Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL drops the foreign key.
The following article provides an outline for PostgreSQL to drop the foreign key. PostgreSQL provides different types of keys to the user; a foreign key is one of the types of keys in the PostgreSQL database. The foreign key is used to reference the table or column with the help of the primary key, and drop the foreign key means we drop the foreign key from the table or columns. When we use a drop cascade in a statement, it will automatically delete all referenced rows from the table, as this type of foreign key we call a dependent foreign key. Another way to drop foreign keys is to delete foreign keys, which does not depend on any other column or table.
Syntax:
Alter table table_name drop constraint key name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use the alter table statement to drop foreign key constraint where table_name means specified table name from the database, and drop is used to delete the foreign key control from a database table. Also, the key name means the actual foreign key name from the table we won’t drop.
How to drop the foreign key in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge about PostgreSQL and the key constraints of the database table.
- We must require a database table to perform foreign key constraints.
- Need basic knowledge about the foreign key, that means how it is used.
- We can perform different operations on tables with the help of psql and pgAdmin.
Let’s see how we can implement foreign key constraints, and we will also see how to drop foreign key from database tables.
First, we need a foreign key to perform a drop foreign key constraint, so let’s see how to create a foreign key as follows.
Example #1
Code:
CREATE TABLE sample(
emp_id INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
emp_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(emp_id)
);Explanation:
- In the above example, we use a create table to create a sample table with two attributes such as emp_id and emp_name, and here we assign the primary key to emp_id as shown in the statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we insert a record into the sample table using the following statement.
Code:
INSERT INTO sample(emp_name)
VALUES('John'),
('Samm');Explanation:
- With the help of the above statement, we insert two records into a sample table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we create another table by using the following statement as follows.
Code:
CREATE TABLE details (
cust_id INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
emp_id INT,
cust_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
cust_phone VARCHAR(15),
cust_email VARCHAR(100),
PRIMARY KEY(cust_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_sample
FOREIGN KEY(emp_id)
REFERENCES sample(emp_id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
);Explanation:
- With the help of the above statement, we created details tables with different attributes such as cust_id, cust_name, cust_phone, and cust_email, and here, we created a foreign key name as emp_id with reference to the sample table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we insert records into the details table using the following statement.
Code:
insert into details(emp_id, cust_name, cust_phone, cust_email)
values(1,'John','(202)-555-4321','[email protected]'),
(1,'John','(202)-555-4321','[email protected]'),
(2,'Sam','(101)-444-6541','[email protected]');
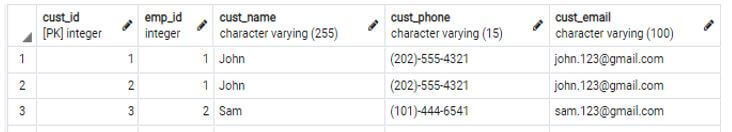
select * from details;Explanation:
- With the help of the above insert statement, we insert records into the details table. See here we insert the same records into the table, as shown in the statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
In the above example, we insert two duplicate records into the table but violate the foreign key constraint. So we delete the first record by using the following statement as follows.
Code:
delete from details
where cust_id = 1;In both examples above, we created two tables: samples and details for implementing foreign key constraint.
So now, let’s see how we can drop the foreign key constraint by using the following statement as follows.
Example #2
Code:
alter table details drop constraint fk_sample;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use an alter table statement to drop foreign key constraints from the database table. In this example, table name details and the foreign key name is fk_sample that we need to drop from the database table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Another way to delete foreign keys is that you can drop tables if they exist.
Syntax:
Drop table if exists table name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we drop table statements to drop the foreign key constraint where if exists means a specified table is present in a database and table name means specified table name from the database.
- See here when we use the above syntax, it deletes tables from databases, not particular foreign key columns, but when we use alter table statements, we can delete specific foreign key constraints.
Let’s see a different example of a drop table as follows.
Example #3
Code:
drop table if exists sample;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use drop table statements to drop foreign key constraints in which that sample is the specified table name from the database that we need to drop. In this example, the sample table does not contain any foreign key; we show how to drop the foreign key constraints using a drop table statement.
- Drop table statement deletes the whole table from the database and directly deletes the table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Similarly, we will drop our second table using a drop table statement containing foreign key constraints as follows.
Example #4
Code:
drop table if exists details;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use a drop table if it exists. In this example, we try to drop a details table containing foreign key constraints, and it references the sample table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we have seen the basic syntax drop foreign key constraint. We have also seen how to implement them in PostgreSQL with different examples of each operation. From this article, we have seen how we can handle drop foreign key constraints in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL drop foreign key” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.