Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL CASE Statement
PostgreSQL case statement is the same as the if-else statement defined in other languages like C and C++. PostgreSQL provides two forms or types of a case statement first is a general form case statement, and a second is a simple form of the case statement. We can use the case statement in PostgreSQL using a when and a keyword like if and else in other programming languages. The case statement is significant in PostgreSQL to formulate the conditional expression; we formulate the conditional by using the when and then keyword in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the case statement.
1. General Case Expression
The below syntax shows a general case expression.
- CASE(starting Case statement)
- WHEN (When keyword used to formulate the condition) condition_1 THEN(Then keyword used to formulate the condition)result_1 (Result of first case statement)
- WHEN (When keyword used to formulate the condition)condition_2 THEN(Then keyword used to formulate the condition)result_2 (Result of second case statement)
- [WHEN …] (We can use multiple conditions in one case statement)
- [ELSE result_n] (If the case statement result fails, then execute this statement)
- END (End of case statement)
2. Simple Case Expression
The below syntax shows simple case expression.
- CASE expression
- WHEN (When keyword used to formulate the condition)value_1 THEN(Then keyword used to formulate the condition)
- result_1(Result of first case statement)
- WHEN(When keyword used to formulate the condition) value_2 THEN(Then keyword used to formulate the condition)
- result_2 (Result of second case statement)
- [WHEN …](We can use multiple conditions in one case statement)
- ELSE
- result_n
- END;(End of case statement)
Parameter
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax.
- Case: We can start the case statement in PostgreSQL by using a case keyword. The body of the case statement will start with the case and end with the END keyword.
- When: When the keyword is used to formulate the condition of the case statement in PostgreSQL.
- Then: Then, a keyword is used to formulate the condition of the case statement in PostgreSQL.
- Condition 1 and 2: We can retrieve the data’s result using a condition statement. If one condition fails, the trigger goes to the second; if it is true, it will display the result of all conditions.
- Result 1 to Result N: This is the actual result of the case statement in PostgreSQL.
- Else: Else keyword defines the true or false condition in the case statement. If the case statement condition is false, then the else part will execute; otherwise, it is not executing.
- End: We can end the case statement in PostgreSQL by using the end keyword. The body of the case statement will start with the case and end with the END keyword.
- Value 1 and 2: Value is nothing but a condition in the case statement.
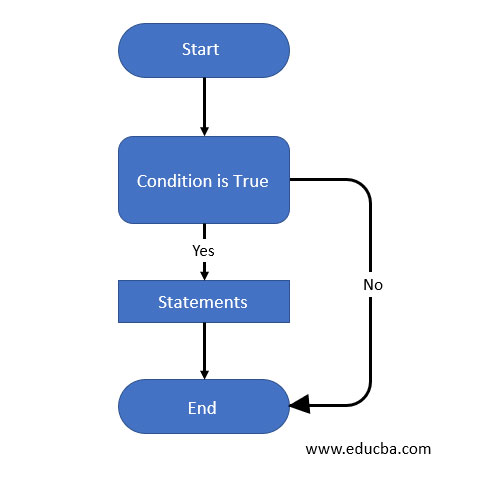
Flowchart
The below diagram shows the flowchart of the case statement.
- The above flowchart states that the case statement starts with the case or starts with a keyword. Normally we use a case keyword to start the case statement.
- After that cursor goes to a condition we used in the statement. If the given condition is true, it will execute a statement we wrote in the case statement.
- If the condition is false, then the cursor directly goes to the end statement.
- Before executing any case statement, we need to define the flowchart of the case statement.
- The flowchart is the pictorial representation of a case statement we have used in our query.
- The flowchart is most important and useful while creating a case statement in PostgreSQL.
How does the CASE statement work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working:
- When and then, the keyword is used to formulate the condition of the case statement.
- We can use a condition statement to retrieve the result of the data. If one condition fails, the trigger goes to the second; if it is true, it will display the result of the first condition. The case statement’s conditional expression is most important to display the result.
- The Else keyword defines the true or false condition in the case statement. If the case statement condition is false, the else part will execute; otherwise, it is not executing in the PostgreSQL case statement.
- We can start the case statement in PostgreSQL by using a case keyword and end with the end keyword. The body of the case statement will start with the case and end with the END keyword.
- PostgreSQL case statement is the same as the if-else statement defined in another language like C and C++.
- The case statement was significant in PostgreSQL to formulate the conditional expression; we formulate the condition using the when and keyword.
- PostgreSQL provides two forms or types of a case statement first is a general form case statement, and the second is a simple form case statement.
- We can use the case statement in PostgreSQL using a when and then keyword like if and else in other programming languages.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL CASE Statement
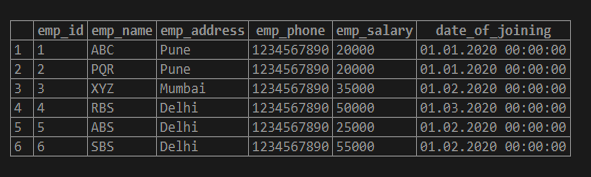
Below are the examples as follows. We have used the employee table to describe the example of the case statement.
Code:
select * from employee;Output:
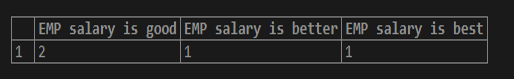
1. General PostgreSQL case expression
The below example shows a general PostgreSQL case expression. In this example, we find the employee’s good, better, and best salary.
Code:
SELECT
SUM (CASE WHEN emp_salary = 20000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is good",
SUM (CASE WHEN emp_salary = 35000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is better",
SUM (CASE WHEN emp_salary = 55000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is best"
FROM Employee;Output:
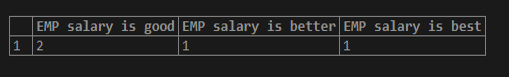
2. Simple PostgreSQL case expression
The below example shows a simple PostgreSQL case expression. In this example, we find the employee’s good, better, and best salary.
Code:
SELECT
SUM (CASE emp_salary WHEN 20000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is good",
SUM (CASE emp_salary WHEN 35000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is better",
SUM (CASE emp_salary WHEN 55000 THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS "EMP salary is best"
FROM Employee;Output:
Conclusion
When and then, the keyword is used to formulate the condition of the case statement. The case statement is the same as the if-else statement defined in another language like C and C++. We can start the case statement in PostgreSQL by using the case keyword and end with the end keyword.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL CASE Statement” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.