Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Synonyms
PostgreSQL provides synonyms functionality to the user. A synonym is an identifier and it is used to reference other database objects we can also call alternate names of objects. A synonym is useful in a fully qualified schema name and referenced by PostgreSQL statement. It is not necessary a referenced object is must available at the time we create synonyms. A synonym is useful for non-existing schema or objects. When we delete a referenced object or schema that means your synonyms are not valid. If we have two synonyms with the same name that means it is unqualified so at that time the server uses a search path.
Syntax:
create [or replace] [public] synonyms [sche.]synonyms_name
for obj_sche.obj_name [#database_link_name];Explanation:
1. synonyms_name:
It is used as the name of synonyms. A synonym must be unique within the database or schema.
2. sche:
If we don’t specify the schema name, Sche specified schema name, it is automatically created in the first existing schema in the search path.
3. obj_name:
Obj_name means it specifies the object name.
4. obj_sche:
Obj_sche specifies the object schema name of the schema and its object reference.
5. database_link_name:
It is a defined database link, and we can access objects with the help of this link.
How Synonyms works in PostgreSQL?
We must install PostgreSQL in your system. Required basic knowledge of PostgreSQL. We must require a database table to perform synonyms. Need basic knowledge about the synonyms syntax, which means how it is used. We can perform different operations on database tables with the help of psql and pgAdmin. The advanced server supports views, tables, functions, procedures, sequences, types, objects, etc.
Let’s see how we can implement synonyms by using the following example.
Examples
First, we create a table college using the following statement.
Example #1
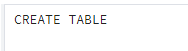
create table college (emp_id serial PRIMARY KEY, emp_name varchar(30), emp_dept varchar[],emp_city varchar[],emp_salary text[]);Explanation
With the help of the above statement, we created a college table with different attributes such as emp_id, emp_name, emp_dept, emp_city, and emp_salary. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Example #2
Now we implement synonyms as follows.
A synonym is not to be supported in the PostgreSQL database because PostgreSQL clearly differentiates between schema and user. But Oracle, we need to use synonyms because of this reason. When we use syntax to create synonyms in PostgreSQL at that time, it shows syntax errors. Let’s see an example of synonyms as follows.
create or replace public synonym test for public.college;Explanation
In the above example, we try to implement synonyms in PostgreSQL, but it shows error messages because PostgreSQL does not support synonyms. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Example #3 – Search Path
Sometimes we create synonyms by using database links or paths. At that time, we used this function as follows.
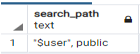
show search_path;Explanation
The above statement shows the search path command to see the existing schema. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Example #4 – DROP Synonyms
On the other hand, we can DROP synonyms. So let’s see how we can DROP synonyms in PostgreSQL. Suppose users need to delete synonyms at that time, and users use the following syntax as follows.
Syntax:
Drop public synonym synonyms name;Explanation
We use the drop synonym command to delete synonyms in the above syntax. When we want to delete synonyms but two synonyms have the same name at that time, we check whether the schema is qualified.
Example #5 – Synonym Dictionary
PostgreSQL provides the user with a synonyms dictionary function and is used to replace words with synonyms. Synonyms dictionary is used to overcome the similar word problem. For example, suppose our schema has two similar words, Paris and Pari. So with the help of a synonyms dictionary, we solve that problem.
Example #6 – Conversion of Oracle synonyms to PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL does not support synonyms. But some users or customers need to migrate to PostgreSQL from Oracle. At that time, we had a schema conversion tool. With the help of AWS tools, we can convert Oracle synonyms to PostgreSQL synonyms.
Example #7 – Synonyms package conversion of Oracle to PostgreSQL
AWS is not able to convert the Oracle synonyms package to PostgreSQL. So let’s see how we can convert as follows.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE ORA_PACKAGE AS
TYPE oracle_type IS REC (
name VARCHAR2(512),
amount NUMBER);
TYPE r_ora_type IS TABLE OF oracle_type;
v_pi CONSTANT NUMBER(8) :=2.24;
mini_balance CONSTANT REAL := 1.00;
max_balance CONSTANT REAL := 9.00;
CURSOR cur IS SELECT 'Monday' AS "day" FROM dual;
END ORA_PACKAGE;So we must write a script to convert this package into PostgreSQL.
Script for PostgreSQL Constant
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION
schema_name."s_ora_package$schema_name$ora_package$max_balance$c"()
RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
LANGUAGE
AS $function$
BEGIN
RETURN 9.00;
END;
$function$
;Explanation
In the above example, we convert the Oracle synonyms package to PostgreSQL. The above example is specific to the PostgreSQL constant, in the above script, we create a function as shown in scripts.
Uses
- PostgreSQL synonyms reference another database object, table, functions, etc.
- The synonyms we use to hide our original content from users mean it is used for security purposes.
- The synonym is an alias or alternate name for a view, table, sequence, function, procedure, etc.
- It also provides backward compatibility for existing objects or schema when you rename them.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the PostgreSQL synonyms. PostgreSQL does not support PostgreSQL, but it supports Oracle. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of synonyms. We also know how to implement them in PostgreSQL with different operation examples. We also learned how to convert Oracle synonyms to PostgreSQL synonyms using a schema conversion tool. From this article, we have learned how we can handle synonyms in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Synonyms” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.