Updated May 24, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Rename Database
PostgreSQL renamed the database statement used to change the database name to another name; we can rename any database using the alter database statement. To rename the database in PostgreSQL, we first need to disconnect from the database from which we have connected; after disconnecting from the database, we need to connect to a different database. To rename any database in PostgreSQL, we need the privileges of the owner of the database or need admin of the database server. If we have to change the database name after database creation, we have changed or renamed the database name using the alter database statement.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the renamed database in PostgreSQL.
Alter database old_database_name (Name of database which was we have change to different name.) RENAME TO new_database_name (New name of database which was we have changing.)Below is the parameter description syntax of the renamed database
- Alter database –We use the alter database statement to rename the database with a different name. We can also use the alter database statement to change the feature of the database.
- Old database name –This is defined as an old database name from the database server, which we have renamed to a different name.
- Rename To –This keyword is defined as using this keyword, we can change the database name with a different name in PostgreSQL. We have used rename to keyword with alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
- New database name –This is defined as the new database name, which we have changed using the alter database command. This parameter is also important to alter the database statement to change the database name.
How to Rename a Database in PostgreSQL using various methods?
- Below are the various methods which were used in PostgreSQL to rename the database in PostgreSQL.
- We have renamed the database using the alter database statement in PostgreSQL as follows.
- To rename the database using an alter database statement, we need to have superuser privileges or owner of the database privileges to rename the database.
- The example below shows that we need superuser or admin privileges to change the database name in PostgreSQL.
psql -U postgres -d postgres
alter database db_testing rename to db_test;
psql -U db_test -d postgres
alter database db_test rename to db_testing;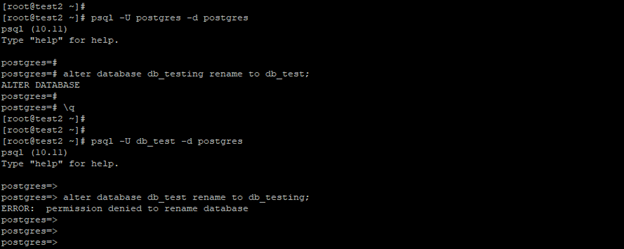
- In the above first example, we have to change the name from Postgres user, Postgres user has superuser privileges; using superuser privileges, it is possible to change the name of the database.
- In the second example, we have to change the name from db_test user; the db_test user doesn’t have privileges to rename the database.
- If we have to change the database name, we need to disconnect from the current database and connect to another database.
- The below example shows that we need to change the database connection before renaming the database with a different name.
psql -U postgres -d postgres
\c db_test
alter database db_test rename to db_testing;
\c postgres
alter database db_test rename to db_testing;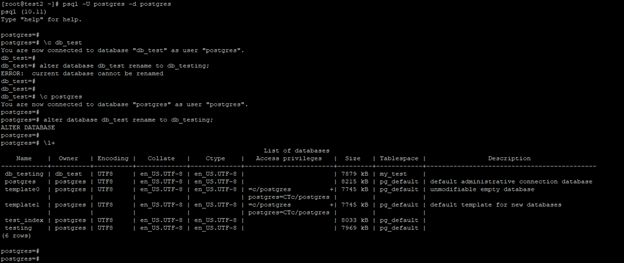
- In the above example, we have renamed the database by disconnecting the database with a different database.
To change the database name, we need to follow the below steps.
- First, we need super user privileges or admin privileges to change the database name in PostgreSQL.
- Disconnect from the database, which name we have changed with a different name.
- Disconnect all the sessions connected to the database to check this session using the pg_stat_activity catalog table.
- Check all active sessions and terminate the same using the pg_terminate_backend command in PostgreSQL.
1. Rename the database by using alter database statement –
- Below is an example of renaming a database using an altered database statement in PostgreSQL.
- In the below example, we have to change the database name by using an altered database statement in PostgreSQL.
- In the below example, we have to change the database name from db_testing to db_test.
- We have used Postgres users to change the database name in PostgreSQL.
\l+
alter database db_testing rename to db_test;
\l+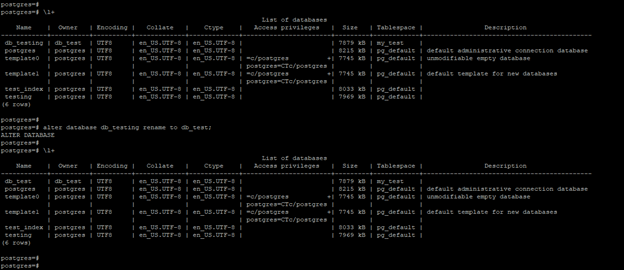
2. Alter the database using a command prompt
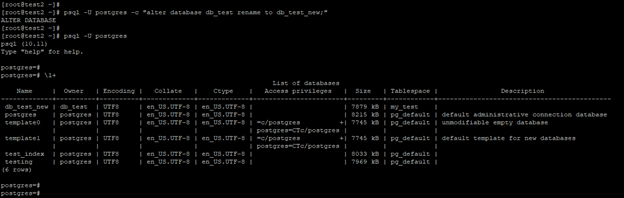
- In the below example, we have to change the database name from the command prompt by using the alter database statement in PostgreSQL.
- We have to change the database name by using Postgres user, Postgres user is the admin user of the database server.
- In the above example, we must change the database name from db_test to db_test_new using the altered database statement.
3. Alter the database to change the name by disconnecting the sessions
- In the below example, we have to change the database name by disconnecting the session from the database.
- We have to change the database name from db_test_new to db_test as follows.
- After disconnecting all the sessions connected to the “db_test_new” database, we need to change the database name using the Postgres user.
select * from pg_stat_activity where datname='db_test_new';
alter database db_test_new rename to db_test;
\l+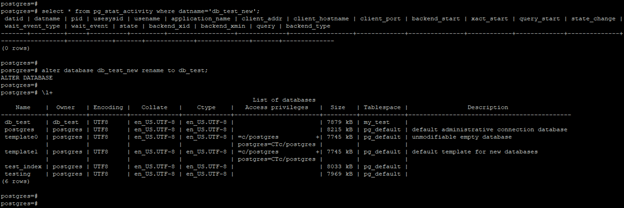
- In the above example, we checked the active sessions using the pg_stat_activity catalog table.
- Using this catalog table, we have checked the connected session of the db_test_new database. It will show the zero session is connected to the db_test_new database.
- After disconnecting all the sessions successfully, we renamed the database db_test_new to db_test in PostgreSQL.
Conclusion
We have renamed the database by using the alter database statement in PostgreSQL. We can rename the database using the shell prompt and from the database prompt. To rename the database in PostgreSQL, we need to have the privileges of the database owner or super user privileges.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Rename Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

