_table (Table name from which we have modifying row.) SET
name_of_column1 = value1 (Value which we have setting to the column.),
name_of_column2 = value2 (Value which we have setting to the column.), …,
name_of_columnN = valueN (Value which we have setting to the column.);2. Update the statement with where clause
Update name_of_table (Table name from which we have modifying row.) SET
name_of_column1 = value1 (Value which we have setting to the column.),
name_of_column2 = value2 (Value which we have setting to the column.), …,
name_of_columnN = valueN (Value which we have setting to the column.) where [condition];Below is the parameter description syntax of the update statement in PostgreSQL.
- Update –This statement is used to modify the existing rows from the table.
- Table name –This is defined as the table name from which we have updating rows. We have updated selected or all rows from the table.
- Set –This keyword is used to set the value of table column rows we have set.
- Column name –We have used a column name with an update statement in PostgreSQL. We have used a column name from which column we have modified the value from the table. We can change multiple columns or single column values using the update command.
- Value –This is defined as the value in which we have a setting to column rows. We have set different values to a different columns in PostgreSQL.
- Where condition – We have used the where clause to update specific rows in PostgreSQL. If we have not used the where condition with the update statement, it will update all rows from the table.
How to Update statement work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the update statement in PostgreSQL. To execute the update statement in PostgreSQL, we need to have update privileges on the table, or we need to have superuser privileges to execute the statement.
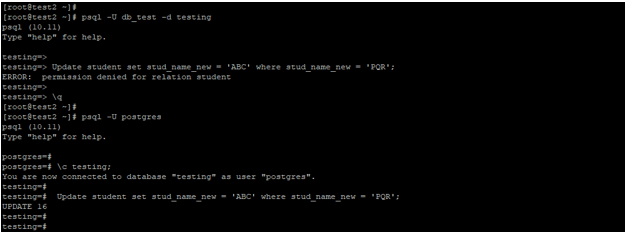
Below is an example of an update statement requiring update privileges on the table or superuser privileges to execute the update statement in PostgreSQL.
psql -U db_test -d testing
Update student set stud_name_new = 'ABC' where stud_name_new = 'PQR';
psql -U Postgres
\c testing;
Update student set stud_name_new = 'ABC' where stud_name_new = 'PQR';Output:
- In the above first example, we have used the user as db_test, this user doesn’t have privileges to update the student table or superuser, so it will issue an error while executing the update statement.
- In the second example, we have updated the table rows using the username Postgres, after using this user, we have to update the column name of stud_name_new from PQR to ABC from the table student.
- We used an update statement to modify the existing rows using the where clause in PostgreSQL.
- After inserting the data into the table, you can modify it using the update command. We can update the column values using the identifier, constants, expression, and other data types in PostgreSQL.
- This condition will apply to the specified column or all columns with the condition used in the update query.
- If we have to update all rows from the table, this is very easy without using the where clause with an update statement in PostgreSQL.
- We have used an update statement to modify both single and multiple columns.
- We have also used from clause to update the table using other data sets or tables. To update the rows in the table, we use select operations on various data sets.
- Also, we have used a join condition to update the rows from the table. We have used two tables with join conditions to update rows in PostgreSQL.
Examples
Below is an example of an update statement as follows. We are using stud1 and stud2 tables to describe the example of the update statement.
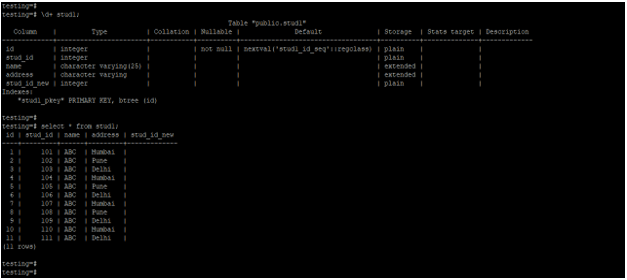
Below is the table and data description of the stud1 table.
\d+ stud1;
select * from stud1;Output:
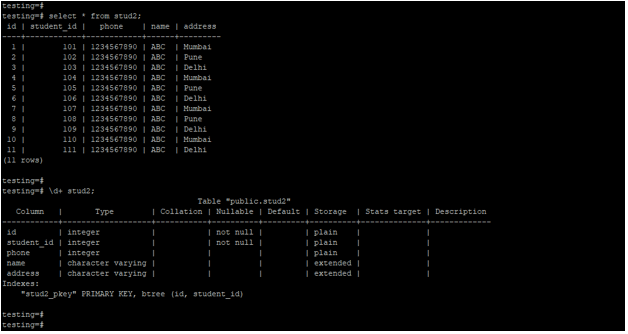
Below is the table and data description of the stud2 table.
\d+ stud2;
select * from stud2;Output:
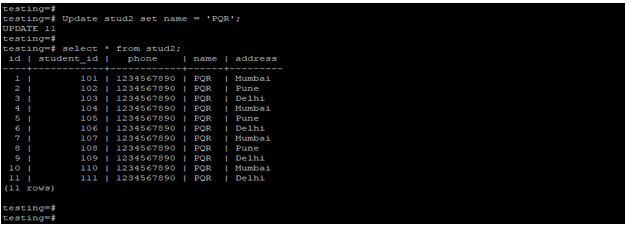
Example #1 – Without using the where clause
The below example shows that update statement without using the where clause. We have updated the name from ABC to PQR from the stud2 table.
Update stud2 set name = 'PQR';
select * from stud2;Output:
Example #2 – Using where clause
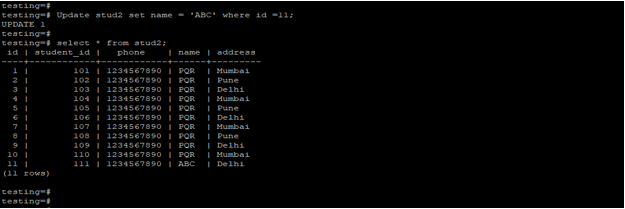
The below example shows that update statement using where clause. We have updated the name ABC which has an id is 11.
Update stud2 set name = 'ABC' where id =11;
select * from stud2;Output:
Example #3 – Using multiple columns
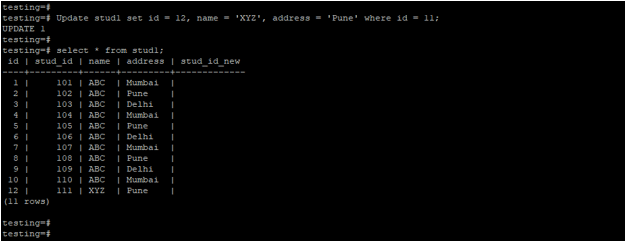
The below example shows that update statement using multiple columns.
Update stud1 set id = 12, name = 'XYZ', address = 'Pune' where id = 11;
select * from stud1;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Update” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.