Updated May 8, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL NULLIF
PostgreSQL nullif is a common conditional expression used to handle null values or expressions in PostgreSQL. nullif is also used with the coalesce function to handle the null values. PostgreSQL nullif function returns a null value if provided expressions are equal. If two expressions provided are equal, then it provides a null value; as a result, otherwise, it will return the first expression as a result.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of the nullif function as follows.
Select (Argument1 (First value which is used to handle null values), Argument2 (Second value which is used to handle null values))SELECT Column1, …, ColumnN
COALESCE (
NULLIF (Column_name, ''), )
FROM table_name;Parameter:
- Select: In PostgreSQL, you can use the NULLIF function with the SELECT statement to fetch data from a table while handling null values or expressions. We can use multiple columns or a single column at one time to fetch data from the table.
- Coalesce: Coalesce states that function name in PostgreSQL, which returns as a first non-null value. Coalesce function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL.
We have used coalesce function with nullif function in PostgreSQL.
- Argument 1 to Argument 2: Argument is nothing but an integer or character value that we have passing with nullif function. If we have passing two-argument and both contain a different value, then the nullif function will return the first value in a result. If we have to pass both the same values, then it will return a null value as a result.
- Column 1 to Column N: This is the table’s column name. If we want to fetch data from a table using nullif function in PostgreSQL, we pass multiple columns simultaneously. Also, we have given the column name with the nullif function in PostgreSQL.
- From: In PostgreSQL, you can retrieve data from the keyword FROM with the table name in a SELECT query.
- Table name: Table name used with nullif function to fetch data from a table.
- Nullif: It is used to handle null values in PostgreSQL; nullif is also used with the coalesce function to handle the null values. nullif function returns a null value if provided expressions are equal; if provided two expressions are equal, then it provides a null value; otherwise, it will return the first expression as a result.
How does NULLIF Function work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of nullif function in PostgreSQL.
- We can use the coalesce function with nullif function in PostgreSQL. Coalesce states that the function name in PostgreSQL which returns as first non-null value as a result. Coalesce function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL.
- In PostgreSQL, you can use the common conditional expression NULLIF to handle null values or expressions.
- If we have passing two nullif function arguments and the first contains a null value, then the nullif function will return the first value in a result. If we pass both the same value, it will return a null value in a result.
- We have used the nullif function in PostgreSQL to prevent the division error by zero.
- In PostgreSQL, you can use the nullif function to prevent errors that may occur when comparing two values.
Examples
Below is an example of nullif function.
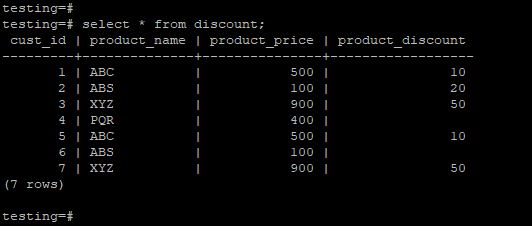
- We have using a discount table to describe an example of the nullif function as follows.
- Below is the data description of the discount table, which we have used to describe an example of nullif function.
Example #1
testing=# select * from discount;Output:
Example #2
In the below example, we have passing values like 50 and 50. The nullif function will return null values because both the arguments which we have passing are the same.
testing=# select nullif (50, 50);Output:
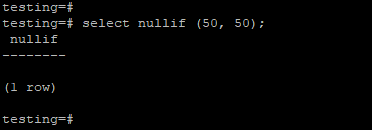
In the above example, we pass the same argument with the nullif function so that it will return the null value as a result.
Example #3
In the below example, we have passing values as 50 and 100. Nullif function will return the first value, i.e., 50 because both the arguments which we have passing are different.
testing=# select nullif (50, 100);Output:
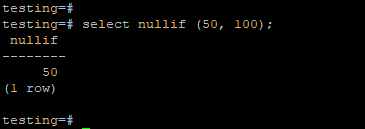
In the above example, we have a different passing argument with the nullif function so that it will return the first value as a result.
Example #4
In the example below, we have passing values as A, and the P. Nullif function will return the first value, i.e., A, because both the arguments we pass are different.
testing=# select nullif ('A', 'P');Output:
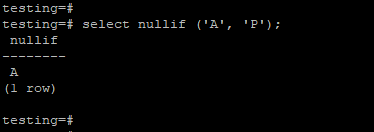
In the above example, we have a passing different argument with the nullif function so that it will return the first value as a result.
Example #5
In the below example, we have to retrieve data from a discount table using the nullif function.
testing=# SELECT cust_id, product_name, COALESCE ( NULLIF (Product_price, '')) AS Product_price FROM discount;Output:

Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL NULLIF” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

