Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Performance Tuning
PostgreSQL performance tuning is defined as tune the database for better performance and quick access of data; we can tune the PostgreSQL database performance by tuning the query and database performance related parameter. For better performance, we need to find a slow and long-running query from the database by using the pg_stat_activity catalog table; after finding a slow query, we need to find an explain plan of the query. For better database performance, we need to tune the performance-related parameter like shared_buffers, wal_buffers, effective_cache_size, work_mem, maintainance_work_mem, and synchronous_commit also; we need to change this parameter based on resources.
How to perform Performance Tuning in PostgreSQL?
We can perform performance tuning in PostgreSQL by using the following conditions. Below is the parameter we have to tune to increase the performance of the database.
- Query tuning
- Index tuning
- Memory tuning
- Storage tuning
- Operating system tuning
- Network tuning
- Application tuning
- Configuration parameter tuning
1. Query tuning
- We need to find a log running a query on the database server to tune the database performance.
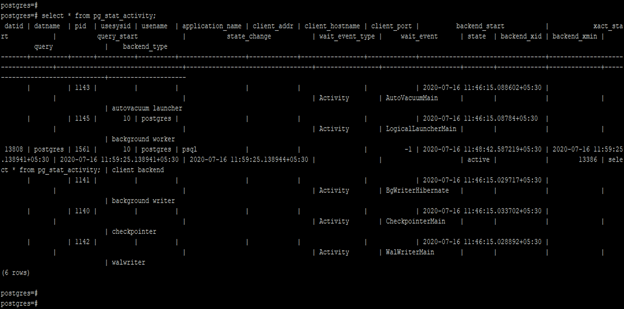
- We can find a long-running query by using the pg_stat_activity catalog table. The below example shows that find the long-running or slow query in PostgreSQL.
select * from pg_stat_activity;- We can find the long-running query in the above example state that is using the exact start time.
- After finding a slow query, we need to create the explain plan of that query; explain plan will show the below information related to the slow query.
- Nodes
- Cost
- Actual time
- Rows
- Width
- Index scan
- Loop
- Index condition
- Using the above parameter, we are tuning the query to increase the performance of the database.
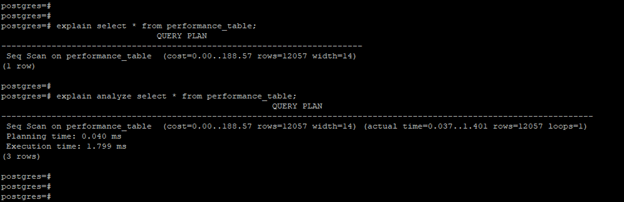
- The example below shows that find explains and analyzes the query plan in PostgreSQL.
explain select * from performance_table;
explain analyze select * from performance_table;- We have also used explain analysis with the query; it will show the additional information related to the query’s execution time.
- Nodes are defined as the block of code executing at the time of query execution in PostgreSQL.
- Node in explained plan consists of the logical unit of work.
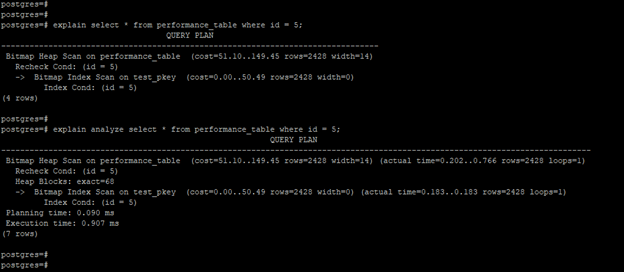
- Cost is defined as how much work will be required to execute the query. Cost is defined as two numbers the first number contains the startup cost, and the second contains the incurred process cost.
- The actual time is defined as the required time to execute the query and retrieve its output. This time is shown in milliseconds.
- Rows are defined as the number of rows defined in the query. The row is important to factor in a while finding and explaining the plan of the query.
2. Index tuning
- Index tuning is also important in PostgreSQL because the index will increase the performance of the select query.
- We need to turn the statistics collector for tuning an index in PostgreSQL. The statistics collector will collect the performance statistics.
- Also, we have tuning missing indexes from the query. After finding the missing index, we must create the same on the column.
3. Storage tuning
- Storage tuning is also important for the great performance of the PostgreSQL database. We need to define the right file system, and the right RAID level will increase the performance of the database.
- The right file system and right raid level will increase the I/O of the database server.
4. Memory tuning
- Memory tuning is also important while tuning a PostgreSQL database system. We can tune the performance-related parameter related to memory.
5. Network tuning
- We have also checked the connectivity between the application server and the client-server. We have to configure the proper link of the network while tuning a database server in PostgreSQL.
