Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN
We can update the records stored within the table in various ways; PostgreSQL provides UPDATE JOIN to do the same. In some cases, we need to update one table’s records based on another table’s records. To join another table in the statement, we have to define the PostgreSQL FROM clause with the joined table and specify the PostgreSQL WHERE clause with a JOIN condition. We must add the SET clause and specify the PostgreSQL FROM clause immediately after it.
Syntax
Consider the following syntax:
UPDATE table1
SET table1.col1 = expression
FROM table2
WHERE table1.col2 = table2.col2;Explanation: Join another table in the statement using the PostgreSQL FROM clause. Add the SET clause and specify the PostgreSQL FROM clause immediately after it.
How UPDATE JOIN works in PostgreSQL?
Consider the syntax defined in the above section to understand the working of the PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN. As per the syntax, we are updating the values of the table1 by using the values from the table2. Here we have specified a JOIN condition on col2 of table1 and table2. So if every row in table1 and table2 contains matching/same value, then the UPDATE statement updates the col1 column value in table1 and sets the value per the expression defined in the set clause.
Examples
Below are some examples mentioned:
Example #1
To understand the basic example, we will create two tables of name ‘table1’ and ‘table2’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
Code:
CREATE TABLE table1
(
t_ID INT,
t_Name VARCHAR(80)
);
CREATE TABLE table2
(
t_ID INT,
t_Name VARCHAR(80)
);We will insert some data into the table1 table using the INSERT INTO statement as follows.
INSERT INTO table1 VALUES
(1,'DDD'),
(2,'EEE'),
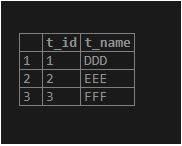
(3,'FFF');Output:
select * from table1;Now, we will insert some data into the table2 table using the INSERT INTO statement.
INSERT INTO table2 VALUES
(1,'PPP'),
(2,'QQQ'),
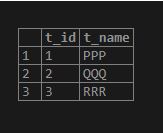
(3,'RRR');Illustrate the result of the above INSERT INTO statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from table2;Now we will use the PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN Statement to update the values of table2 if the t_ID field is matching/same with the table2.
UPDATE table2
SET t_Name = table1.t_Name
FROM table1
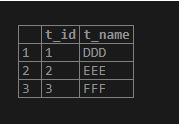
WHERE table1.t_ID = table2.t_ID;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from table2;Example #2
We will create two tables of name ‘student’ and ‘department’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows to understand the examples:
Code:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_total_marks int NOT NULL,
department_id int NOT NULL
);
create table department
(
department_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
department_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
);We will insert some data into the department table using the INSERT INTO statement as follows.
INSERT INTO department(department_name)
VALUES
('Computer'),
('Electrical'),
('IT'),
('Civil'),
('Chemical'),
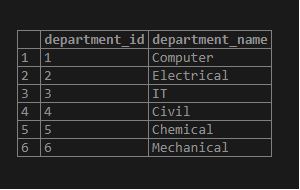
('Mechanical');Output:
select * from department;We will insert some data into the student table using the INSERT INTO statement as follows.
INSERT INTO student(stud_fname, stud_lname, stud_total_marks, department_id)
VALUES
('Smith','Johnson',576,1),
('Williams','Jones',678,1),
('Harper','James',876,2),
('Jack','Liam',786,2),
('Harry','Mason',879,3),
('Jacob','Oscar',765,3),
('Michael','Charlie',878,4),
('William','Joe',787,4),
('Oliver','John',676,5),
('Jack','Richard',686,5),
('Harry','Joseph',696,5),
('George','Thomas',797,6),
('Brown','Charles',785,6);Illustrate the result of the above INSERT INTO statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
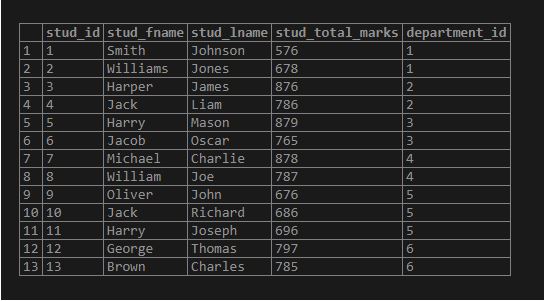
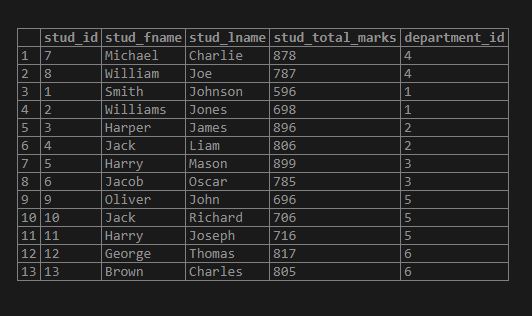
select * from student;Now consider the example where we have to give extra 20 marks to each student except the Civil department, whose department_id is 4. So we will use the UPDATE JOIN statement as follows:
UPDATE student
SET stud_total_marks = stud_total_marks + 20
FROM
department
WHERE
student.department_id = department.department_id AND department.department_id <> 4;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from student;Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN and how the PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN works. Also, we have added several examples of PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.