Updated May 12, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL DROP INDEX
PostgreSQL drop index statement is used to drop or delete the existing index from a table column; we have used the drop index command to drop the existing index in PostgreSQL. To use the drop index command, we need to have superuser privileges or need to have the owner of that specific index. If the object depends on the index, then the index is not dropped error will be given that the index will not drop; basically, cascade operations with concurrent are not supported in the PostgreSQL drop index command. Drop index command is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to drop the unused index.
Syntax and Parameter
Below is the syntax of the drop index statement in PostgreSQL.
- Drop index index_name; — Name of the index we dropped using the drop index command.
- Drop index index_name1, index_name2, index_name3, …., index_nameN.
- Drop index [Concurrently (Drop index without affecting or locking other operations like select, insert, update, and delete)] [if exists (Drop the index if it exists in the database also do not throw the error if the index in not exist)] name_of_index (Name of the index which was we have dropping) [Cascade | Restrict ]
Parameter:
Below is the parameter description syntax of the drop index statement.
- Drop index: You can use this command to drop the existing index and remove the unused index from the database table column in PostgreSQL.
- Index name: We define the index name we want to drop from the database table.
- Concurrently: Drop the index without affecting the other operations like select, insert, update, and delete. Drop index in PostgreSQL will acquire the exclusive lock on the table; it will block operations access until the drop index was not completed successfully. After using concurrent options with the drop index command, it is not possible to perform cascade operations.
- If it exists: This option is used when the index is not present on the database table; after using these options, it will not show the error of the index cannot exist. The index will issue a notice if it is not on the database table.
- Cascade: We use this option to drop the index object that depends on the index automatically. But cascade options are not supported with concurrent options in PostgreSQL.
- Restrict: It is used when we do not have to use the drop index option on an index forcefully. It will refuse the drop index command when any other object depends on that index. This is a default parameter of the drop index command.
How to DROP INDEX Statement Work in PostgreSQL?
- Below is the working of the drop index statement in PostgreSQL.
- The index will increase the performance of select operations from the table. But it will degrade the performance of insert and update operations.
- If our database table contains the insert and update operations more than select, then we need to delete the same index from the table at that time, we have using the drop index statement to drop unused index from the database.
- We need a superuser or owner of index privileges to drop the index from the database table.
- The example below shows that we need a superuser or owner of index privileges to drop the index.
psql -U index_test -d testing
drop index index_test;
psql -U postgres -d testing
drop index index_test;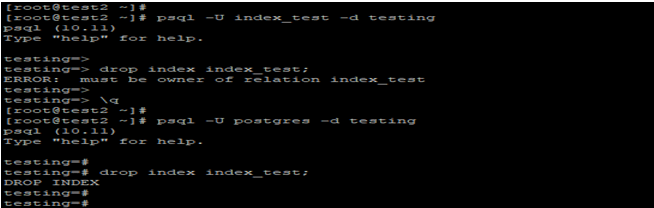
- In the above first example, we have used the user index_test to drop the index name as index_test from the student table. But it will throw the error of “ERROR: must be the owner of the relation index_test”.
- In the second example, we have used the superuser of the database, i.e., Postgres; using the superuser, it is possible to drop the index in PostgreSQL.
- We can drop multiple indexes in a single statement using the drop index command in PostgreSQL.
- If the object depends on the index, the same index will not dropped using the drop index operations.
- The below example shows that if any object depends on the index, it will not be dropped.
drop index student_pkey;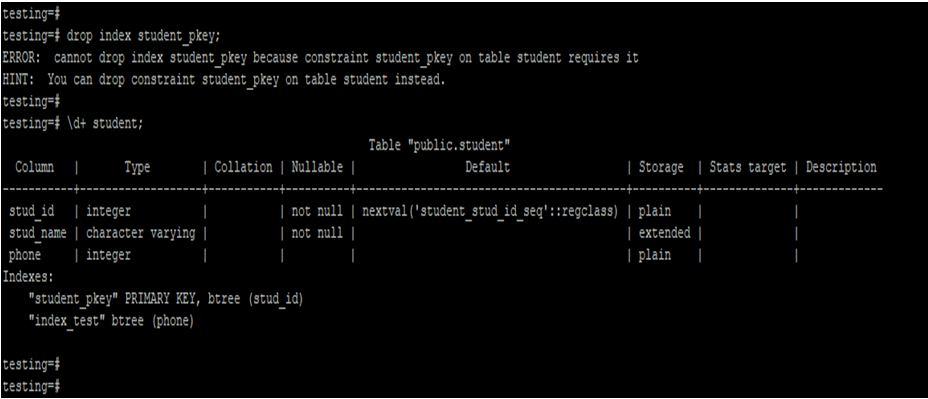
- In the above example, we have to try to drop the index of student_pkey, but it will not be dropped because other objects depend on this index.
- It will show the error of “ERROR: cannot drop index student_pkey because constraint student_pkey on table student requires it”.
Examples of PostgreSQL DROP INDEX
Below is an example of the drop index command in PostgreSQL.