6. Operating system tuning
- To increase the performance of the query, we need to choose the proper operating system for our database in PostgreSQL.
- Choosing an accurate operating system for the database is also important to tune the PostgreSQL database.
7. Application tuning
- In PostgreSQL performance tuning, we need to tune the application in PostgreSQL. We have to check the proper compatibility of the application with the database.
8. Configuration parameter tuning
- We are tuning the configuration parameter below to increase the performance of the PostgreSQL database in PostgreSQL.
- Shared_buffers
- Effective_cache_size
- Work_mem
- Maintainance_work_mem
- Wal_buffers
- Syncronous_commit
- We have tuned the above configuration parameter as resources allocated to the PostgreSQL database system.
- Increasing the performance of the database configuration parameter plays a very important role.
Examples of PostgreSQL Performance Tuning
Below is an example of PostgreSQL Performance Tuning:
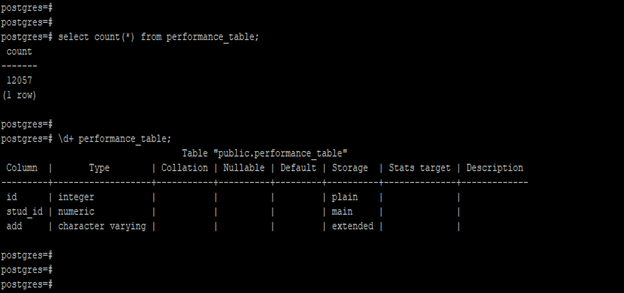
- Below is an example of performance tuning in PostgreSQL. We are using performance_table to describe examples of PostgreSQL performance tuning.
- Below is the count and structure of the performance_table.
select count(*) from performance_table;
\d+ performance_table;1. Create an index to increase performance –
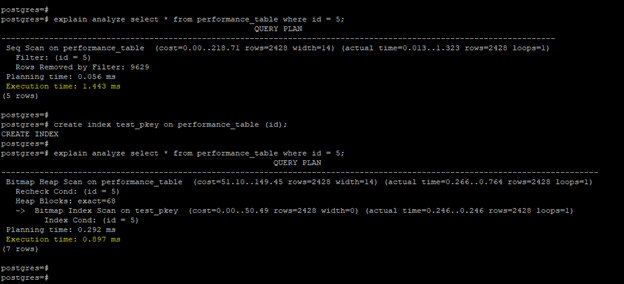
- The below example shows that create an index increases the performance of the query.
- In the above example, performance is automatically increased after creating an index query.
explain analyze select * from performance_table where id = 5;
create index test_pkey on performance_table (id);
explain analyze select * from performance_table where id = 5;2. Create an explained plan of the query to increase performance
- The below example shows that create an explanation plan for the query to increase the performance of the query.
explain select * from performance_table where id = 5;
explain analyze select * from performance_table where id = 5;3. Change the configuration parameter to increase performance
- The below example shows that changing the configuration parameter increases the performance of the database.
- We have changed configuration parameters as per the resources allocated to the database server.
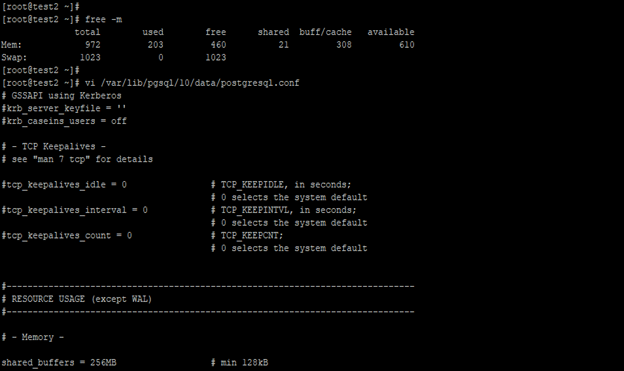
free–m
vi /var/lib/pgsql/10/data/postgresql.conf
max_connections = 200
shared_buffers = 256MB
effective_cache_size = 768MB
maintenance_work_mem = 64MB
checkpoint_completion_target = 0.7
wal_buffers = 7864kB
random_page_cost = 1.1
effective_io_concurrency = 200
work_mem = 1310kB
min_wal_size = 1GB
max_wal_size = 4GBConclusion
We can increase the performance by using Query tuning, Index tuning, Memory tuning, Storage tuning, Operating system tuning, Network tuning, Application tuning, and Configuration parameter tuning. The explain plan is used to show that the query’s execution plan will show the proper execution time of our query.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Performance Tuning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.