Updated May 22, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL EXECUTE
PostgreSQL EXECUTE statement is used to execute the previously created prepared statement, to execute that statement using execute the command, we need to give the name of the prepared statement and the parameter. Prepare statement in PostgreSQL only exist duration of the current session we have used, after session disconnection prepare statement will automatically remove from the database server. We can use the execute command in the prepared statement to select, delete, and insert statement.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax :
Execute (name of prepared statement) [(parameter)]Parameter
Below is the parameter description syntax of EXECUTE statement in PostgreSQL:
- Execute: This statement is used to execute the prepared statement in PostgreSQL.
- Name: This is defined as the prepared statement used with execute statement in PostgreSQL.
- Parameter: This is defined as actual value of the parameter prepared statement. This data type value was compatible with the parameter of prepared statement in PostgreSQL.
How PostgreSQL EXECUTE Statement works?
Below is the working of EXECUTE statement :
- We must first create a prepared statement to use the execute statement in PostgreSQL. Without creating a prepared statement, we cannot use the complete statement.
- It will return the syntax error while executing the statement.
In the below example, we need first to create a prepared statement.
Code:
EXECUTE exe_test(1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai');
PREPARE exe_test (int, text, text) AS INSERT INTO exe_test VALUES($1, $2, $3);
EXECUTE exe_test(1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai');
select * from exe_test;Output:
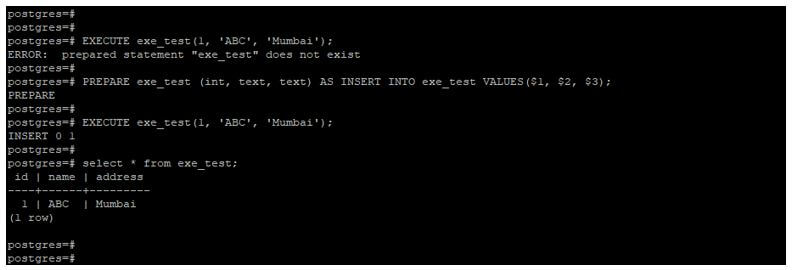
- In the above first line of code, we used to execute the statement with the exe_test prepare statement, but it will show the error.
- So we need to create the prepared statement to use the execute statement.
- In the second line of code, we have successfully executed the execute statement because, with this statement, we have used a prepared statement.
- We created the prepared statement name as exe_test after creating the same one we used in execute the statement.
In the next example, we will see the prepare statement is only valid in the current session, which we have connected, after disconnecting from the session prepare statement is automatically removed from the database server.
Code:
PREPARE exe_test (int, text, text) AS INSERT INTO exe_test VALUES($1, $2, $3);
EXECUTE exe_test(1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai');
select * from exe_test;
psql -U postgres
EXECUTE exe_test(1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai');Output:
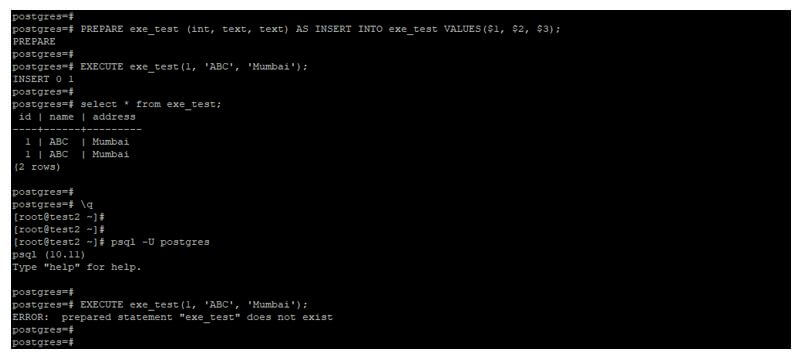
- In the above code, we have created a prepared statement name as exe_test after creating the same, we have use this using execute the statement.
- After executing this, we have disconnected from the session and are again trying to log in with the same user credentials.
