Updated May 12, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL DECODE() Function
PostgreSQL DECODE() function is used to decode or extract the binary data from the input string, which is in textual format and has been encoded by using PostgreSQL Encode() function. The PostgreSQL DECODE() function takes input text that needs to be decoded and a parameter type that the user wants to decode. The parameter given to the PostgreSQL Decode() function should be the same as the type of parameter used in the case of the PostgreSQL Encode() function. This supports various formats for Encode and DECODE functions such as base64, escape, etc.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax to illustrate the PostgreSQL DECODE() function:
decode(string input_text, format type_text)Explanation:
- input_text – This defines the input text string, which will be decoded.
- type_text – This defines the in which the input text we expect to be decoded.
How does PostgreSQL DECODE() Function Works?
- The PostgreSQL DECODE() function takes two input parameters; the first is the text the user wants to decode, and the second is the parameter type the user wants it to decode.
- The parameter given to the PostgreSQL Decode() function should be the same as the type of parameter used in the case of the PostgreSQL Encode() function.
- The PostgreSQL DECODE() function returns us the text’s decoded binary data based on the specified type.
Examples
- Consider the following example where we will encode a string ‘encode base64 string’ with the format ‘base64’ by using the following SQL statement.
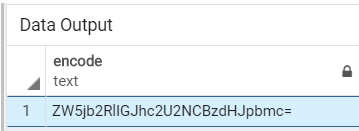
select encode('encode base64 string', 'base64');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
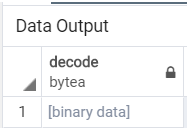
We will use the encoded ‘ZW5jb2RlIGJhc2U2NCBzdHJpbmc=’ from the above encoded example and use it for decoding by using the following SQL statement.
select decode('ZW5jb2RlIGJhc2U2NCBzdHJpbmc=', 'base64');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
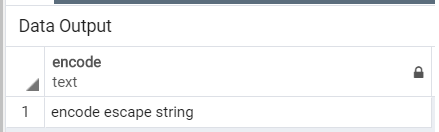
- Consider the following example where we will encode a string ‘encode escape string’ with the format ‘escape’ by using the following SQL statement.
select encode('encode escape string', 'escape');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
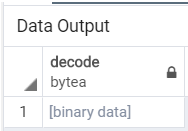
We will then use the encoded ‘encode escape string’ from the above encode example and use it for decode by using the following SQL statement.
select decode('encode escape string', 'escape');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
- Consider the following example where we will create a new table using the CREATE TABLE statement, which will store the details of the tuitions.
CREATE TABLE tuitions (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
tuition_name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
tuition_start_tm TIME NOT NULL,
tuition_end_tm TIME NOT NULL
);Now we will encode the name of the tuitions using base64 format and then will insert some data into the tuitions table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follow:
INSERT INTO tuitions(tuition_name, tuition_start_tm, tuition_end_tm)
VALUES
( encode('Maths','base64'), '07:00:00', '08:45:00'),
( encode('English','base64'), '09:00:00', '11:45:00'),
( encode('Algebra','base64'), '12:15:00', '14:00:00'),
( encode('CS','base64'), '14:15:00', '17:00:00'),
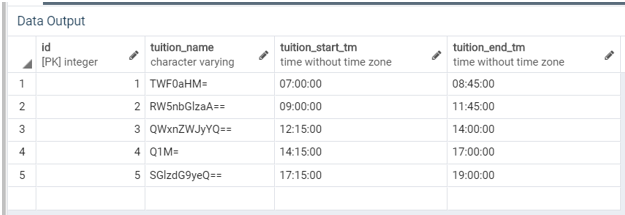
( encode('History','base64'), '17:15:00', '19:00:00');Illustrate the result of the tuitions table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
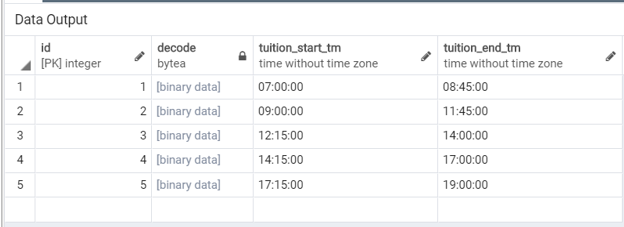
SELECT * FROM tuitions;Consider the following example of this function, which will return us the binary data from the tuition_name column, her,e we will be using the ‘base64’ as a format type because we have used the same while inserting data into the table.
select id, decode(tuition_name, 'base64'), tuition_start_tm, tuition_end_tm from tuitions;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above table’s above state, all rows had encoded records for the tuition_name column. We will insert some records in the ‘tuitions’ table without encoding the tuition_name using the INSERT INTO statement.
INSERT INTO tuitions(tuition_name, tuition_start_tm, tuition_end_tm)
VALUES('Maths', '07:00:00', '08:45:00'),
('English', '09:00:00', '11:45:00'),
('Algebra', '12:15:00', '14:00:00'),
('CS', '14:15:00', '17:00:00'),
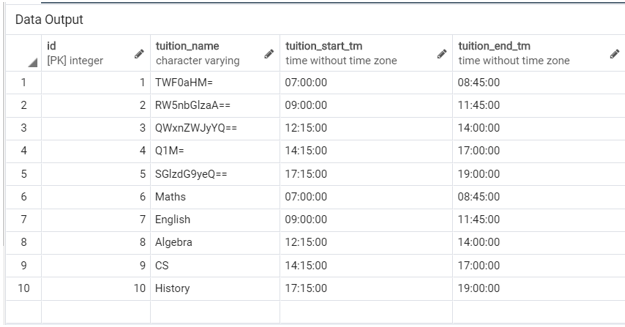
('History', '17:15:00', '19:00:00');Illustrate the result of the tuitions table by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM tuitions;Now, we have mixed encoded and decoded data in the ‘tuitions’ table, so we will get the exception whenever we try to retrieve the records by decoding the ‘tuition_name’.
Illustrate the expected exception by using the following SQL statement and snapshots:
select id, decode(tuition_name, 'base64'), tuition_start_tm, tuition_end_tm from tuitions;
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL DECODE() function and how the PostgreSQL DECODE() function works. Also, we have added several examples of the PostgreSQL DECODE() function to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL DECODE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.