1. Drop single Index Using Drop Index Command
In the below example, we have dropped a single index using the drop index command. In the below example, we have drop the index name as index_test from the student table.
\d+ student
drop index "index_test";
\d+ student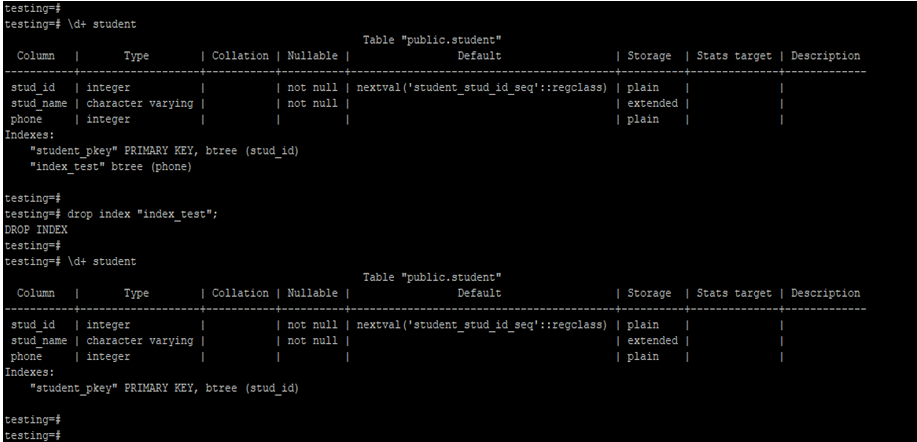
2. Drop Multiple Index Using the Drop Index Command
In the below example, we have dropped multiple indexes using the drop index command. In the example below, we have dropped the index names p_index and n_index from the student table.
\d+ student
drop index p_index, n_index;
\d+ student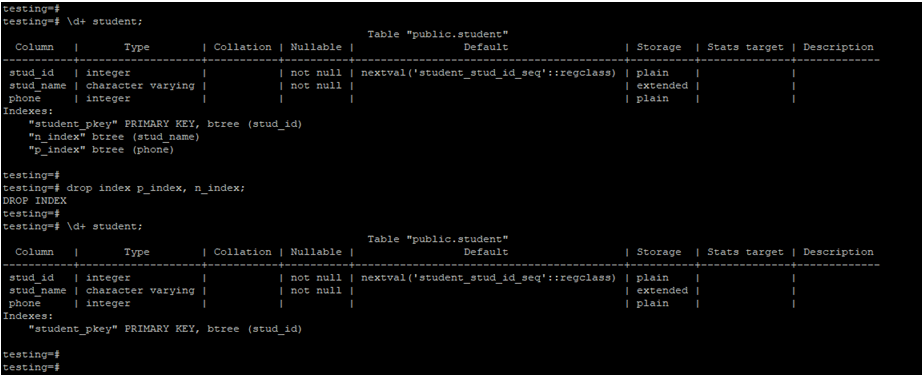
3. Drop the Index Using the if Exists Parameter
In the below example, we have used if exists a parameter with the drop index command. If exists parameter will skip the index.
\d+ student
drop index IF EXISTS p_index;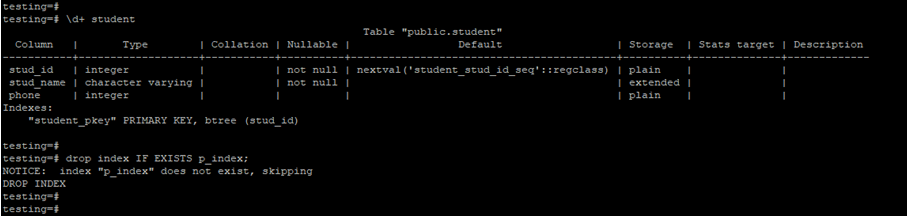
4. Drop Index Using Concurrently Parameter
In the below example, we have used the parameter concurrently with the drop index command. We have drop the c_index from the student table.
\d+ student
drop index concurrently "c_index";
\d+ student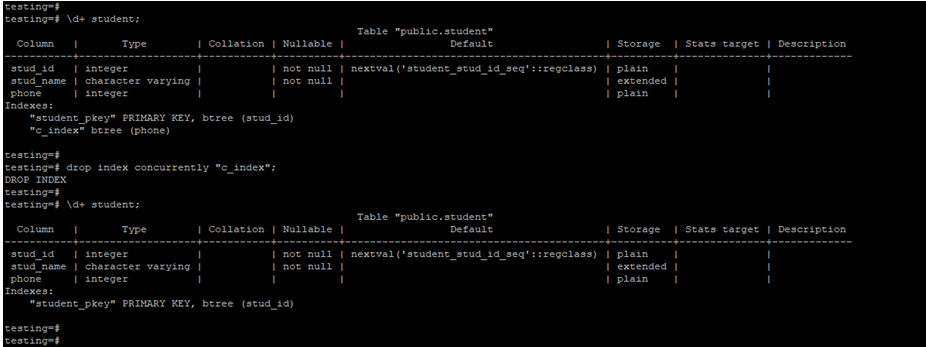
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL DROP INDEX” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