- By following the above steps, we have again connected to the session, but the prepared statement will not exist into the database because it will automatically delete from the server after disconnecting from the current session.
Examples of PostgreSQL EXECUTE
Given below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
Insert data into the table by using execute statement.
Below example shows how to insert the data into the table by using execute statement in PostgreSQL.
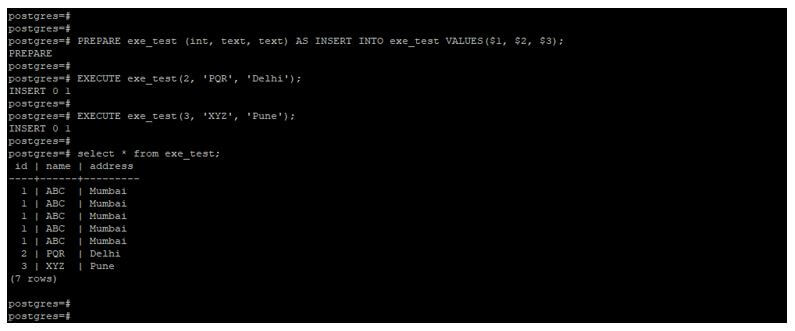
- In the example, we first created a prepared statement name as exe_test.
- Using this prepared statement, we execute the command and insert data or rows into the exe_test table.
Code:
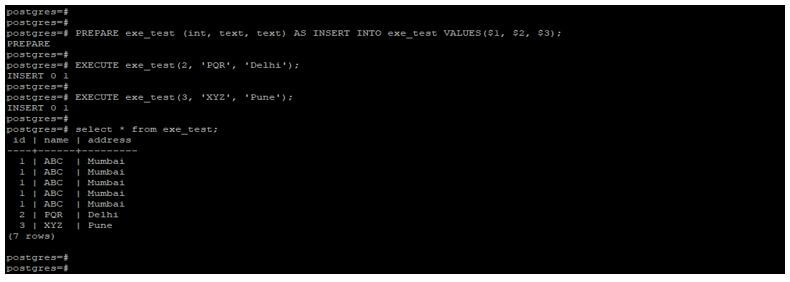
PREPARE exe_test (int, text, text) AS INSERT INTO exe_test VALUES($1, $2, $3);
EXECUTE exe_test(2, 'PQR', 'Delhi');
EXECUTE exe_test(3, 'XYZ', 'Pune');
select * from exe_test;Output:
Example #2
Select data from the table by using execute statement.
Below example shows how to select the data from the table by using execute statement in PostgreSQL.
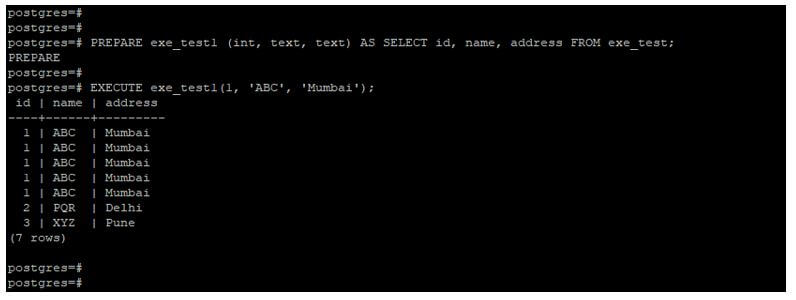
- In the example, we have created a prepared statement name as exe_test1. Using this prepared statement, we select the data from the exe_test table using execute the command.
Code:
PREPARE exe_test1 (int, text, text) AS SELECT id, name, address FROM exe_test;
EXECUTE exe_test1(1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai');Output:
Example #3
Delete data from the table by using execute statement.
Below example shows how to delete the data from the table by using execute statement in PostgreSQL.
- In the example, we have created a prepared statement name as exe_test2. Using this prepared statement, we are deleting the data from the exe_test table by using execute the command.
Code:
PREPARE exe_test2 (int) AS delete from exe_test where id =1;
EXECUTE exe_test2(1);
select * from exe_test;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL EXECUTE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

