Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL STRING_AGG()
PostgreSQL supports various kinds of aggregate functions, The STRING_AGG() function is one of the aggregate functions which is used to concatenate the list of strings, and it will add a place to a delimiter symbol or a separator between all of the strings. The separator or a delimiter symbol will not be included at the end of the output string. The PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function is supported by PostgreSQL 9.0 version, which performs the aggregate option related to the string. We can use various separators or delimiter symbols to concatenate the strings.
Syntax
Consider the following syntax:
STRING_AGG ( expression, separator|delimiter [order_by] )Explanation:
The STRING_AGG() function takes input ORDER BY clause is an optional and other two arguments as follows:
- expression: This is a character string that is any valid expression.
- separator/delimiter: This defines the separator/delimiter used for string concatenation.
The ORDER BY clause is optional and defines the order of concatenated string results.
The ORDER BY has the syntax as follows:
ORDER BY expression1 {ASC | DESC}, [...]How does PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function works?
- The input expression needed should be a character string data type. We can also use other data types but only need to ensure that we have explicitly cast other data types to the character string data type.
- The PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() returns us the result in string type.
- The STRING_AGG() is generally used with the GROUP BY clause like we use other PostgreSQL aggregate functions such as MIN(), MAX(), AVG(), SUM(), COUNT(), etc.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function
We will create a table named ‘student’ and ‘course’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
STUDENT TABLE:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_grade CHAR(1) NOT NULL,
stud_country VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
course_id int NOT NULL
);COURSE TABLE:
create table course
(
course_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
course_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
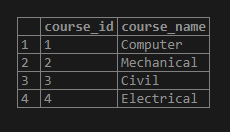
);Now, we will insert some data into the ‘course’ table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO course(course_name)
VALUES
('Computer'),
('Mechanical'),
('Civil'),
('Electrical');Illustrate the above INSERT statement’s result using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
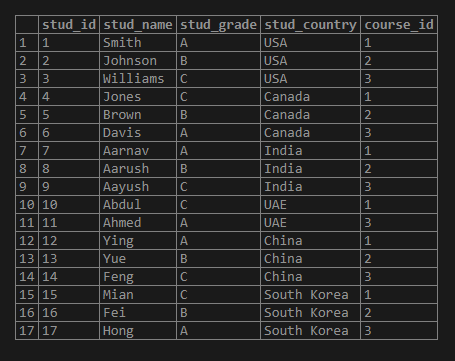
select * from course;Now, we will insert some data into the ‘student’ table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO student(stud_name,stud_grade,stud_country,course_id)
VALUES
('Smith','A','USA',1),
('Johnson','B','USA',2),
('Williams','C','USA',3),
('Jones','C','Canada',1),
('Brown','B','Canada',2),
('Davis','A','Canada',3),
('Aarnav','A','India',1),
('Aarush','B','India',2),
('Aayush','C','India',3),
('Abdul','C','UAE',1),
('Ahmed','A','UAE',3),
('Ying', 'A','China',1),
('Yue','B','China',2),
('Feng', 'C','China',3),
('Mian','C','South Korea',1),
('Fei','B','South Korea',2),
('Hong','A','South Korea',3);Illustrate the above INSERT statement’s result using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
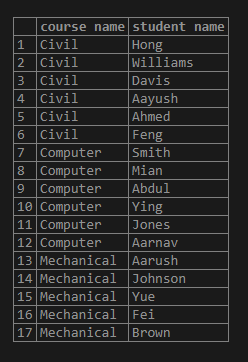
select * from student;SELECT c.course_name AS "course name", s.stud_name AS "student name"
FROM course c RIGHT JOIN student s ON c.course_id = s.course_id
ORDER BY 1;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above example, the resulting snapshot has each row as a separate entry for the matched course with the student’s course.
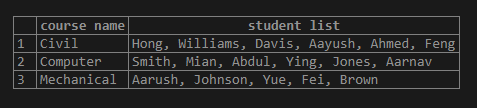
We can concatenate the student names by using the STRING_AGG() function by modifying the above SQL statement as follows:
SELECT
crs.course_name AS "course name",
string_agg(stud.stud_name, ', ') AS "student list"
FROM course crs
JOIN student stud ON crs.course_id = stud.course_id
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 1;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
SELECT stud_grade, STRING_AGG(stud_name,', ') AS StudentsPerGrade
FROM student
GROUP BY stud_grade
ORDER BY 1 ;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above example, the resulting snapshot shows us the students concatenated by a comma separator with a similar grade obtained.
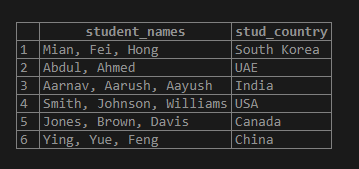
SELECT STRING_AGG(stud_name, ', ') AS "student_names", stud_country
FROM student
GROUP BY stud_country;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above example, we observe that the code groups and concatenates all students from the same country, utilizing a comma separator.
Advantages
- We can control the order of the result by using the ORDER BY clause.
- The PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function returns the result in string format.
- We can use the STRING_AGG() function to concatenate all strings and add a delimiter symbol or separator between them.
- The PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() supports various types of delimiter symbols or separators and does not include delimiter symbols or separators at the end of the string.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function and how the PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function works. Also, we have added several examples of the PostgreSQL STRING_AGG() function to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL STRING_AGG()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.