Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL List Users
In any database, we need to create and have multiple users who can access the database. Each user should have certain access privileges and should be authorized, the user. By default, in PostgreSQL database server has a default user named Postgres. This superuser has all the rights and privileges granted for all the databases and tables. He can itself create new users and assign roles to them, grant and revoke permissions to other users, and so on. Often, the superuser or the database administrator must know about all the users in the current database server. In this article, we will learn how we can list out all the users that are present in our current database server. Let’s examine where the database stores and manages user-related data.
PostgreSQL List Users
Below are the three different List Users:
1. User Data in PostgreSQL
All the user-related data is stored in the table named pg_user, which belongs to the schema named pg_catalog. This table consists of all the information such as username, usesysid, usecreatedb, usesuper, userepl, usebypassrls, passwd, valuntil, and useconfig. Username, usesysid, and passwd are the name, id, and password stored in the md5 hash encryption system of the user. Simultaneously, all other parameters are the boolean parameters that specify whether the user has that privilege, such as usesuper, which specifies whether that user is a superuser or not. If yes, it contains a value as t that stands for true else, f that means false. Let us see what all the other fields retrieved mean in practicality.
- Usecreatedb: This field tells us whether that particular user can create a new database and has the privilege to do so.
- Userepl: We can create replications of a single table in many other databases. Only a specific user who has that privilege can do so. So, if the user has permission to create new replicas, the field will show as true.
- Usebypassrls: This field is set to true only if the user is allowed to bypass the RLS
We will first see how we can retrieve the user-related information from the pg_user table. We will need to build our query in the following way –
Code:
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;Output:
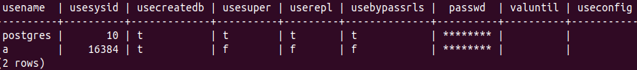
If you only want to get the list of users containing their names, you can fire the following query.
Code:
SELECT usename FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;Output:
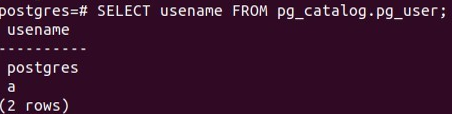
2. Using MetaCommands
PostgreSQL provides us with a wonderful utility named psql, where we can use metaCommands. MetaCommands are the short ready-made utilities that are available to use, making the work of database administrator very easy. For retrieving the user-related data \, du is the meta-command that can be used. For this, you will need to use the psql command prompt in PostgreSQL. Let us fire this command and see the result we are getting:
Code:
\duOutput:
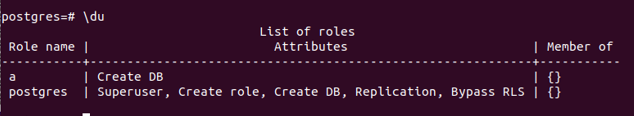
- Here, the Role Name is the name of the user. List of roles, i.e., attributes that are the roles which that a particular user has for himself. Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, and Bypass RLS are rules assigned to the superuser, meaning the superuser can create new roles and users, create new databases, perform replications of the existing objects, and bypass the RLS.
- The “Member of” field specifies whether the user is a group member. In PostgreSQL, the database administrator can create multiple groups and add different users to different groups, which helps him to manage the users properly while grating and revoking permissions. If there are any groups to which the user belongs, the field “Member Of” displays the name of the corresponding group.
- This metaCommands internally fires a query on the pg_catalog.pg_user table to retrieve the user information. Here, we get the role name as the user’s name, and a list of role attributes helps us to know which privileges are granted to that particular user. At the same time, a field member tells us if the user is a member of any particular group if present. The query which internally gets fire after using \du metacommand is somewhat similar to the below query statement:
Code:
SELECT u.usename AS "Role name",
CASE WHEN u.usesuper AND u.usecreatedb THEN CAST('Create DB, Superuser' AS pg_catalog.text)
WHEN u.usesuper THEN CAST('Superuser' AS pg_catalog.text) WHEN u.usecreatedb THEN CAST('Create DB' AS pg_catalog.text)
ELSE CAST('' AS pg_catalog.text) END AS "Attributes"
FROM pg_catalog.pg_user u ORDER BY 1;3. Using pg_shadow
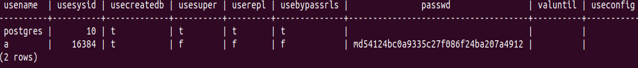
One more way to get the list of the users is by using the table pg_shadow, that also contains information about the users in the PostgreSQL server. The table is maintained for backward compatibility with PostgreSQL versions earlier than 8.1. This table stores the roles that can log in and flag rolcanlogin as 1 in the pg_authid table. Pg_user is the view created on the base table pg_shadow table, which is available publicly. pg_shadow is only accessible by the superuser. pg_user view contains the password field as blank to maintain security. The pg_ shadow table contains username, usesysid, usecreatedb, usesuper, userepl, usebypassrls, passwd, valuntil and useconfig fields for all the users in the database server.
Code:
SELECT * FROM pg_shadow;Output:
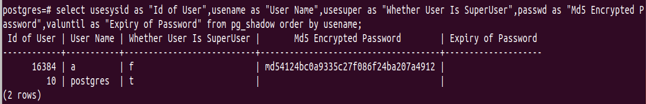
select usesysid as "Id of User", usename as "User Name",
usesuper as "Whether User Is SuperUser", passwd as "Md5 Encrypted Password", valuntil as "Expiry of Password"
from pg_shadow order by usename;Output:
Conclusion
In the PostgreSQL database server, we can retrieve the user’s information by retrieving the records from the table pg_user that belongs to the pg_catalog schema. Another way is to use the meta-command \du, which internally fires the query on the pg_user table. In addition, the PostgreSQL database server contains another table called pg_shadow that stores user information, which you can use to list all the users on the server. Note that the scope of all these methods is the whole database server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL List Users” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

