Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Port
PostgreSQL provides a facility to make connections between client and server using port number, IP address, and the default port number of PostgreSQL is 5432. The Port number and IP address are the database’s administrative part. It plays an important role in the database management system to establish a connection with remote users, which we call TCP/IP connection; it uses a local socket for configuration. With the help of port number and IP address, we can connect multiple connections in the network to remote access server and database. It also includes security for Windows operating systems.
Syntax:
Port = Port Number
listen_addresses = 'ip address'Explanation:
- In the above syntax, where Port Number is the specified Port number that we need to change, and listen_connection is used for the IP address.
- With the help of the above syntax, we can change the Port number and IP.
How does Port work in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge of PostgreSQL.
- We must require knowledge about configuration files.
- Need basic knowledge about TCP/IP.
Basic term related to the port number:
1. listen_addresses
listen_address specifies TCP/IP single or multiple address on the server to establish a connection from the client site. If the listen_address value is *, it is available for all IP addresses. The IP address 0.0.0.0 allows listing all IPv4 addresses, and:: allows all IPv6 addresses. If the above two addresses are empty, the server cannot listen to any IP.
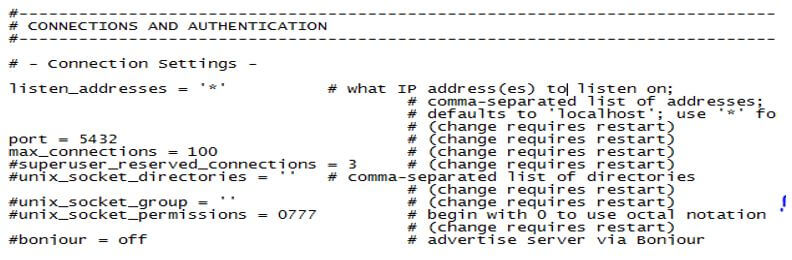
2. Port
The default port number is 5432. TCP port uses this port number to listen to all IP addresses on the server.
3. max_connections
It determines the maximum number of connections on the database server. Typically 100 connections may allow, but sometimes it may be less. It depends on your system’s kernel setting. If we increase the size of the number of users, then it is harmful to PostgreSQL.
4. superuser_reserved_connections
It checks the number of connection slots available for PostgreSQL superusers. The max size of the connection is 3, which means a superuser is allowed.
5. What is the requirement for port number
Suppose we need to access data in the database on the client location, which we call remote users on various locations in the network. At that time, we need Port Number.
6. How to check the port IP address
Suppose we need to check the Port number and IP address; at that time, we use the following command for the Windows operating system and Linux.
Code:
grep port numberExplanation:
- In the above command where grep is commanded along with the port number of the current system. It shows the IP address.
- Another way to check Port Number and IP address is to open postgresql directly.conf file and check the Port number and IP.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
7. Edit PostgreSQL. conf
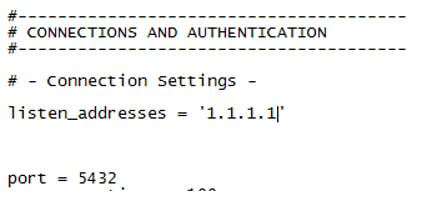
Suppose we need to take remote access to the database. At that time, we need to make some changes in the postgresql.conf file. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Explanation:
- In the above snapshot, the listen_addresses we mentioned are 1.1.1.1, and the port number is, by default, 5432. Here we can change the port number and IP address as per requirement.
8. How to restart PostgreSQL
After editing of listen to addresses and IP, we must restart the postgresql service. We directly start the postgresql service on the Linux system through the terminal. And Windows, we need to search for services in the search option of the start menu. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
9. Configuration of pg_hba.conf for authentication
In this file, we allow remote access using IP4 and IP5 IP addresses to access databases and all users with the help of the md5 protocol.
10. Windows firewall port
We can now run the PostgreSQL database on a Windows server with a firewall.
In the above scenario, you can turn off the firewall.
The steps for turn off the Windows firewall are as follows:
- Open Control Panel.
- Select System and Security.
- Select Windows Firewall.
- Select Turn Windows Firewall on or off option.
- Save the setting and exit.
Other options for the setup of a firewall are as follows:
- Open Control Panel.
- Select System and Security.
- Select Windows Firewall.
- Select Advanced Setting.
- Right-click on Inbound Rule.
- Select a new one.
- Select Port in Rule Type.
- Select the TCP program and enter the port number (here, you can use the default port number of any other user-defined).
- Next, select Allow the connection.
- Then select when we need to apply the rule (Domain, Private, and Public checked all three options).
- Then assign any name that you want.
- Finally, click on finish.
Remotely Access the User and Database
Suppose we need to access databases and users on different systems. If we don’t have another machine, we can execute on pgAdmin4. When we complete the above setting, open pgAdmin4 and follow the following steps.
- First, create a new server (right-click on the server and create the server).
- Then give the name to the server.
- Then click on the connection and give the remote machine’s IP address. We also need to provide a password and save the setting.
- Then see the new server on the left side of the window.
- Select the created server and open with, entering a password.
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw basic terms of networking and those related to port numbers. From this article, we can use the remote machine, and we also we can do setup set up or configureSQL Port on Windows operating systems. The same thing applies to Linux operating systems. Finally, from this article, we can configure the remote machine.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Port” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.